Sequential Movement: Reaching into the future
Recently a friend introduced me to Beat Saber, a virtual reality game that involves using virtual swords to rhythmically slash through colored blocks that come streaming towards the player. After twenty minutes of flailing my arms around with minimal success, I gave up. My friend then passed the headset to his eight-month-pregnant wife who, after being helped off the couch, switched the difficulty to ‘expert’ and within seconds blew past my score with unbelievable grace and efficiency. Watching her, one thing became clear: while I had been focusing on how to slash the blocks nearest to me, she had already started to think about and prepare for the blocks in the distance as she slashed through those closest to her.
This ability to prepare future movements allows us to perform everyday tasks, like writing and washing dishes. However, many questions remain about how this continuous planning works in the brain. For instance, how many movements can the brain prepare in advance, and how malleable are these planned movements to change? Now, in eLife, J Andrew Pruszynski and colleagues – including Mehrdad Kashefi as first author – report new findings that help to answer these questions (Kashefi et al., 2024).
The team (who are based at Western University and San Diego State University) asked human participants to perform a task like Beat Saber (Figure 1A), where each individual had to reach towards a series of targets that appeared one after the other on a screen. However, unlike other sequential reaching tasks (Glaser et al., 2018; Zimnik and Churchland, 2021), this task also sometimes showed future targets beyond the upcoming one, allowing participants to plan multiple movements in advance, if they were able to.
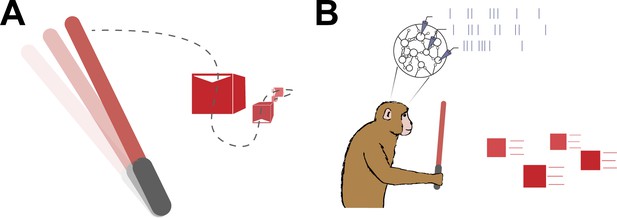
Planning a sequence of movements.
(A) A schematic representation of the virtual reality game Beat Saber, during which the player must use a sword (left) to slash a stream of blocks (right) that are coming towards them – similar to the task Kashefi et al. used in their study. Based on results from Kashefi et al., knowing about future blocks influences planned movements (dashed line) and helps players to slash the boxes as they arrive. (B) A natural follow-up study would be to repeat the experiment in monkeys and use electrodes (triangles) to measure the spiking neural activity of their motor cortex (represented as a stream of vertical lines from each electrode) as they plan ahead.
Image credit: Raeed H Chowdhury; monkey illustration is by Carolina Massumoto.
Kashefi et al. found that participants could indeed plan at least two movements ahead. As they were given information on future targets, their movements became faster and more coordinated, with each movement smoothly transitioning into the next. It seemed that plans for movements in the distant future were not simply added to a queue, but instead modified movements in the near future to improve their efficiency.
Kashefi et al. confirmed this with a clever manipulation that involved making one of the targets jump, thus forcing the participants to re-plan their movements on the fly. When a target suddenly jumped to a new position on the screen, subjects were slower to respond to the jump if they already had information about the next future target. Overall, the results suggest that plans for future movements interact with and modify each other.
This interdependence between movement plans might suggest that short sequences of movements are planned together as a single trajectory, or ‘motor chunk’ (Ramkumar et al., 2016). In this scenario, once one chunk is completed, the subject moves onto the next, effectively planning one chunk – rather than one movement – at a time. However, Kashefi et al. show that this is not the case in their experiment. Participants transitioned smoothly and continuously between movements, without any discernible breaks that would indicate motor chunks. Furthermore, when a target jumped to a new position, participants were able to flexibly change individual movement plans to compensate, rather than having to re-plan a whole chunk.
In the brain, movement planning is accompanied by specific patterns of neural activity in the motor cortex, a brain region critical for skilled motions like playing a musical instrument (Strick et al., 2021). These patterns of neural activity help the brain prepare for an upcoming movement and are distinct from the activity patterns that control the actual movement (Ames et al., 2019; Churchland et al., 2010; Elsayed et al., 2016; Schimel et al., 2024).
One highly relevant study explored these preparatory neural patterns in monkeys reaching for two consecutive targets (Zimnik and Churchland, 2021). Like the study performed by Kashefi et al., the researchers found that monkeys did not prepare movements in chunks. Instead, the preparatory neural patterns that arose during the first movement prepared the monkeys to reach for the second target. However, while the study in monkeys suggested that sequential movements are prepared independently, Kashefi et al. went further by using trials with many movements and adding more targets to the planning horizon. In doing so, they showed that the preparation of future movements is in fact interrelated.
This difference between the two studies opens up a number of questions. For instance, what does neural activity look like during multi-movement planning tasks like the one conducted by Kashefi et al. (Figure 1B)? Also, what happens in the brain when plans for future targets interact, or when planned movements must change as targets unexpectedly jump to new positions?
While researchers have a reasonably good understanding of how individuals prepare single movements, much less is known about preparing movement sequences. The task and behavioral analysis undertaken by Kashefi et al. provides an excellent foundation upon which to build this knowledge. Until then, I will just have to continue practicing to get better at Beat Saber.
References
-
Chunking as the result of an efficiency computation trade-offNature Communications 7:12176.https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12176
-
The cortical motor areas and the emergence of motor skills: a neuroanatomical perspectiveAnnual Review of Neuroscience 44:425–447.https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-070918-050216
-
Independent generation of sequence elements by motor cortexNature Neuroscience 24:412–424.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00798-5
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
Copyright
© 2024, Chowdhury
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 659
- views
-
- 44
- downloads
-
- 0
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Computational and Systems Biology
- Neuroscience
Accumulating evidence to make decisions is a core cognitive function. Previous studies have tended to estimate accumulation using either neural or behavioral data alone. Here, we develop a unified framework for modeling stimulus-driven behavior and multi-neuron activity simultaneously. We applied our method to choices and neural recordings from three rat brain regions—the posterior parietal cortex (PPC), the frontal orienting fields (FOF), and the anterior-dorsal striatum (ADS)—while subjects performed a pulse-based accumulation task. Each region was best described by a distinct accumulation model, which all differed from the model that best described the animal’s choices. FOF activity was consistent with an accumulator where early evidence was favored while the ADS reflected near perfect accumulation. Neural responses within an accumulation framework unveiled a distinct association between each brain region and choice. Choices were better predicted from all regions using a comprehensive, accumulation-based framework and different brain regions were found to differentially reflect choice-related accumulation signals: FOF and ADS both reflected choice but ADS showed more instances of decision vacillation. Previous studies relating neural data to behaviorally inferred accumulation dynamics have implicitly assumed that individual brain regions reflect the whole-animal level accumulator. Our results suggest that different brain regions represent accumulated evidence in dramatically different ways and that accumulation at the whole-animal level may be constructed from a variety of neural-level accumulators.
-
- Neuroscience
Our propensity to materiality, which consists in using, making, creating, and passing on technologies, has enabled us to shape the physical world according to our ends. To explain this proclivity, scientists have calibrated their lens to either low-level skills such as motor cognition or high-level skills such as language or social cognition. Yet, little has been said about the intermediate-level cognitive processes that are directly involved in mastering this materiality, that is, technical cognition. We aim to focus on this intermediate level for providing new insights into the neurocognitive bases of human materiality. Here, we show that a technical-reasoning process might be specifically at work in physical problem-solving situations. We found via two distinct neuroimaging studies that the area PF (parietal F) within the left parietal lobe is central for this reasoning process in both tool-use and non-tool-use physical problem-solving and can work along with social-cognitive skills to resolve day-to-day interactions that combine social and physical constraints. Our results demonstrate the existence of a specific cognitive module in the human brain dedicated to materiality, which might be the supporting pillar allowing the accumulation of technical knowledge over generations. Intensifying research on technical cognition could nurture a comprehensive framework that has been missing in fields interested in how early and modern humans have been interacting with the physical world through technology, and how this interaction has shaped our history and culture.






