Correction: Dichotomous role of the human mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+/Li+ exchanger NCLX in colorectal cancer growth and metastasis
Main text
Pathak T, Gueguinou M, Walter V, Delierneux C, Johnson MT, Zhang X, Xin P, Yoast RE, Emrich SM, Yochum GS, Sekler I, Koltun WA, Gill DL, Hempel N, Trebak M. YYYY. Dichotomous role of the human mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+/Li+ exchanger NCLX in colorectal cancer growth and metastasis. eLife 9:e59686. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59686.
Published 11 September 2020
We have been made aware through PubPeer of a mistake in Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Although the issues identified on PubPeer do not change the conclusions of the paper, they warrant correction. All sequences of primers and guide RNAs used in generating knockout (KO) cell clones and in genotyping are correct. Unfortunately, two sets of sequences were inadvertently swapped by the first author, a confusion that was caused by the fact that the NCLX gene is reversed in mammals. Although there is no excuse for such errors, unfortunately none of the contributing authors noticed these issues. We corrected this and added the sequences of the primers for the housekeeping genes that were identified as missing. Therefore, we modified the Appendix 1—key resources table and the cartoon in Figure 3—figure supplement 1 to reflect these corrections. Finally, we provide a Supplementary file 1, which contains genomic sequencing data for all our NCLX KO clones that provide decisive evidence that the NCLX is indeed knocked out in these cells. The details of the corrections are as follow:
We have corrected the text in the Methods section to change the guide RNA from g1 to g2 and add the predicted location of the stop codon for NCLX KO #33. The corrected text is shown here:
For the case of HCT116 cells, which we generated first, NCLX KO #33 was generated using a guide RNA (g2) which resulted in a single cut at nucleotide 150 in exon one causing a frameshift mutation and introduction of a stop codon at predicted position 181–183 bp and 184–186 bp in the NCLX open reading frame (Figure 3—figure supplement 1A).
Original text for reference:
For the case of HCT116 cells, which we generated first, NCLX KO #33 was generated using a guide RNA (g1) which resulted in a single cut at nucleotide 150 in exon one causing a frameshift mutation and introduction of a stop codon at position 180 in the NCLX open reading frame (Figure 3—figure supplement 1A).
We have corrected the text in the Results section to change the guide RNA from g1 to g2 and add the predicted location of the stop codon for NCLX KO #33. The corrected text is shown here:
For in vivo studies NCLX KO clone #33 was used, which was generated using a guide RNA (g2) resulting in a single cut at nucleotide 150 in exon one causing a frameshift mutation and introduction of a stop codon at predicted position 181–183 bp and 184–186 bp in the NCLX open reading frame (Figure 2A).
Original text for reference:
For in vivo studies NCLX KO clone #33 was used, which was generated using a guide RNA (g1) resulting in a single cut at nucleotide 150 in exon one causing a frameshift mutation and introduction of a stop codon at position 180 in the NCLX open reading frame (Figure 2A).
We have corrected the text in the Results section to fix the gene name from Fox3 to Foxo3. The corrected text is shown here:
In agreement with these findings, we found that transcript levels of stem cell markers NANOG, Oct4, Sox2, and Foxo3, as well as regulators of the glutathione synthesis pathway implicated in regulating these transcription factors in breast cancer, SLC7A11 and GCLM (Lu et al., 2015), were significantly upregulated in NCLX KO cells (Figure 5H–J, Figure 5—figure supplement 1G–O).
Original text for reference:
In agreement with these findings, we found that transcript levels of stem cell markers NANOG, Oct4, Sox2, and Fox3, as well as regulators of the glutathione synthesis pathway implicated in regulating these transcription factors in breast cancer, SLC7A11 and GCLM (Lu et al., 2015), were significantly upregulated in NCLX KO cells (Figure 5H–J, Figure 5—figure supplement 1G–O).
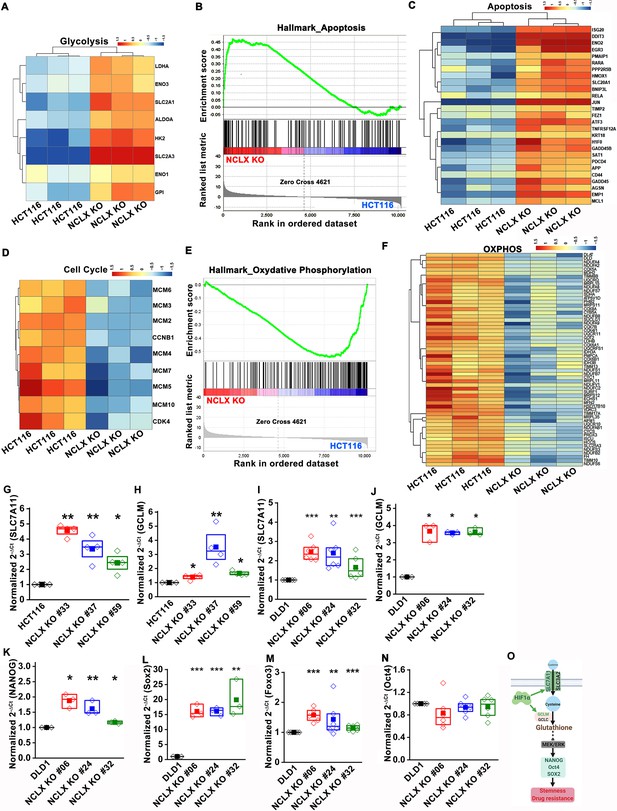
We have corrected the figure legend of Figure 5—figure supplement 1M to fix the gene name from Fox3 to Foxo3. The corrected text is shown here:
(G–N) RT-qPCR data plotted as the 2-ΔCt mRNA value of SLC7A11 (G), GCLM (H) in clones of HCT116 NCLX KO cells normalized to control HCT116 cells, and SLC7A11 (I), GCLM (J) NANOG (K), Sox2 (L), Foxo3 (M), and Oct4 (N) in clones of DLD1 NCLX KO cells relative to tubulin and normalized to control DLD1 cells.
Original text for reference:
(G–N) RT-qPCR data plotted as the 2-ΔCt mRNA value of SLC7A11 (G), GCLM (H) in clones of HCT116 NCLX KO cells normalized to control HCT116 cells, and SLC7A11 (I), GCLM (J) NANOG (K), Sox2 (L), Fox3 (M), and Oct4 (N) in clones of DLD1 NCLX KO cells relative to tubulin and normalized to control DLD1 cells.
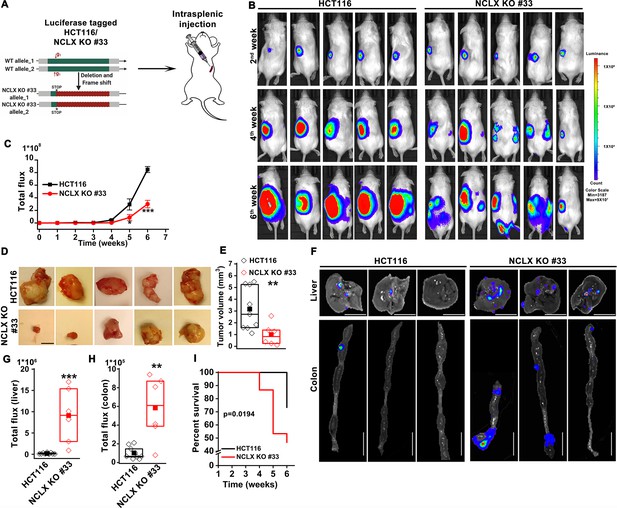
The unfortunate confusion described above led to mislabelling of primers and the two guide RNA in the cartoon of Figure 3—figure supplement 1A-F. This confusion occurred because the NCLX gene is reversed in mammals. We now include an updated version of Figure 3—figure supplement 1, where the guide RNAs and primers within the cartoons are drawn as much to scale as possible with the relative positions of primers and guide RNAs and the predicted positions of the STOP codons introduced by CRISPR/Cas9. In the case of DLD1 cells in Figure 3—figure supplement 1G, the correct primer combination is 4+5 and not 3+6 as originally stated. The corrected Figure 3—figure supplement 1 is shown here:

The originally published Figure 3—figure supplement 1 is shown for reference:

The original Figure 3—figure supplement 1A was reproduced in Figure 2A for convenience. Therefore, we also need to fix the cartoon in Figure 2A. The corrected Figure 2 is shown here:
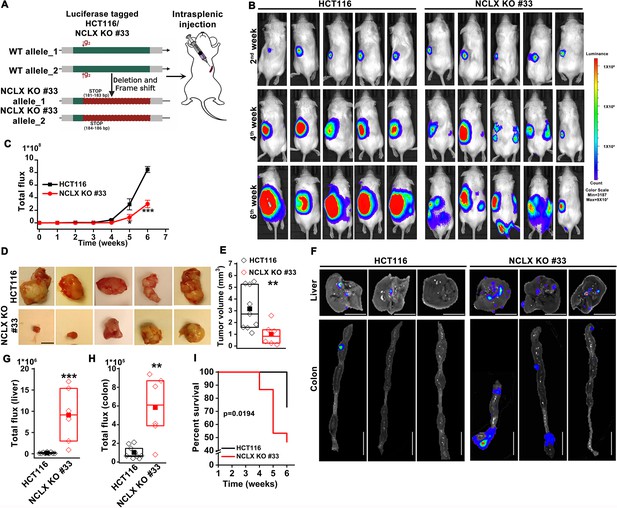
The originally published Figure 2 is shown for reference:
We also corrected the gene name Fox3 to Foxo3 in Figure 5—figure supplement 1M. The corrected Figure 5—figure supplement 1 is shown here:
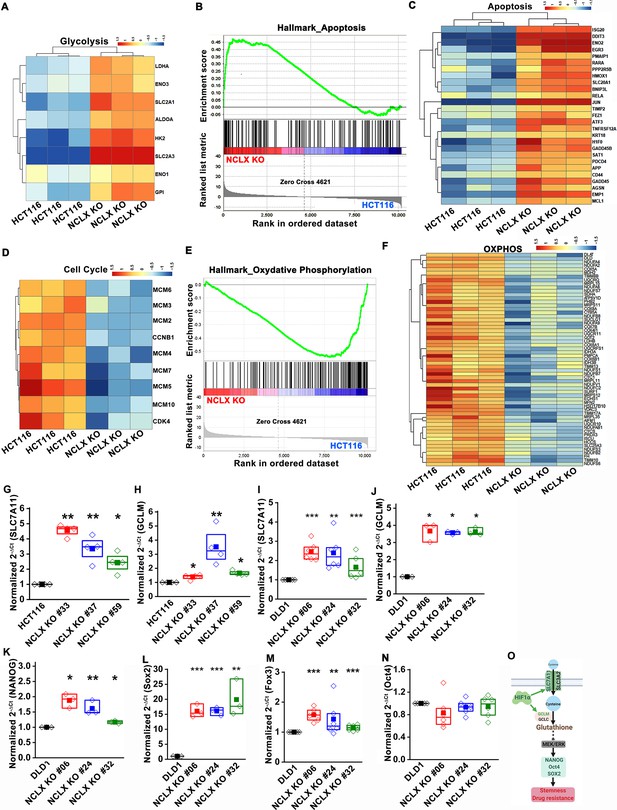
The original Figure 5—figure supplement 1 is shown here for reference:
The GAPDH and FOXO3 primers were identified wrong, and the primers for two housekeeping genes, NONO and Tubulin, were missing from the Appendix 1—key resources table. We have updated the Appendix 1—key resources table to include these primer pairs. In addition, we have corrected the primer sequences of qNCLX1_F, qNCLX1_R, NCLX_1, and NCLX_2, which were inadvertently swapped in the original Appendix 1—key resources table. We have also corrected the name from HCT116 shNCLX KO and DLD1 shNCLX KO to HCT116 shNCLX and DLD1 shNCLX in the Appendix 1—key resources table. The latter mistakes happened because we uploaded the wrong version of the Appendix 1—key resources table in the original manuscript. The corrected Appendix 1—key resources table is shown here (The corrections are highlighted in bold for illustrative purposes):
Appendix 1—key resources table
| AReagent type(species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Homo sapiens) | SLC8B1/NCLX | GenBank | Gene ID: 80024 | |
| Gene Mus musculus | Slc8b1/NCLX | GenBank | Gene ID: 170756 | |
| Genetic reagent Mus musculus | NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid/J | Jackson Laboratory | Stock No: 010636, RRID:IMSR_JAX:010636 | Male |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116 (colon, epithelial) | ATCC | ATCC# CCL-247 | Male |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HT29 (colon, epithelial) | ATCC | ATCC# HTB-38 | Female |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | DLD1 (colon, epithelial) | ATCC | ATCC# CCL-221 | Male |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116 NCLX KO (colon, epithelial) | This paper | NCLX Knockout clones of HCT116 cells were generated by the Trebak lab using CRISPR/Cas9 and are available upon request | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | DLD1 NCLX KO (colon, epithelial) | This paper | NCLX Knockout clones of DLD1 cells were generated in the Trebak lab using CRISPR/Cas9 and are available upon request | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116 shNCLX (colon, epithelial) | This paper | HCT116 cells with stable shRNA-mediated knockdown of NCLX (shNCLX) were generated by the Trebak Lab using shRNA sequences (listed below in this table) cloned in the lentiviral vector pLKO. These plasmids are available upon request | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | DLD1 shNCLX (colon, epithelial) | This paper | DLD1 cells with stable shRNA-mediated knockdown of NCLX (shNCLX) were generated by the Trebak Lab using shRNA sequences (listed below in this table) cloned in the lentiviral vector pLKO. These plasmids are available upon request | |
| Antibody | anti-Hif1α (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 14,179 s, RRID:AB_2622225 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti- ALDOA (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 8060 S, RRID:AB_2797635 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- HK2 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2867 S, RRID:AB_2232946 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- LDHA (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2012 S, RRID:AB_2137173 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- MMP1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab38929, RRID:AB_776395 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- MMP2 (Mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-13594, RRID:AB_627956 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti- MMP9 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab73734, RRID:AB_1860201 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- LC3B (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab51520, RRID:AB_881429 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- OXPHOS (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab110413, RRID:AB_2629281 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | anti- GAPDH (Mouse monoclonal) | Millipore Sigma | Cat# MAB374, RRID:AB_2107445 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | anti- HSC70 (Mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-24, RRID:AB_627760 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | anti- p62 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab109012, RRID:AB_2810880 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- cleaved caspase-3 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9661 S, RRID:AB_2341188 | WB (1:1000), IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti- pAMPK (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2535 S, RRID:AB_331250 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- AMPK (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 5831 S, RRID:AB_10622186 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- pS6K (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9234 S, RRID:AB_2269803 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- S6K (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2708 S, RRID:AB_390722 | WB (1:1000) |
| Sequence-based reagent | SLC7A11_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGGGTCACCTTCCAGAAATC |
| Sequence-based reagent | SLC7A11_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GAAGATAAATCAGCCCAGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | GCLM _F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CATTTACAGCCTTACTGGGAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | GCLM _R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ATGCAGTCAAATCTGGTGGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | FOXO3_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CGGACAAACGGCTCACTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | FOXO3_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGACCCGCATGAATCGACTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | NANOG _F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TTTGTGGGCCTGAAGAAAACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | NANOG _R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGGGCTGTCCTGAATAAGCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OCT4_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TTCAGCCAAACGACCATCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OCT4_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CACGAGGGTTTCTGCTTTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | SOX2_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GCCGAGTGGAAACTTTTGTCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | SOX2_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGCAGCGTGTACTTATCCTTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | GLUT1_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TATCGTCAACACGGCCTTCACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | GLUT1_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AACAGCTCCTCGGGTGTCTTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | HK2_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GCCATCCTGCAACACTTAGGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | HK2_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GTGAGGATGTAGCTTGTAGAGGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | GPI_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TGTGTTCACCAAGCTCACAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | GPI_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GTAGAAGCGTCGTGAGAGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | ALDOA_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGGCCATGCTTGCACTCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ALDOA_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGGGCCCAGGGCTTCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ENO1_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GACTTGGCTGGCAACTCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ENO1_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGTCATCGGGAGACTTGAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | LDHA_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGTTGGTGCTGTTGGCATGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | LDHA_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TGCCCCAGCCGTGATAATGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP1_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ATGCTGAAACCCTGAAGGTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP1_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GAGCATCCCCTCCAATACCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP2_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ACCAGCTGGCCTAGTGATGATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP2_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGCTTCCGCATGGTCTCGATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP9_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ACGCACGACGTCTTCCAGTA |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP9_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CCACCTGGTTCAACTCACTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | qNCLX_1_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GCGTGCTGGTTACCACAGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | qNCLX_1_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CCACGGAAGAGCATGAGGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | qNCLX_2_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CCGGCAGAAGGCTGAATCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | qNCLX_2_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ACCTTGCGGCAGTCTACCAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | GAPDH_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CCCTTCATTGACCTCAACTACA |
| Sequence-based reagent | GAPDH_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ATGACAAGCTTCCCGTTCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | NONO_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TCCGAGGAGATACCAGTCGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | NONO_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CCTGGGCCTCTCAACTTCGAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tubulin_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGTCCAAGCTGGAGTTCTCTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Tubulin_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CAATCAGAGTGCTCCAGGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | G6PD_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CGAGGCCGTCACCAAGAAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | G6PD_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GTAGTGGTCGATGCGGTAGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | PGD_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ATGGCCCAAGCTGACATCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | PGD_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AAAGCCGTGGTCATTCATGTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | TKT_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TCCACACCATGCGCTACAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | TKT_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CAAGTCGGAGCTGATCTTCCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | g1 | This paper | Guide RNA sequences (Figure 2A and Figure 3—figure supplement 1A) | GCGCAGATTCAGCCTTCTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | g2 | This paper | Guide RNA sequences (Figure 3—figure supplement 1B and C) | GGGATACTCACGTCTACCAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | g3 | This paper | Guide RNA sequences (Figure 3—figure supplement 1E) | GTAGACGTGAGTATCCCGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | g4 | This paper | Guide RNA sequences (Figure 3—figure supplement 1E) | ACCCACACCAGCAGTCCGTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA (shNCLX#2) | This paper | Figure 3—figure supplement 1I | GCCTTCTTGCTGTCATGCAAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA (shNCLX#3) | This paper | Figure 3—figure supplement 1I | GCTCCTCTTCTACCTGAACTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA (siNCLX) | This paper | Figure 4—figure supplement 1M | AACGGCCCCUCAACUGUCUT |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_1 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | GCCAGCATTTGTGTCCATTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_2 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | AATTCGTCTCGGCCACTTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_3 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | ACTTAGCACATCGCCACCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_4 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | CTGATCTGCACGCTGAATGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_5 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | GAGGTACACAGCAGTTCT CCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_6 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | CAGCTGGTGCCCTCAAACAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | PX75 NCLX test F | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO HCT116 cells | GTTGTTGAGACAGAGTCTTGC TTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | PX76 NCLX test R | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO HCT116 cells | TCCAGCGAGACTGTGCAGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | px77 | This paper | PCR primers for genotyping NCLX -/- mice | TACAGTCTGGCTCGTTCC CT |
| Sequence-based reagent | px78 | This paper | PCR primers for genotyping NCLX -/- mice | CGGTCCCAGACGCCG T |
| Sequence-based reagent | px79 | This paper | PCR primers for genotyping NCLX -/- mice | CGCTGGGGTCCATCT TTG AT |
| Sequence-based reagent | px80 | This paper | PCR primers for genotyping NCLX -/- mice | TGGGTCTCCGGTCCCAGT A |
| Commercial assay or kit | cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit | Applied biosystems | Cat# 4368814 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Seahorse XFp Mito Fuel Flex Test Kit | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103270–100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Seahorse XFp Glycolysis Stress Test Kit | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103017–100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Seahorse XFp Cell Mito Stress Test Kit | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103010–100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | BCA assay kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A53225 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | TMRE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# T669 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | CyQUANT | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# C35006 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Antibiotic and Antimycotic | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15240062 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | McCoy’s 5 A | Corning | Cat# 10-050CV | |
| Chemical compound, drug | RPMI-1640 | Corning | Cat# 10-040CV | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamine 2000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11668019 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TrypLE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 12605028 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CoCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 15862 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D8375 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 5-Fluorouracil | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F6627 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D9434 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Puromycin | MP Biomedical | Cat# 02100552 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | RIPA buffer | Sigma | Cat# R0278 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ATP | Sigma | Cat# A9187 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextrose | Fisher Scientific | Cat# D14 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris Base | Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP152-5 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NaCl | Fisher Scientific | Cat# S671 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | MOPS SDS running buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# NP0001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris-Glycine transfer buffer | Bio-rad | Cat#161–0734 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | KCl | Fisher Scientific | Cat# P217 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | MgCl2 | Fisher Scientific | Cat# M33 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CaCl2 | Fisher Scientific | Cat# C614 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HEPES | Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP310 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | LDS sample buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# NP0007 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NuPAGE Bis-Tris precast gels | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# NP0321 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Polyvinylidene difluoride membrane | Li-Core Biosciences | Cat# 88518 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Odyssey Blocking Buffer (TBS) | Li-Core Biosciences | Cat# 937–50003 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextran sulfate sodium | MP Biomedical | Cat# 0216011080 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Azoxymethane | Sigma | Cat# A5486 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DNase I | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 18068–015 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TRIzol | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15596018 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Seahorse XF DMEM Medium pH 7.4 | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103575–100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Seahorse XF 100 mM pyruvate solution | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103578–100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Seahorse XF 200 mM glutamine solution | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103579–100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Seahorse XF 1.0 M glucose solution | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103577–100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Zymogram Developing Buffer (10 X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# LC2671 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Zymogram Renaturing Buffer (10 X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# LC2670 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris-Glycine SDS Running Buffer (10 X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# LC2675 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tween 20 | Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP337 | |
| Software, algorithm | Image J | https://imagej.net/ | RRID:SCR_003070 | |
| Other | DAPI | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D9542 | 1 µg/ml |
| Other | Hoechst | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# H3570 | 1 µg/ml |
| Other | IRDye 800CW Goat anti-Mouse | Li-Core Biosciences | Cat# 925–32210 | 1:10000 |
| Other | IRDye 800CW Donkey anti-Rabbit | Li-Core Biosciences | Cat# 925–32213 | 1:5000 |
| Other | MitoSox Red | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# M36008 | |
| Other | Mito TEMPO | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# SML0737 | |
| Other | Mito Tracker Green FM | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# M7514 | |
| Other | Mito Tracker Deep red FM | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 8778 S | |
| Other | Fura-2 AM | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# F1221 | |
| Other | FluoroBlok | Corning | Cat# 351152 | |
| Other | BioCoat Tumor Invasion Plate | Corning | Cat# 80774380 | |
| Other | SYBER select master mix | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 4472920 | |
| Other | Novex 10% Zymogram Plus (Gelatin) Protein Gels, 1.0 mm, 10-well | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# ZY00100 | |
| Other | SimplyBlue Safe Stain | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# LC6060 |
The originally published Appendix 1—key resources table is shown for reference:
Appendix 1—key resources table
| Reagent type(species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Homo sapiens) | SLC8B1/NCLX | GenBank | Gene ID: 80024 | |
| Gene Mus musculus | Slc8b1/NCLX | GenBank | Gene ID: 170756 | |
| Genetic reagent Mus musculus | NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid/J | Jackson Laboratory | Stock No: 010636, RRID:IMSR_JAX:010636 | Male |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116 (colon, epithelial) | ATCC | ATCC# CCL-247 | Male |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HT29 (colon, epithelial) | ATCC | ATCC# HTB-38 | Female |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | DLD1 (colon, epithelial) | ATCC | ATCC# CCL-221 | Male |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116 NCLX KO (colon, epithelial) | This paper | NCLX Knockout clones of HCT116 cells were generated by the Trebak lab using CRISPR/Cas9 and are available upon request | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | DLD1 NCLX KO (colon, epithelial) | This paper | NCLX Knockout clones of DLD1 cells were generated in the Trebak lab using CRISPR/Cas9 and are available upon request | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | HCT116 shNCLX KO (colon, epithelial) | This paper | HCT116 cells with stable shRNA-mediated knockdown of NCLX (shNCLX) were generated by the Trebak Lab using shRNA sequences (listed below in this table) cloned in the lentiviral vector pLKO. These plasmids are available upon request | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | DLD1 shNCLX KO (colon, epithelial) | This paper | DLD1 cells with stable shRNA-mediated knockdown of NCLX (shNCLX) were generated by the Trebak Lab using shRNA sequences (listed below in this table) cloned in the lentiviral vector pLKO. These plasmids are available upon request | |
| Antibody | anti-Hif1α (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 14,179 s, RRID:AB_2622225 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti- ALDOA (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 8060 S, RRID:AB_2797635 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- HK2 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2867 S, RRID:AB_2232946 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- LDHA (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2012 S, RRID:AB_2137173 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- MMP1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab38929, RRID:AB_776395 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- MMP2 (Mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-13594, RRID:AB_627956 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti- MMP9 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab73734, RRID:AB_1860201 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- LC3B (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab51520, RRID:AB_881429 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- OXPHOS (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab110413, RRID:AB_2629281 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | anti- GAPDH (Mouse monoclonal) | Millipore Sigma | Cat# MAB374, RRID:AB_2107445 | WB (1:10000) |
| Antibody | anti- HSC70 (Mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-24, RRID:AB_627760 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | anti- p62 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab109012, RRID:AB_2810880 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- cleaved caspase-3 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9661 S, RRID:AB_2341188 | WB (1:1000), IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | anti- pAMPK (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2535 S, RRID:AB_331250 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- AMPK (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 5831 S, RRID:AB_10622186 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- pS6K (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 9234 S, RRID:AB_2269803 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | anti- S6K (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 2708 S, RRID:AB_390722 | WB (1:1000) |
| Sequence-based reagent | SLC7A11_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGGGTCACCTTCCAGAAATC |
| Sequence-based reagent | SLC7A11_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GAAGATAAATCAGCCCAGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | GCLM _F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CATTTACAGCCTTACTGGGAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | GCLM _R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ATGCAGTCAAATCTGGTGGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | FOX3_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CGGCTTCGGCTCTTAGCAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | FOX3_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CGGACAAACGGCTCACTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | NANOG _F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TTTGTGGGCCTGAAGAAAACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | NANOG _R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGGGCTGTCCTGAATAAGCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OCT4_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TTCAGCCAAACGACCATCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | OCT4_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CACGAGGGTTTCTGCTTTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | SOX2_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GCCGAGTGGAAACTTTTGTCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | SOX2_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGCAGCGTGTACTTATCCTTCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | GLUT1_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TATCGTCAACACGGCCTTCACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | GLUT1_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AACAGCTCCTCGGGTGTCTTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | HK2_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GCCATCCTGCAACACTTAGGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | HK2_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GTGAGGATGTAGCTTGTAGAGGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | GPI_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TGTGTTCACCAAGCTCACAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | GPI_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GTAGAAGCGTCGTGAGAGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | ALDOA_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGGCCATGCTTGCACTCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ALDOA_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AGGGCCCAGGGCTTCAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ENO1_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GACTTGGCTGGCAACTCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | ENO1_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGTCATCGGGAGACTTGAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | LDHA_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGTTGGTGCTGTTGGCATGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | LDHA_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TGCCCCAGCCGTGATAATGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP1_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ATGCTGAAACCCTGAAGGTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP1_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GAGCATCCCCTCCAATACCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP2_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ACCAGCTGGCCTAGTGATGATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP2_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGCTTCCGCATGGTCTCGATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP9_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ACGCACGACGTCTTCCAGTA |
| Sequence-based reagent | MMP9_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CCACCTGGTTCAACTCACTCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | qNCLX_1_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GCCAGCATTTGTGTCCATTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | qNCLX_1_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AATTCGTCTCGGCCACTTAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | qNCLX_2_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CCGGCAGAAGGCTGAATCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | qNCLX_2_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ACCTTGCGGCAGTCTACCAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | GAPDH_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GGGAAACCCATCACCATCTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | GAPDH_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CCAGTAGACTCCACGACATACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | G6PD_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CGAGGCCGTCACCAAGAAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | G6PD_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | GTAGTGGTCGATGCGGTAGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | PGD_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | ATGGCCCAAGCTGACATCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | PGD_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | AAAGCCGTGGTCATTCATGTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | TKT_F | This paper | RT-PCR primers | TCCACACCATGCGCTACAAG |
| Sequence-based reagent | TKT_R | This paper | RT-PCR primers | CAAGTCGGAGCTGATCTTCCT |
| Sequence-based reagent | g1 | This paper | Guide RNA sequences (Figure 2A and Figure 3—figure supplement 1A) | GCGCAGATTCAGCCTTCTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | g2 | This paper | Guide RNA sequences (Figure 3—figure supplement 1B and C) | GGGATACTCACGTCTACCAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | g3 | This paper | Guide RNA sequences (Figure 3—figure supplement 1E) | GTAGACGTGAGTATCCCGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | g4 | This paper | Guide RNA sequences (Figure 3—figure supplement 1E) | ACCCACACCAGCAGTCCGTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA (shNCLX#2) | This paper | Figure 3—figure supplement 1I | GCCTTCTTGCTGTCATGCAAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | shRNA (shNCLX#3) | This paper | Figure 3—figure supplement 1I | GCTCCTCTTCTACCTGAACTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | siRNA (siNCLX) | This paper | Figure 4—figure supplement 1M | AACGGCCCCUCAACUGUCUT |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_1 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | GCGTGCTGGTTACCACAG T |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_2 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | CCACGGAAGAGCATGAGGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_3 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | ACTTAGCACATCGCCACCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_4 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | CTGATCTGCACGCTGAATGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_5 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | GAGGTACACAGCAGTTCT CCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | NCLX_6 | This paper | PCR primers for screening genomic DNA of NCLX KO clones (Figure 3—figure supplement 1F) | CAGCTGGTGCCCTCAAACAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | px77 | This paper | PCR primers for genotyping NCLX -/- mice | TACAGTCTGGCTCGTTCC CT |
| Sequence-based reagent | px78 | This paper | PCR primers for genotyping NCLX -/- mice | CGGTCCCAGACGCCG T |
| Sequence-based reagent | px79 | This paper | PCR primers for genotyping NCLX -/- mice | CGCTGGGGTCCATCT TTG AT |
| Sequence-based reagent | px80 | This paper | PCR primers for genotyping NCLX -/- mice | TGGGTCTCCGGTCCCAGT A |
| Commercial assay or kit | cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit | Applied biosystems | Cat# 4368814 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Seahorse XFp Mito Fuel Flex Test Kit | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103270–100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Seahorse XFp Glycolysis Stress Test Kit | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103017–100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Seahorse XFp Cell Mito Stress Test Kit | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103010–100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | BCA assay kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A53225 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | TMRE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# T669 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | CyQUANT | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# C35006 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Antibiotic and Antimycotic | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15240062 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | McCoy’s 5 A | Corning | Cat# 10-050CV | |
| Chemical compound, drug | RPMI-1640 | Corning | Cat# 10-040CV | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Lipofectamine 2000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11668019 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TrypLE | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 12605028 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CoCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 15862 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D8375 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 5-Fluorouracil | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F6627 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D9434 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Puromycin | MP Biomedical | Cat# 02100552 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | RIPA buffer | Sigma | Cat# R0278 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ATP | Sigma | Cat# A9187 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextrose | Fisher Scientific | Cat# D14 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris Base | Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP152-5 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NaCl | Fisher Scientific | Cat# S671 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | MOPS SDS running buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# NP0001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris-Glycine transfer buffer | Bio-rad | Cat#161–0734 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | KCl | Fisher Scientific | Cat# P217 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | MgCl2 | Fisher Scientific | Cat# M33 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CaCl2 | Fisher Scientific | Cat# C614 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HEPES | Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP310 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | LDS sample buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# NP0007 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NuPAGE Bis-Tris precast gels | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# NP0321 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Polyvinylidene difluoride membrane | Li-Core Biosciences | Cat# 88518 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Odyssey Blocking Buffer (TBS) | Li-Core Biosciences | Cat# 937–50003 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dextran sulfate sodium | MP Biomedical | Cat# 0216011080 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Azoxymethane | Sigma | Cat# A5486 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DNase I | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 18068–015 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TRIzol | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15596018 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Seahorse XF DMEM Medium pH 7.4 | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103575–100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Seahorse XF 100 mM pyruvate solution | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103578–100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Seahorse XF 200 mM glutamine solution | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103579–100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Seahorse XF 1.0 M glucose solution | Agilent Technologies | Cat# 103577–100 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Zymogram Developing Buffer (10 X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# LC2671 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Zymogram Renaturing Buffer (10 X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# LC2670 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris-Glycine SDS Running Buffer (10 X) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# LC2675 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tween 20 | Fisher Scientific | Cat# BP337 | |
| Software, algorithm | Image J | https://imagej.net/ | RRID:SCR_003070 | |
| Other | DAPI | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D9542 | 1 µg/ml |
| Other | Hoechst | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# H3570 | 1 µg/ml |
| Other | IRDye 800CW Goat anti-Mouse | Li-Core Biosciences | Cat# 925–32210 | 1:10000 |
| Other | IRDye 800CW Donkey anti-Rabbit | Li-Core Biosciences | Cat# 925–32213 | 1:5000 |
| Other | MitoSox Red | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# M36008 | |
| Other | Mito TEMPO | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# SML0737 | |
| Other | Mito Tracker Green FM | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# M7514 | |
| Other | Mito Tracker Deep red FM | Cell Signaling Technology | Cat# 8778 S | |
| Other | Fura-2 AM | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# F1221 | |
| Other | FluoroBlok | Corning | Cat# 351152 | |
| Other | BioCoat Tumor Invasion Plate | Corning | Cat# 80774380 | |
| Other | SYBER select master mix | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 4472920 | |
| Other | Novex 10% Zymogram Plus (Gelatin) Protein Gels, 1.0 mm, 10-well | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# ZY00100 | |
| Other | SimplyBlue Safe Stain | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# LC6060 |
Supplementary file 1: Genomic sequencing of NCLX KO clones of HCT116 and DLD1 cells.
Description: This file shows the genome sequencing of NCLX KO clones #33, #37, and #59 of HCT116 and #06, #24, and #32 of DLD1 cells. For genomic sequencing, PCR was performed to amplify specific parts of the NCLX gene using primers listed in the key resources table. The primers used for cloning genomic DNA from HCT116 cells were PX75 NCLX test F and PX76 NCLX test R. The primers used for cloning genomic DNA from DLD1 cells were NCLX_4 and NCLX_5. PCR products were cloned using StrataClone Blunt PCR Cloning Kit and sent to Genewiz for sanger sequencing. The genome sequencing data for the HCT116 NCLX KO clones confirm the introduction of STOP codons in coding sequences of HCT116 NCLX KO #33 at predicted positions 181–183 bp and 184–186 bp, in HCT116 NCLX KO #37 at 16–18 bp and 46–48 bp, and in HCT116 NCLX KO #59 at 31–33 bp, and 52–54 bp. Furthermore, the genomic sequencing of NCLX KO clones of DLD1 cells showed that the middle ~32 kb portion of the NCLX gene was deleted in all clones. Therefore, providing decisive evidence that these cells are indeed NCLX KO.
The corrections do not change any of the scientific conclusions of the figures or the manuscript. We sincerely apologize for the mistakes and the confusion it may have caused.
The article has been corrected accordingly.
Article and author information
Author details
Version history
Copyright
© 2023, Pathak et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 275
- views
-
- 0
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.






