Broca's cerebral asymmetry reflects gestural communication's lateralisation in monkeys (Papio anubis)
Figures
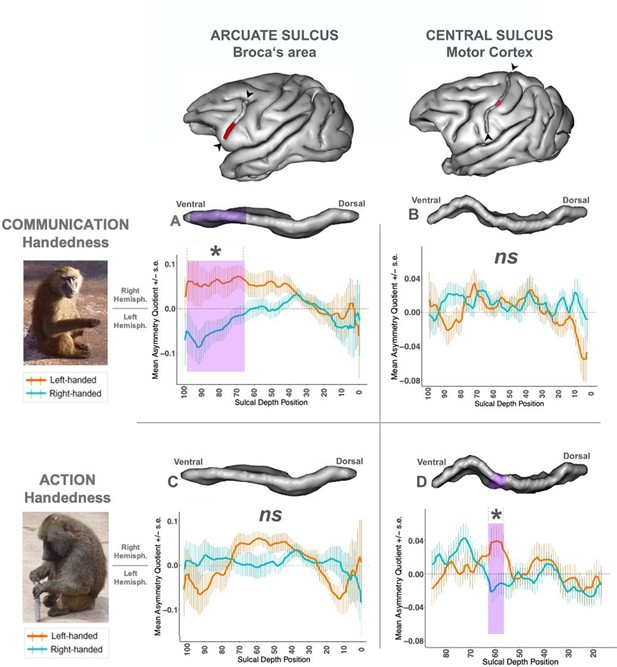
Effect of left-/right-hand direction of two handedness types (communication vs action) on neuroanatomical sulcus depth asymmetries (IA sulcus vs Central sulcus).
Left panel: Pictures of the two types of handedness measures in baboons. ‘Communication Handedness’: a ‘Handslap’ communicative gesture in a juvenile male; ‘Action Handedness’: the non-communicative bimanual coordinated ‘tube task’ performed by an adult male. Top panel: 3-D brain representation from BrainVisa software of the baboon’s left hemisphere, including the IA sulcus; and the Central sulcus with the portion in purple where a significant effect was found in Margiotoudi et al., 2019. Graphs: Sulcus depth’s asymmetry (AQ) comparison between right-handed group versus left-handed group of baboons classified according to the type of manual tasks. Positive Mean Asymmetry Quotient values (AQ) indicate rightward hemispheric asymmetry, negative Mean Asymmetry Quotient values leftward hemispheric asymmetry. +/- SE indicated the Standard Error. (A) IA sulcus AQ between right-handed (N=28) versus left-handed (N=22) groups’ classification for communicative ‘Handslap’ gesture. Significant contralateral AQ difference (p < .01) between the two groups was found for a cluster including positions 65 to 95 (highlighted in purple in the graph and the 3D representation of the IA Sulcus). (B) Central Sulcus AQ between right-handed (N=28) versus left-handed (N=22) groups’ classification for non-communicative bimanual coordinated actions. (C) IA sulcus AQ between right-handed (N=28) versus left-handed (N=22) groups’ classification for non-communicative bimanual coordinated actions. (D) Initial graph (Adapted from Figure 2 from Margiotoudi et al., 2019) of the Central Sulcus AQ showing the significant contralateral AQ differences (p < .05) found between the left-handed (N=28) versus right-handed (N=35) groups group for the non-communicative bimanual coordinated actions (Action condition) for positions 56 to 61 (highlighted in purple in the graph and the 3D representation of the Central Sulcus).
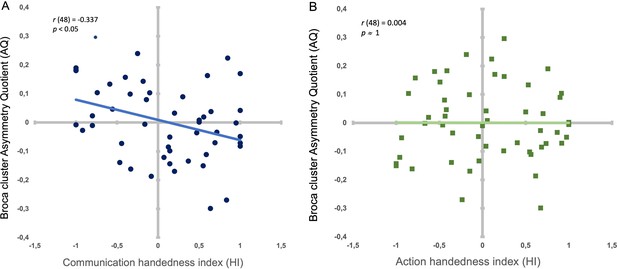
Correlation between handedness degree types and the Broca’s cluster’s asymmetry.
(A) Individual handedness degree (HI) for communicative gestures and AQ depth values of the Broca’s cluster (i.e. from positions 65–95) in dark blue dots. Light blue line: Significant negative correlation between HI and AQ. B. Individual handedness degree (HI) for non-communicative manipulative actions (HI) and AQ depth values of the Broca’s cluster (i.e. from positions 65–95) in dark green squares. Light green line (superposing on x axis): Non-significant correlation between HI and AQ.





