Molecular safeguarding of CRISPR gene drive experiments
Figures
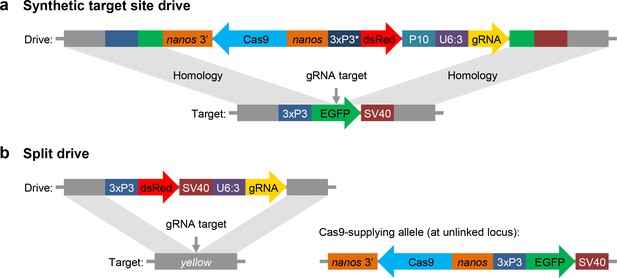
Schematic diagram of our synthetic target site drive and split drive constructs.
(a) The synthetic target site drive constructs contain Cas9 with the germline nanos promoter and 3’UTR, a dsRed marker with a slightly recoded (*) 3xP3 promoter and P10 3’UTR, and a gRNA driven by the U6:3 promoter that targets the synthetic EGFP gene. The two homology arms include the EGFP sequence with its 3xP3 promoter and SV40 3’UTR regions. (b) The split drive contains a dsRed marker gene driven by a 3xP3 promoter together with a SV40 3’UTR, a gRNA expressed by the U6:3 promoter that targets yellow, and two homology arms for yellow. The unlinked supporting element contains Cas9 driven by the nanos promoter with a nanos 3’UTR, and an EGFP marker gene driven by a 3xP3 promoter together with a SV40 3’UTR.
Tables
Drive performances of synthetic target site and split drives compared with the standard drives from our previous studies (Champer et al., 2017; Champer et al., 2018b).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41439.004| Drive | Male drive conversion efficiency | Female drive conversion efficiency | Embryo r2 resistance rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFP site B | 32 ± 3% | 52 ± 3% | 88 ± 1% |
| EGFP site E | 46 ± 4% | 54 ± 5% | 91 ± 2% |
| EGFP site Y | N/A | 53 ± 3% | 80 ± 2% |
| cinnabar | 39 ± 3% | 54 ± 4% | 100 ± 0% |
| white | N/A | 59 ± 2% | 77 ± 2% |
| Split-yellow | N/A | 74 ± 2% | 74 ± 2% |
| yellow | N/A | 63 ± 3% | 20 ± 2% |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Plasmid construction details and oligonucleotide sequences.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41439.005
-
Supplementary file 2
Fly phenotype data and rate calculations.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41439.006
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41439.007





