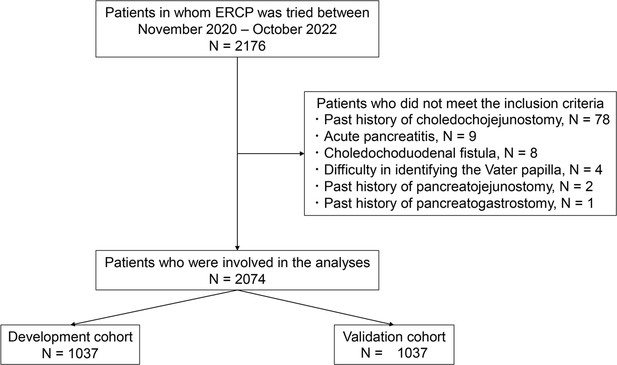
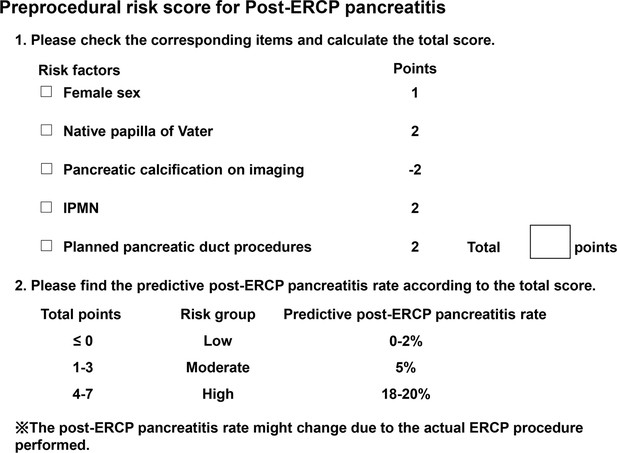
A new preprocedural predictive risk model for post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: The SuPER model
Figures
Tables
Comparison of patient characteristics and ERCP outcomes between the development and validation cohorts.
| Development cohort(n=1037) | Validation cohort(n=1037) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient factors | |||
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 73.8 ± 12.7 | 75.1 ± 12.5 | 0.02 |
| Sex, n, male/female | 642/395 | 629/408 | 0.59 |
| History of pancreatitis, n (%) | 73 (7.0) | 45 (4.4) | 0.01 |
| History of PEP, n (%) | 26 (2.5) | 24 (2.3) | 0.89 |
| History of gastrectomy, n (%) | 82 (7.9) | 88 (8.5) | 0.69 |
| Billroth-I reconstruction, n | 24 | 25 | |
| Billroth-II reconstruction, n | 23 | 25 | |
| Roux-en-Y reconstruction, n | 33 | 36 | |
| Double tract, n | 1 | 1 | |
| Gastric tube reconstruction, n | 1 | 1 | |
| Pancreatic cancer, n (%) | 145 (14.0) | 174 (16.8) | 0.09 |
| IPMN, n (%) | 17 (1.6) | 8 (0.8) | 0.11 |
| Native papilla of Vater, n (%) | 535 (51.6) | 494 (47.7) | 0.08 |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dl, mean ± SD * | 3.5 ± 5.3 | 3.6 ± 5.0 | 0.45 |
| Diameter of the MPD, mm, mean ± SD † | 2.84 ± 2.63 | 3.1 ± 2.9 | 0.10 |
| Pancreatic calcification, n (%) ‡ | 107 (10.6) | 87 (8.7) | 0.15 |
| Periampullary diverticulum, n (%) | 207 (20.0) | 224 (21.6) | 0.39 |
| Pre-ERCP prophylaxis | |||
| Protease inhibitors, n (%) | 709 (68.4) | 703 (67.8) | 0.81 |
| Intravenous hydration, n (%) | 22 (2.1) | 14 (1.4) | 0.24 |
| NSAID suppository, n (%) | 53 (5.1) | 45 (4.3) | 0.47 |
| Factors related to the planned procedure | |||
| EST, n (%) | 449 (43.3) | 434 (41.9) | 0.53 |
| EPBD, n (%) | 31 (3.0) | 40 (3.9) | 0.33 |
| EPLBD, n (%) | 56 (5.4) | 55 (5.3) | 1.0 |
| Biliary stone removal, n (%) | 327 (31.5) | 342 (33.0) | 0.51 |
| Ampullectomy, n (%) | 5 (0.5) | 5 (0.5) | 1.0 |
| Biliary stent, n (%) | 594 (57.3) | 611 (58/9) | 0.48 |
| Plastic stent, n (%) | 445 (42.9) | 436 (42.0) | 0.72 |
| SEMS, n (%) | 119 (11.5) | 122 (11.8) | 0.89 |
| CSEMS, n (%) | 36 (3.5) | 44 (4.2) | 0.43 |
| Biliary stent above the papilla, n (%) | 45 (4.3) | 47 (4.5) | 0.92 |
| Procedures on the pancreatic duct, n (%) | 285 (27.5) | 237 (22.9) | 0.017 |
| PEP occurrence, n (%) | 70 (6.8) | 64 (6.2) | 0.66 |
| Mild, n | 60 | 53 | |
| Moderate, n | 8 | 7 | |
| Severe, n | 2 | 4 |
-
ERCP, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; PEP, post-ERCP pancreatitis; IPMN, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; MPD, main pancreatic duct; EST, endoscopic sphincterotomy; EPBD, endoscopic papillary balloon dilation; SEMS, self-expandable metallic stent; CSEMS, covered SEMS.
-
*
Data were available for 2042 patients.
-
†
Data were available for 1671 patients.
-
‡
Data were available for 2017 patients.
Logistic regression analysis of predictive factors for PEP in the development cohort.
| Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p- Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | Regression coefficient | Points | |
| Age <50 years | 2.42 | 0.99–6.0 | 0.053 | 1.76 | 0.67–4.63 | 0.25 | 0.56 | - |
| Female | 1.91 | 1.17–3.10 | <0.01 | 1.72 | 1.03–2.89 | 0.039 | 0.55 | 1 |
| History of pancreatitis | 1.26 | 0.53–3.0 | 0.61 | |||||
| History of PEP | 1.84 | 0.54–6.28 | 0.33 | |||||
| History of gastrectomy | 0.89 | 0.35–2.27 | 0.81 | |||||
| Pancreatic cancer | 1.03 | 0.51–2.06 | 0.94 | |||||
| IPMN | 8.15 | 2.92–22.7 | <0.01 | 3.04 | 0.97–9.52 | 0.056 | 1.11 | 2 |
| Native papilla of Vater | 4.49 | 2.42–8.30 | <0.01 | 2.72 | 1.30–5.71 | <0.01 | 1.0 | 2 |
| Total bilirubin ≤1.2 mg/dl * | 1.13 | 0.69–1.84 | 0.62 | |||||
| Diameter of the MPD >3 mm† | 1.31 | 0.76–2.25 | 0.33 | |||||
| Pancreatic calcification‡ | 0.36 | 0.11–1.17 | 0.089 | 0.32 | 0.10–1.1 | 0.072 | –1.13 | -2 |
| Periampullary diverticulum | 0.65 | 0.33–1.30 | 0.22 | |||||
| Protease inhibitors | 0.72 | 0.44–1.19 | 0.20 | |||||
| Intravenous hydration | 1.39 | 0.32–6.08 | 0.66 | |||||
| NSAID suppository before ERCP | 1.47 | 0.57–3.83 | 0.43 | |||||
| EST | 1.71 | 1.05–2.79 | 0.03 | 0.83 | 0.45–1.52 | 0.54 | –0.19 | - |
| EPBD | <0.01 | 0–infinity | 0.98 | |||||
| EPLBD | 0.24 | 0.03–1.76 | 0.16 | |||||
| Biliary stone removal | 0.68 | 0.39–1.19 | 0.18 | |||||
| Ampullectomy | 3.49 | 0.39–31.6 | 0.27 | |||||
| Biliary stent | 0.93 | 0.57–1.52 | 0.78 | |||||
| Plastic stent | 0.72 | 0.44–1.20 | 0.21 | |||||
| SEMS | 1.66 | 0.87–3.20 | 0.13 | |||||
| CSEMS | 0.81 | 0.19–3.43 | 0.77 | |||||
| Biliary stent above the papilla | 0.30 | 0.04–2.24 | 0.24 | |||||
| Procedures on the pancreatic duct | 4.77 | 2.89–7.89 | <0.01 | 3.49 | 1.99–6.12 | <0.01 | 1.25 | 2 |
-
PEP, post–endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis; IPMN, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; MPD, main pancreatic duct; EST, endoscopic sphincterotomy; EPBD, endoscopic papillary balloon dilation; EPLBD, endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation; SEMS, self-expandable metallic stent; CSEMS, covered SEMS.
-
*
Data were available for 1024 patients in the development cohort.
-
†
Data were available for 985 patients in the development cohort.
-
‡
Data were available for 1012 patients in the development cohort.
Patient distribution in terms of risk score and classification.
| Risk score | Development cohort (n=1012) * | Validation cohort (n=1005) † | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEP occurrence, N | PEP rate (95% CI) (%) | p-Value ‡ | PEP occurrence, N | PEP rate (95% CI) (%) | p-Value ‡ | ||
| -2 | 0/29 | 0 (0–11.9) | <0.01 | 0/33 | 0 (0–10.6) | <0.01 | |
| -1 | 0/9 | 0 (0–33.6) | 0/5 | 0 (0–52.2) | |||
| 0 | 0/289 | 0 (0–1.3) | 8/293 | 2.7 (1.2–5.3) | |||
| 1 | 6/140 | 4.3 (1.6–9.1) | 5/160 | 3.1 (1.0–7.1) | |||
| 2 | 8/202 | 4.0 (1.7–7.7) | 14/195 | 7.2 (4.0–11.8) | |||
| 3 | 13/150 | 8.7 (4.7–14.4) | 8/158 | 5.1 (2.2–9.7) | |||
| 4 | 18/97 | 18.6 (11.4–27.7) | 14/84 | 16.7 (9.4–26.4) | |||
| 5 | 17/83 | 20.5 (12.4–30.8) | 14/71 | 19.7 (11.2–30.9) | |||
| 6 | 3/9 | 33.3 (7.5–70.1) | 0/3 | 0 (0–70.8) | |||
| 7 | 1/4 | 25.0 (0.6–80.6) | 1/3 | 33.3 (0.8–90.6) | |||
| Risk classification | Risk score | PEP occurrence, N | PEP rate (95% CI) (%) | p-Value ‡ | PEP occurrence, N | PEP rate (95% CI) (%) | p-Value ‡ |
| Low | ≤0 | 0/327 | 0 (0–1.1) | <0.01 | 8/331 | 2.4 (1.0–4.7) | <0.01 |
| Moderate | 1–3 | 27/492 | 5.5 (3.6–7.9) | 27/513 | 5.3 (3.5–7.6) | ||
| High | 4–7 | 39/193 | 20.2 (14.8–26.6) | 29/161 | 18.0 (12.4–24.8) | ||
-
PEP, post–endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis.
-
*
There were missing data for 25 patients.
-
†
Data for 32 patients were missing.
-
‡
The correlations between the risk score or classification and PEP occurrence were evaluated via the Cochran–Armitage test.
Goodness of fit of the risk score model.
| Development cohort | Validation cohort | |
|---|---|---|
| C statistic (95% CI) | 0.77 (0.72–0.82) | 0.71 (0.64–0.78) |
| Hosmer‒Lemeshow test, p value | 0.59 | 0.40 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Risk classification and unpredictable intraprocedural risk factors for PEP (multivariate logistic regression).
PEP, post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis. a Patients with missing data for variables selected in the risk score model were removed.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/101604/elife-101604-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Risk of PEP following implantation of pancreatic stents (logistic regression).
PEP, post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/101604/elife-101604-supp2-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/101604/elife-101604-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf
-
Source data 1
The dataset was original raw data without personal information.
The data was anonymized and deidentified.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/101604/elife-101604-data1-v1.xlsx