Oral transfer of chemical cues, growth proteins and hormones in social insects
Main text
LeBoeuf AC, Waridel P, Brent CS, Gonçalves AN, Menin L, Ortiz D, Riba-Grognuz O, Koto A, Soares ZG, Privman E, Miska EA, Benton R, Keller L. 2016. Oral transfer of chemical cues, growth proteins and hormones in social insects. eLife 5:e20375 . doi: 10.7554/eLife.20375.
Published 29, November 2016
Prof. Jocelyn Millar has pointed out some errors in our GC-MS-based identifications of hydrocarbons detected in trophallactic fluid (TF) (Table 1). With his feedback, we have refined our method of assignment to account for ambiguity due to the sparse representation of these compounds in the NIST Webbook, and reanalyzed the data.
We have made the necessary corrections to Table 1, the paragraph on these results the main text, the legend for Figure 3, Figure 3 - figure supplement 1 and the "Identification of trophallactic fluid hydrocarbons" section of the methods. We regret the presence of these errors in our published manuscript but would like to stress that the fundamental conclusions of the paper remain unchanged. We thank Prof. Millar for pointing out this issue.
Table 1
The corrected Table 1 is shown here:
| Rt (min) | MW | Proposed MF | Proposed structure | RI(a) | Peak ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.35 | 212 | C15H32 | Pentadecane | 1500 | |
| 14.05 | 226 | C16H34 | 5-methylpentadecane | 1541 | |
| 15.05 | 226 | C16H34 | Hexadecane | 1600 | |
| 16.47 | 240 | C17H36 | Heptadecane | 1700 | |
| 17.06 | 254 | C18H38 | 7-methylheptadecane | 1742 | |
| 17.83 | 254 | C18H38 | Octadecane | 1800 | |
| 19.15 | 268 | C19H40 | Nonadecane | 1900 | |
| 19.89 | 295 | C21H44 | *-trimethyloctadecane | 1950 | |
| 19.97 | 256 | C16H32O2 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 1956 | |
| 20.17 | 282 | C18H34O2 | Hexadecenoic acid, ethyl ester | 1970 | |
| 20.50 | 284 | C18H36O2 | Ethyl palmitate | 1992 | |
| 20.62 | 282 | C20H42 | Eicosane | 2000 | |
| 20.98 | 268 | C18H36O | Octadecanal | 2020 | |
| 22.89 | 280 | C18H32O2 | Linoleic acid | 2125 | |
| 23.03 | 282 | C18H34O2 | Oleic acid | 2137 | ● |
| 23.46 | 308 | C20H36O2 | *-Octadecadienoic acid, ethyl ester (possibly Ethyl linoleate) | 2155 | |
| 23.59 | 310 | C20H38O2 | Ethyl oleate | 2165 | ● |
| 24.30 | 310 | C22H46 | Docosane | 2200 | |
| 26.27 | 322 | C23H46 | *-tricosene | 2279 | ● |
| 26.56 | 324 | C23H48 | Tricosane | 2300 | |
| 29.08 | 338 | C24H50 | Tetracosane | 2400 | |
| 30.76 | 352 | C25H52 | 2-methyltetracosane | 2461 | |
| 31.05 | 350 | C25H50 | *-pentacosene | 2472 | |
| 31.26 | 350 | C25H50 | *-pentacosene | 2480 | |
| 31.80 | 352 | C25H52 | Pentacosane | 2500 | |
| 34.69 | 366 | C26H54 | Hexacosane | 2600 | |
| 36.37 | 380 | C27H56 | 4-methylhexacosane | 2658 | |
| 36.91 | 378 | C27H54 | *-heptacosene | 2675 | |
| 37.70 | 380 | C27H56 | Heptacosane | 2700 | |
| 39.19 | 394 | C28H58 | 5-methylheptacosane | 2755 | |
| 40.63 | 394 | C28H58 | Octacosane | 2800 | |
| 41.36 | 422 | C30H62 | *-trimethylheptacosane | 2835 | |
| 41.88 | 408 | C29H60 | 4-methyloctacosane | 2860 | |
| 42.23 | 406 | C29H58 | *-nonacosene | 2877 | |
| 42.47 | 422 | C30H62 | 2,10-dimethyloctacosane | 2889 | G |
| 42.70 | 408 | C29H60 | Nonacosane | 2900 | H |
| 42.90 | 422 | C30H62 | *-dimethyloctacosane | 2918 | |
| 43.29 | 422 | C30H62 | 9-methylnonacosane | 2938 | |
| 43.36 | 422 | C30H62 | 7-methylnonacosane | 2942 | |
| 43.51 | 422 | C30H62 | 5-methylnonacosane | 2951 | |
| 43.79 | 436 | C31H64 | 7,11-dimethylnonacosane | 2968 | |
| 43.90 | 422 | C30H62 | 3-methylnonacosane | 2976 | E |
| 43.96 | 436 | C31H64 | 5,9-dimethylnonacosane | 2980 | K |
| 44.12 | 450 | C32H66 | *-trimethylnonacosane | 2991 | |
| 44.42 | 436 | C31H64 | 3,7-dimethylnonacosane | 3008 | B |
| 44.74 | 450 | C32H66 | 3,7,11-trimethylnonacosane | 3036 | Q |
| 45.01 | 464 | C33H68 | 3,7,11,15-tetramethylnonacosane | 3056 | |
| 45.05 | 436 | C31H64 | *-methyltriacontane (likely 4-) | 3060 | R |
| 45.30 | 434 | C31H62 | *-hentriacontene | 3074 | |
| 45.45 | 450 | C32H66 | 4,10-dimethyltriacontane | 3088 | S |
| 45.54 | 386 | C27H46O | Cholesterol-like | 3090 | A |
| 45.70 | 436 | C31H64 | Hentriacontane | 3100 | M |
| 46.00 | 464 | C33H68 | *-dimethylhentriacontane (likely 9,13) | 3139 | C |
| 46.56 | 464 | C33H68 | 5,9-dimethylhentriacontane | 3187 | D |
| 46.69 | 492 | C35H72 | *-pentamethyltriacontane (possibly 7,11,15,19,23) | 3199 | J |
| 46.93 | 478 | C34H70 | *-trimethylhentriacontane (likely 3,7,11-) | 3223 | O |
| 47.15 | 492 | C35H72 | 5,9,11,15-tetramethylhentriacontane | 3245 | N |
| 47.59 | 492 | C35H72 | *-trimethyldotriacontane or *-tetramethylhentriacontane | 3289 | P |
| 48.78 | 506 | C36H74 | *-Trimethyltritriacontane (possibly 9,13,17) | 3412 | L |
| 49.67 | 520 | C37H76 | *-trimethyltetratriacontane | 3500 | |
| 50.28 | 534 | C38H78 | *-tetramethyltetratriacontane | 3554 |
The original Table 1 is shown here:
| Retention Time | Proposed MF | Proposed structure | RI | Peak ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.35 | C15H32 | Pentadecane | 1500 | |
| 14.05 | C16H34 | 4-Methyltetradecane | 1600 | |
| 14.34 | C10H10O3 | Mellein | 1674 | |
| 15.05 | C16H34 | Hexadecane | 1600 | |
| 16.47 | C17H36 | Heptadecane | 1700 | |
| 17.06 | C20H42 | 7,9-Dimethylheptadecane | 1710 | |
| 17.83 | C18H38 | Octadecane | 1800 | |
| 19.15 | C19H40 | Nonadecane | 1900 | |
| 19.89 | C21H44 | 7,10,11-Trimethyloctadecane | 1920 | |
| 19.97 | C16H32O2 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 1962 | |
| 20.5 | C18H36O2 | Ethyl palmitate | 1968 | |
| 20.62 | C20H42 | Eicosane | 2000 | |
| 20.98 | C18H36O | Octadecanal | 1999 | |
| 22.89 | C18H32O2 | Linoleic acid | 2133 | |
| 23.03 | C18H34O2 | Oleic acid | 2179 | • |
| 23.46 | C20H36O2 | Ethyl-9-Cis-11-Trans-octadecadienoate | 2193 | |
| 23.59 | C20H38O2 | Ethyl oleate | 2173 | • |
| 24.3 | C22H46 | Docosane | 2200 | |
| 26.27 | C23H46 | 7Z-Tricosene | 2296 | • |
| 26.45 | C20H38O2 | Cis-13-Eicosenoic acid | 2368 | |
| 29.08 | C24H50 | Tetracosane | 2400 | |
| 32.51 | C25H52 | Pentacosane | 2500 | |
| 34.69 | C26H54 | Hexacosane | 2600 | |
| 36.37 | C27H56 | 4-Methylhexacosane | 2640 | |
| 36.91 | C27H54 | Heptacosene | 2672 | |
| 38.76 | C28H58 | 9-Methylheptacosane | 2740 | |
| 39.19 | C28H58 | 5-Methylheptacosane | 2740 | |
| 40.05 | C28H58 | *-Trimethylpentacosane | 2610 | |
| 40.63 | C28H58 | Octacosane | 2800 | |
| 40.76 | C28H58 | 7-Methylheptacosane | 2753 | |
| 41.36 | C29H60 | 5,7,11-Trimethylhexacosane | 2783 | |
| 41.88 | C29H60 | 4-Methylnonacosane | 2810 | |
| 42.23 | C29H58 | Nonacosene | 2875 | |
| 42.47 | C30H62 | 2,10-Dimethyloctacosane | 2874 | G |
| 42.7 | C29H60 | Nonacosane | 2900 | H |
| 42.9 | C31H64 | 9,16-Dimethylnonacosane | 2974 | |
| 43.29 | C31H64 | 9,20-Dimethylnonacosane | 2974 | |
| 43.36 | C30H62 | 7-Methylnonacosane | 2940 | |
| 43.51 | C31H64 | 4-Methyltriacontane | 3045 | |
| 43.79 | C31H64 | 7,16-Dimethylnonacosane | 2974 | |
| 43.9 | C31H64 | 2-Methyltriacontane | 3045 | E |
| 43.96 | C31H64 | 10-Methyltriacontane | 3045 | K |
| 44.12 | C32H66 | 10,11,15-Trimethylnonacosane | 3023 | |
| 44.42 | C32H66 | *-Dimethyltriacontane | 3083 | B |
| 44.74 | C32H66 | 8,12-Dimethyltriacontane | 3083 | Q |
| 45.02 | C33H68 | *-Trimethyltriacontane | 3119 | R |
| 45.3 | C31H62 | Hentriacontene | 3100 | |
| 45.45 | C33H68 | 5,10,19-Trimethyltriacontane | 3119 | S |
| 45.54 | C27H46O | Cholest-5-en-3-ol / Cholesterol | 3100 | A |
| 45.7 | C31H64 | Hentriacontane | 3100 | M |
| 46 | C34H70 | 9,13-Dimethyldotriacontane | 3185 | C |
| 46.56 | C33H68 | 5,9-Dimethyldotriacontane | 3185 | D |
| 46.69 | C34H70 | *-Tetramethylnonacosane | 3160 | J |
| 46.93 | C34H70 | *-Multiramified tetratriacontane | 3220-3100 | O |
| 47.15 | C34H70 | 5,9,13,17,21-Pentamethylnonacosane | 3100 | N |
| 47.28 | C33H68 | *-Dimethylhentriacontane | 3185 | T |
| 47.58 | C34H70 | 10,14,18,22-Tetramethyldotriacontane | 3160 | P |
| 48.01 | C34H70 | *-Tetramethyldotriacontane | 3160 | |
| 48.12 | C35H72 | 11,15-Dimethyltritiacontane | 3380 | F |
| 48.77 | C35H72 | *-Methyltetratriacontane | 3440 | L |
| 49.54 | C36H74 | 14-Methylpentatriacontane | 3540 | |
| 49.67 | C36H74 | *-Multiramifiedhexatriacontane | 3420-3300 | |
| 50.28 | C37H76 | *-Tetramethyltetratriacontane | 3480 |
Main results
The corrected section of the main results:
“We identified 61 molecules in TF (Table 1), including fatty acids and fatty acid esters, linear alkanes, double bonded hydrocarbons, branched hydrocarbons, and a cholesterol-like molecule. The most abundant TF compounds comprised 27 or more carbons.”
These changes were made to reflect the updated identifications and improve the clarity that these are the molecules we were able to identify rather than a complete list of all components found in TF. The last sentence places the emphasis on the molecules of interest (i.e., those abundant in TF) rather than on the molecules we were able to identify.
The original section of the main results:
“We identified 63 molecules in TF (Table 1), including eight fatty acids and fatty acid esters, 13 unbranched and 36 branched hydrocarbons with one to five methyl branches. The majority (40/63) of the TF compounds comprised 27 or more carbons.”
Figure 3 legend
The corrected legend for Figure 3 is shown here:
… "The abundant component (peak A) found in TF samples but not on the cuticle was a cholesterol-like molecule that insects cannot synthesize but must receive from their diet. Three molecules outside this window were found only in TF and not on the cuticle: *-tricosene, oleic acid, ethyl oleate (Table 1)”….
The original legend for Figure 3 is shown here:
… “The abundant component (peak A) found in TF samples but not on the cuticle was cholesterol, a molecule that insects cannot synthesize but must receive from their diet. Three molecules outside this window were found only in TF and not on the cuticle: 7Z-tricosene, oleic acid, ethyl oleate (Table 1).”…
Methods
A number of changes were made to the section of the Methods, “Identification of trophallactic fluid hydrocarbons”. These changes were made to reflect the updated method for identification, the updated identifications and to improve clarity. This section of the methods is shown here in full with corrected sections in italics.
“Characterization of branched alkanes by GC-MS remains a challenge due to the similarity of their electron impact (EI) mass spectra and the paucity of corresponding spectra listed in EI mass spectra databases. A typical GC-MS chromatogram (Figure 3—figure supplement 1A) reveals the complexity of the TF sample. The workflow described here was systematically used to characterize the linear and branched hydrocarbons present in TF samples summarized in Table 1. The parent ion was first determined for each peak after background subtraction. Ambiguities remained in some cases due to the low intensity or absence of the molecular ion.
Linear alkanes present in TF samples were localized using a standard mixture of C8-C40 alkanes. Then RI values were deduced for all compounds present in the samples based on their retention times (Figure 3-figure supplement 1G, red).
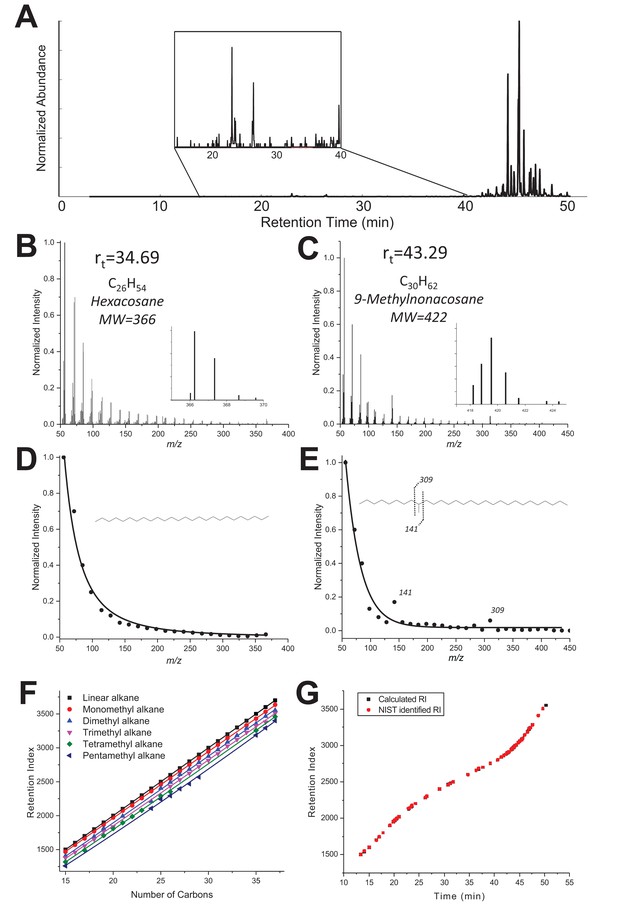
To determine the number of methyl branches for alkanes, we examined the distribution of fragment ions in the spectrum by fitting their intensities with an exponential decay function and specifically looking for the fragment ions that do not fit to the calculated exponential decay function. From the experimental mass spectrum (Figure 3—figure supplement 1B–C), the intensity of all fragment ions was extracted and fitted with the function (Figure 3—figure supplement 1D–E). Figure 3—figure supplement 1 clearly shows two different resulting EI mass spectra profiles: on the left a linear alkane corresponding to n-hexacosane (Rt = 34.69 min, MF C26H54); on the right, a monomethyl-branched structure most likely corresponding to 9-methylnonacosane (Rt = 43.29 min, MF C30H62) with two enhanced fragment ions at m/z 141 and 309 emerging from the curve.
Extracting and fitting the fragment ion profiles first helped to discriminate between linear and branched hydrocarbons, but also to estimate the number of methyl branches. To confirm for each compound the number of carbons and branches obtained, we used Kovats retention index (RI) values in the NIST Chemistry WebBook (Linstrom et al., 2000). Based on the RI values for similar GC stationary phase from C15 to C38 hydrocarbons, six different curves of RI vs. number of carbons were constructed from linear to pentamethylated alkanes (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F). To construct the curves, average RI values were taken of all hydrocarbons available in the database, with a given number of carbons and a given number of methyl branches. For example, the RI value of 2409 obtained for C25 and two branches is the average of 3,(7/9/11/13)-dimethyltricosane, 3,(3/5)-dimethyltricosane and 5,(9/11)-dimethyltricosane values listed in the NIST Chemistry WebBook for the same stationary phase. Those curves were used to check for every compound that, from the measured RI value and the number of carbons found, the number of ramifications found fit properly with the curves.
Once the number of branches and the parent ion mass were known, the position of the different branches could be deduced from the fragment ion values. When ambiguity remained on the position of the branch or double bond, this is indicated with an asterisk in Table 1.
The plot of experimental retention times for each compound as a function of the RI index closely fitted the plot using RI values given by NIST for the identified compounds (Figure 3—figure supplement 1G), bringing additional confidence to the identifications.
Table 1 summarizes the proposed structures for hydrocarbons and other compounds detected in TF samples.”
Figure 3—figure supplement 1
The corrected Figure 3—figure supplement 1 is shown here:
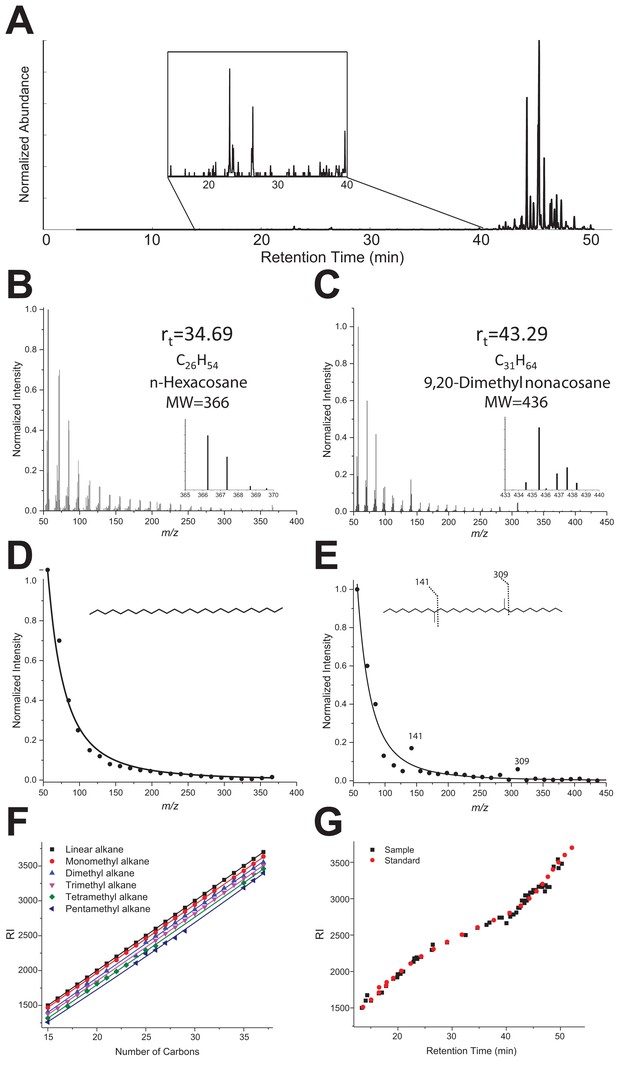
The original Figure 3—figure supplement 1 is shown here:
Legend for Figure 3—figure supplement 1
Changes were made to reflect the updated identifications, to correct typographical errors, and to improve clarity of the methods.
Corrected legend (corrections shown in italics):
… “(B–C) GC-MS Mass spectra of a linear alkane (C26, elution time 34.69 min, panel B) and a methylated alkane (C30, Rt 43.29 min, panel C). (D-E) Extracted MS spectra were fitted with an exponential decay equation with their proposed structure based on enhanced fragment ions (m/z 141 and 309 in the case of 9-methylnonacosane). (F) RI values vs. number of carbons extracted from the NIST Chemistry WebBook library, depending on the number of methyl branches: linear (black), monomethyl (red), dimethyl (blue), trimethyl (pink), tetramethyl (green) and pentamethyl (dark blue) alkanes. (G) Retention index values calculated for each compound listed in Table 1 are based on the elution time and RIs of a hydrocarbon ladder from C8-C40 (black) overlaid with NIST RI values reported in the NIST database for the identified hydrocarbons (red).”
Original legend:
… “(B–D) GC-MS Mass spectra of linear alkane (n-hexacosane at Rt 34.69 min, panel B) and a dimethylated alkane at Rt 43.29 min (C). Extracted MS profiles were fitted with an exponential decay equation (B, D). The proposed structure for the branched alkane based on fragments ions (141 and 309) is 9,20-dimethyl nonacosane (D). (E) RI values vs. number of carbons extracted from the NIST Chemistry WebBook library, depending on the number of ramifications: linear (black), monomethyl (red), dimethyl (blue), trimethyl (pink), tetramethyl (green) and pentamethyl (dark blue). (F) The black dots represent experimental retention times with the calculated RI index for all identified hydrocarbons of the TF sample. The red dots represent the experimental retention times and with their RI index for the linear C8-C40 alkane standard.”
The article has been corrected accordingly.
Article and author information
Author details
Version history
Copyright
© 2019, LeBoeuf et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 487
- views
-
- 3
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.






