Whole-brain in situ mapping of neuronal activation in Drosophila during social behaviors and optogenetic stimulation
Figures
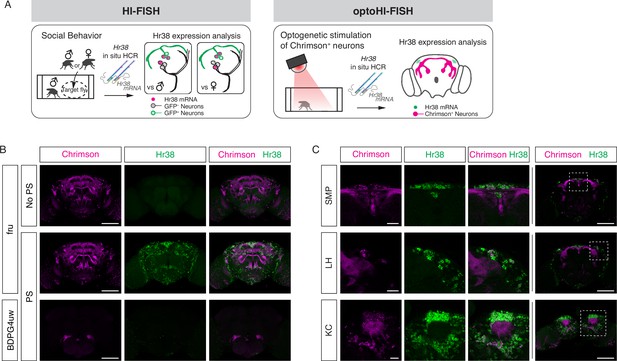
Mapping neuronal activities using Hr38 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).
(A) Illustrated summary of this study for mapping Hr38 expression induced by social behavior or artificial activation of specific neuronal populations. (B) Representative images of Hr38 expression before (fru-No PS) and after photostimulation of fru-GAL4>Chrimson neurons (fru-PS). BDPG4uw-PS represents the images after photostimulation of empty-GAL4>Chrimson neurons. magenta: Chrimson::tdT (native fluorescence), green: Hr38 hybridization chain reaction (HCR) signals. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Magnified confocal section images of Hr38 expression (left three columns) from the boxed region (far right column) after photostimulation of fru-GAL4>Chrimson neurons. SMP, superior medial protocerebrum; LH, lateral horn; KC, Kenyon cells. Scale bar: 20 µm (left three columns) or 100 µm (far right column).
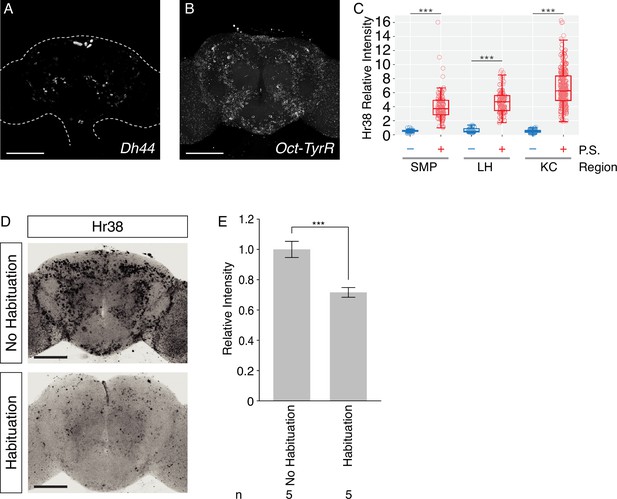
Hybridization chain reaction (HCR) fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and Hr38 signals in the adult fly brain.
(A, B) Examples of whole mount FISH on adult fly brains. Scale bar: 100 µm. (A) Dh44 from neuropeptides, high copy number genes. (B) Octopamine-Tyramine receptor from G-protein-coupled receptors, low copy number gene. (C) Expression level of Hr38 HCR signals in Fru-GAL4+ neurons in the non-photostimulated (P.S.−) or photostimulated (P.S.+) conditions in the indicated regions. SMP, superior medial protocerebrum; LH, lateral horn; KC, Kenyon cells. Mann–Whitney U test was performed (***p < 0.001). Number of neurons analyzed; SMP (−): 40, LH (−): 32, KC (−): 79, SMP (+): 97, LH (+): 87, KC (+): 207. (D) Representative images of Hr38 expression with or without habituation after transfer procedure. Scale bar: 100 µm. (E) Comparison of the relative expression of Hr38 signals between samples with or without habituation. Independent samples T-test was performed (***p < 0.001).
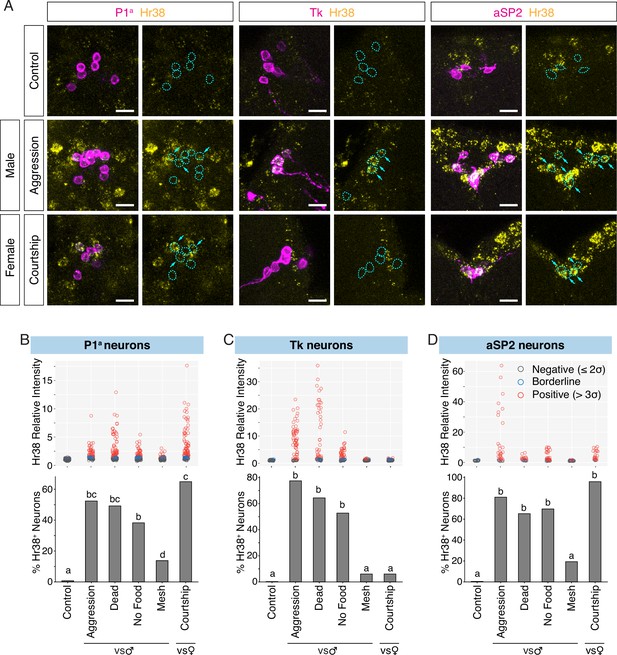
Investigation of neurons activated by social behavior with Hr38 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).
(A) Hr38 expression in the neurons labeled with P1a-split GAL4, Tk-GAL4, and aSP2-GAL4 drivers. magenta: myr::GFP, yellow: Hr38 hybridization chain reaction (HCR) signals. Dotted lines depicted the outlines of myr::GFP-labeled cell bodies. Arrows: cell bodies of Hr38-positive neurons. Scale bar: 10 µm. Upper, scatter plots indicate expression level (relative intensity) of Hr38 HCR signals; lower, bar plots indicate percentage of Hr38-positive neurons (‘positive’ defined as neurons with a relative signal intensity >3σ above the average signal intensity of the control condition) in P1a (B), Tk (C), and aSP2 cells (D) after different behavioral episodes. Aggression: aggressive behavior against another male, Dead: interaction with a dead male, No Food: interaction with another male without food (no fighting), Mesh: interaction with another male, separated with mesh (no physical contact), Courtship: courtship behavior with a virgin female. Bar plots indicate the percentage of Hr38+ neurons among GFP-labeled cells. Bars with the same letter are not statistically significantly different; bars with no common letter are significantly different (p < 0.05, chi-square test). Number of neurons and individuals analyzed; P1a-Control: 135 (N = 8), P1a-Aggression: 84 (N = 5), P1a-Dead Male: 126 (N = 7), P1a-No Food: 115 (N = 6), P1a-Mesh: 87 (N = 6), P1a-Courtship: 114 (N = 6), Tk-Control: 45 (N = 4), Tk-Aggression: 69 (N = 6), Tk-Dead Male: 61 (N = 6), Tk-No Food: 63 (N = 6), Tk-Mesh: 82 (N = 8), Tk-Courtship: 66 (N = 6), aSP2-Control: 20 (N = 3), aSP2-Aggression: 36 (N = 4), aSP2-Dead Male: 23 (N = 3), aSP2-No Food: 49 (N = 4), aSP2-Mesh: 36 (N = 4), aSP2-Courtship: 24 (N = 3).
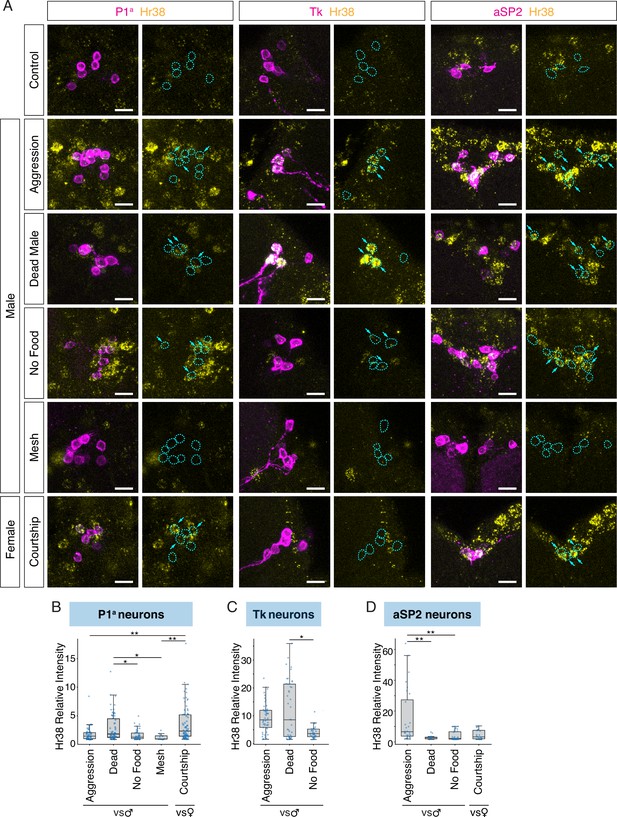
Complete dataset of Hr38 expression after social behaviors.
(A) Hr38 expression in the neurons labeled with P1a-split GAL4, Tk-GAL4, and aSP2-GAL4 drivers. magenta: myr::GFP, yellow: Hr38 hybridization chain reaction (HCR) signals. Dotted lines depicted the outlines of myr::GFP-labeled cell bodies. Arrows: cell bodies of Hr38-positive neurons. Scale bar: 10 µm. Expression level (relative intensity) of Hr38 HCR signals in Hr38-positive neurons (defined as cells with signals >3σ above the average value of the control condition) in the P1a (B), Tk (C), and aSP2 (D) populations after different behavioral episodes. The behaviors for which quantification of intensity is presented in (B–D) were only those conditions where the cells exhibited a statistically significantly higher % of Hr38+ neurons compared to the control condition (see Figure 2B–D, lower). Mann–Whitney U test with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. Aggression: aggressive behavior against another male, Dead: interaction with a dead male, No Food: interaction with another male without food (no fighting), Mesh: interaction with another male, separated with mesh (no physical contact), Courtship: courtship behavior with a virgin female. Number of neurons analyzed; P1a-Aggression: 44, P1a-Dead Male: 62, P1a-No Food: 44, P1a-Mesh: 12, P1a-Courtship: 74, Tk-Aggression: 53, Tk-Dead Male: 41, Tk-No Food: 35, aSP2-Aggression: 28, aSP2-Dead Male: 15, aSP2-No Food: 33, aSP2-Courtship: 23. Note that the Hr38 relative intensity values in panels B–D are derived only from the Hr38-positive neurons (defined as cells with signals >3σ above the average value of the control condition), whereas the numbers in Figure 2B (upper) are from all GFP+ neurons counted.
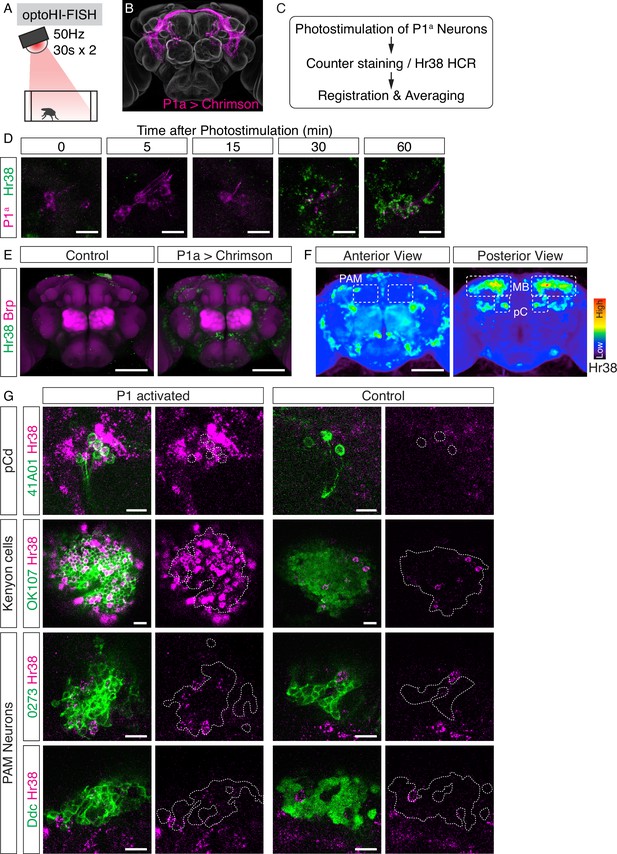
Investigation of downstream neurons activated by optogenetic activation of P1a neurons.
(A) Illustration of the experimental setup. (B) Expression pattern of Chrimson::tdT driven by P1a split GAL4. (C) Scheme of the data analysis procedure. (D) Time-course study of Hr38 hybridization chain reaction (HCR) expression after P1a photostimulation in P1a-labeled neurons and the surrounding area. By 30–60 min, most of the P1a-labeled neurons expressed Hr38 (96.8% of P1a-labeled neurons at 30 min). Scale bars: 10 µm. (E) Average image of Hr38 expression of control (BDPG4Uw) and P1a-activated brains. Five individual brains from each condition were registered into a template brain and averaged. Green: Hr38 HCR signals, magenta: Brp. Scale bar: 100 µm. (F) Heat map analysis of Hr38 expression. Areas depicted by dotted lines represent the areas of PAM neurons (PAM), mushroom bodies (MB), and pC neurons (pC). Scale bar: 100 µm. (G) Confocal images of Hr38 expressions in pCd neurons (R41A01), Kenyon cells (OK107), and PAM neurons (0273 or Ddc) of control and P1a activated brains. Green: myr::GFP, magenta: Hr38. Dotted lines depicted the outlines of cell bodies (pCd) or cluster of neurons (KC, PAM). Scale bar: 10 µm.
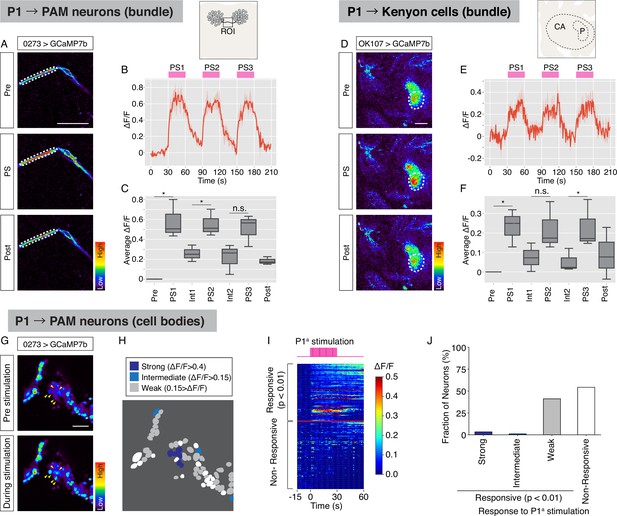
Calcium imaging of PAM neurons and mushroom body neurons combined with P1a photostimulation.
(A–C) Calcium imaging of PAM neurons, labeled with 0273 GAL4 driver while P1a neurons were optogenetically activated. Region of interest (ROI) is depicted in an illustrated image. (A) Representative image of GCaMP signals in neuronal bundles of PAM neurons before, during, and after P1a activation. Scale bar: 20 µm. dF/F (B) and average dF/F (C) of PAM neurons in response to photostimulation of P1a neurons (n = 3 individuals; mean ± SEM (B) and a box and whisker plot (C)). (D–F) Calcium imaging of nerve bundle of mushroom body Kenyon cells, labeled with OK107 GAL4 driver while P1a neurons were optogenetically activated. The imaging area is depicted as an illustrated image. CA: calyx, P: peduncle. (D) Representative image of GCaMP signals in mushroom body peduncle before, during, and after P1a activation. Scale bar: 20 µm. dF/F (E) and average dF/F (F) of Kenyon cells in response to photostimulation of P1a neurons (n = 3 individuals; mean ± SEM (E) and a box and whisker plot (F)). For (C, F), Mann–Whitney U tests were performed (*p < 0.05). (G–J) Calcium imaging of cell bodies of PAM neurons while P1a neurons were optogenetically activated. (G) Representative image of GCaMP signals in PAM neurons averaged from three consecutive trials of P1a stimulation. Arrowheads: cell bodies shows strong responses (dF/F > 0.4) to P1a stimulation. Scale bar: 20 µm. (H) Distribution of responsive PAM neurons. Colored by the strength of responses (dark blue: strong response, light blue: intermediate response, gray: weak response, white: no response). (I) Temporal profiles of responses evoked by P1a photostimulation. Average dF/F during P1a stimulation are higher than that before the stimulation (Mann–Whitney U test, p < 0.05, red line segregates between responded and non-responded groups). (J) Fraction of PAM neurons responsive to P1a stimulation (n = 175 cells from 3 individuals).
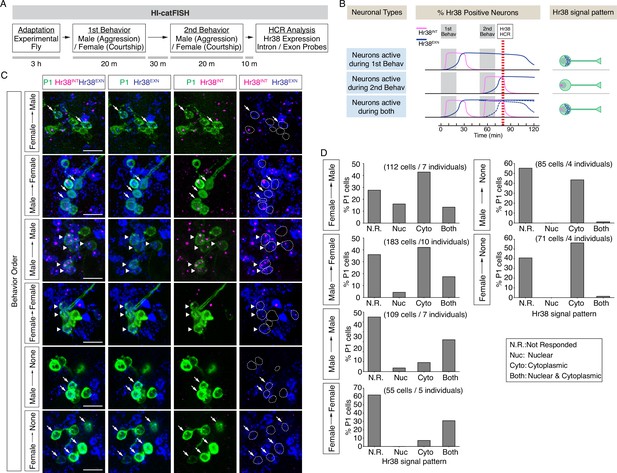
Drosophila catFISH reveals P1a subpopulations activated by two different social behaviors.
(A) Experimental design of the fly catFISH. Each fly experienced the first behavior (aggression or courtship) followed by second behavior (aggression or courtship), and the hybridization chain reaction (HCR) was performed with the Hr38 probes targeted for the exon or the intron sequence. (B) Time-course of Hr38 signals detected by the exon- or the intron-targeted Hr38 HCR probes and expected Hr38 signals in each neuron. (Top) The intron-targeted Hr38 HCR signals (magenta) induced by first behavior disappear at the timing of HCR analysis while the exon-targeted Hr38 signals (blue) remain in the cytoplasmic area. (Middle) Both intron- and exon-targeted signals are present in the nucleus. (Bottom) Both intron- and exon-targeted signals induced by the second behavior are present in the nucleus, and exon-targeted Hr38 signals induced by the first behavior are present in the cytoplasmic area. In 'Neurons active during both', the exon probe signals from the first behavior decline (dotted blue line *1) after 60 min (also see Figure 4—figure supplement 1). However, it is canceled out as the signals from second behavior are increased (dotted blue line *2). As a result, the combined Hr38 exon probe signals (solid blue line) remain high at the time point for Hr38 HCR. (C) Representative images of Hr38 HCR signals in P1a neurons after six different behavioral conditions. Green: myr::GFP, magenta: intron-targeted Hr38 HCR signals: exon-targeted Hr38 signals. Scale bar: 10 µm. The images shown are for illustration purposes only and represent single optical sections covering only a portion of the P1a neuronal cluster. They exclude P1a cells present in other Z-planes. Quantification (D) was based on signals measured in all P1a cells contained within an entire Z-stack. See also Figure 4—figure supplement 1D. (D) Fraction of responsive P1a neurons across indicated conditions. N.R.: not responded, Nuc: nuclear signal only (responded to only second target), Cyto: cytoplasmic signal only (responded to only first target), Both: nuclear and cytoplasmic signal (responded to both first and second targets).
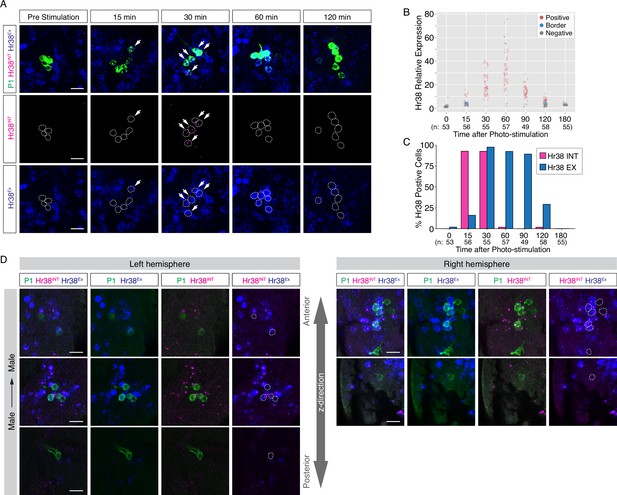
Time-course study of the expression of Hr38 with the exon- or intron-targeted probes after photostimulation of P1a neurons.
(A) Confocal images of Hr38 expression detected by the exon-targeted (Hr38Ex, blue) and the intron-targeted (Hr38INT, magenta) probe in the area including P1a cell body (Chrimson::tdT, green). Arrows: Cells positive for both Hr38INT and cytoplasmic Hr38Ex signals. Scale bar: 10 µm. (B) Relative expression of Hr38 RNA detected by the exon-targeted probe over time. Red: positive (the expression level > +3σ), blue: borderline (+3σ > the expression level > +2σ), gray: negative (< +2σ). (C) Percentage of Hr38-positive neurons detected by the intron-targeted probe (magenta) and the exon-targeted probe (blue) over time. (D) Different Z-plane images of Hr38 hybridization chain reaction (HCR) signals in P1a neurons after Male → Male exposure. Images of P1a neurons in the left and right hemisphere were taken from the same individual as shown in Figure 4C (Male → Male). Green: myr::GFP, magenta: intron-targeted Hr38 HCR signals: exon-targeted Hr38 signals. Scale bar: 10 µm.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
The table provides information about the fly genotypes used in this research, including the names used in the manuscript, corresponding figure numbers, fly strain names, sources, identifiers, and FlyBase IDs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92380/elife-92380-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92380/elife-92380-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf





