The Natural History of Model Organisms: The unlimited potential of the great pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis
Figures
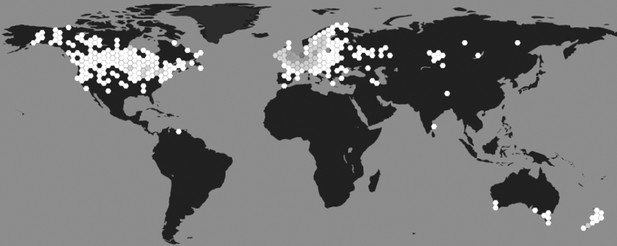
Geographical distribution of L. stagnalis.
Places where this species of snail has been reported to occur (hexagons), shaded based on population density (white indicates low density and dark grey indicates high density; source data from GBIF Secretariat, 2019).
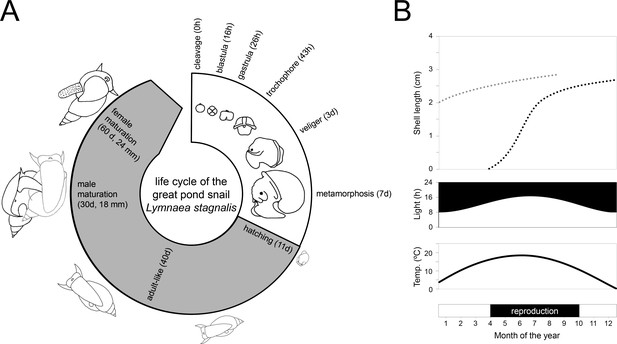
Life cycle and wild reproductive habit of L. stagnalis.
(A) The embryonic development in the egg from zygote to hatching (over 11–12 days) is depicted in the white area of the life cycle and consists of six main stages: cleavage, blastula, gastrula, trochophore, veliger and metamorphosis (Source data from Ivashkin et al., 2015). The grey area of the life cycle depicts growth and development after hatching. Although L. stagnalis is a simultaneous hermaphrodite, the male reproductive organs are functional before the female ones (Koene and Ter Maat, 2004): specimens reach male and female maturation on average at an age of 30 and 60 days, respectively (based on Koene, 2010). (B) In the wild, generations only partly overlap, as depicted by the two dotted growth curves (top; based on Nakadera et al., 2015). Individuals that are born during spring and summer, overwinter as adults (light grey dotted line) after which they overlap with the adult generation of the next year (black dotted line). The external conditions such as light and temperature (middle), which strongly influence when egg laying occurs (bottom), are depicted for the situation in a typical temperate zone.
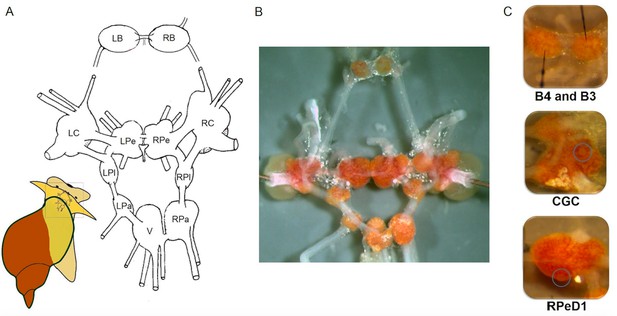
The central nervous system and identified single neurons of L. stagnalis.
(A) Schematic map (dorsal view) of the isolated whole central nervous system that is formed of the paired (left and right) buccal (LB, RB), cerebral (LC, RC), pedal (LPe, RPe), pleural (LPl, RPl), parietal (LPa, RPa) and unpaired visceral (V) ganglia. (B) Isolated central nervous system showing the arrangement of the 11 interconnected ganglia. Brightly pigmented orange-coloured neurons are localised on the surfaces of the ganglia. (C) Identified single neurons: B4 (left), B3 (right; motor neurons responsible for the implementation of feeding), CGC (interneuron in cerebral ganglia modulating the feeding and learning) and RPeD1 (interneuron in pedal ganglia regulating the respiration and heartbeat).
Tables
List of some of the most important (neuro)peptides identified in L. stagnalis.
| Molecule | Abbreviation | Function | Accession number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| caudodorsal cell hormones | CDCH | reproduction | P06308 | Vreugdenhil et al., 1988 |
| FMRFamides | FMRF | reproduction, cardiac control | P19802 | Linacre et al., 1990 |
| conopressin | - | reproduction | AAB35220 | Van Kesteren et al., 1995 |
| neuropeptide Y | NPY | reproduction, development | CAB63265 | De Jong-Brink et al., 1999 |
| actin-related diaphanous genes (1, 2) | dia 1, dia 2 | development, chirality | KX387869, KX387870 KX387871, KX387872 | Kuroda et al., 2016 |
| insulin-related peptides (I, II, III, V, VII) | MIPs | development | CAA41989; P25289; AAB28954; AAA09966; AAB46831 | Smit et al., 1991; Smit et al., 1992; Smit et al., 1993b; Smit et al., 1996; Smit et al., 1998 |
| sodium stimulating hormone | SIS | ion and water control | P42579 | Smit et al., 1993a |
| small cardioactive peptide | SCP | feeding, cardiac control | AAC99318 | Perry et al., 1999 |
| myomodulin | MIP | feeding, cardiac control | CAA65635 | Kellett et al., 1996 |
| pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide-like molecule | PACAP-like | learning and memory | - | Pirger et al., 2010 |
| cAMP response element-binding proteins (1, 2) | CREB 1 CREB 2 | learning and memory | AB041522; AB083656 | Sadamoto et al., 2004 |
| glutathione reductase and peroxidase | Gred Gpx | metabolic detoxification | FJ418794, FJ418796 | Bouétard et al., 2014 |
| catalase | CAT | metabolic detoxification | FJ418795 | Bouétard et al., 2014 |
| superoxide dismutase | SOD | metabolic detoxification | AY332385 | Zelck et al., 2005 |
| heat-shock protein | HSP70 | stress response | DQ206432 | Fei et al., 2007 |
| molluscan defence molecule | MDM | immune system | AAC47132 | Hoek et al., 1996 |
| allograft inflammatory factor-1 | AIF-1 | immune system | DQ278446 | van Kesteren et al., 2006 |





