Adiposity may confound the association between vitamin D and disease risk – a lifecourse Mendelian randomization study
Figures
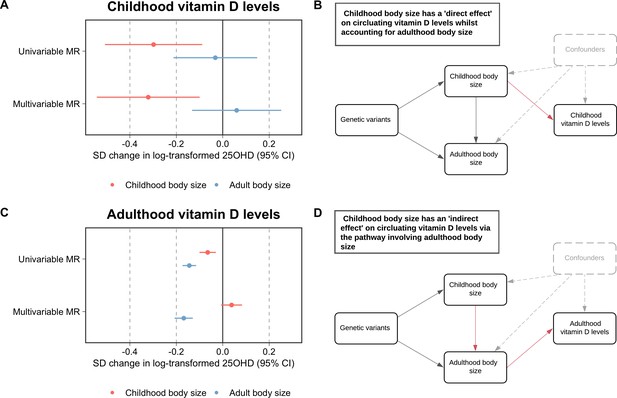
Forest plots and schematic diagrams depicting the findings from this study.
(A) A forest plot illustrating the direct effect of childhood body size on circulating vitamin D levels measured during childhood (mean age: 9.9 years, n=3,800 participants) using data from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) with the corresponding schematic diagram for this finding being located in panel (B). (C) A forest plot depicting the indirect effect of childhood body size on adulthood measured vitamin D levels using data from the UK Biobank study (mean age: 56.5 years, n=401,460 participants) as described in the schematic diagram presented in panel (D). MR – Mendelian randomization. All estimates underlying the forest plots can be found in Supplementary file 1.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Tables with Mendelian randomization estimates supporting the conclusions of this study.
Table 1 includes univariable Mendelian randomization estimates between lifecourse adiposity and vitamin D levels, Table 2 includes multivariable Mendelian randomization estimates between lifecourse adiposity and vitamin D levels, and Table 3 includes repeated analyses using vitamin D estimates from the study by Revez et al.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79798/elife-79798-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79798/elife-79798-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





