Disruption of PIKFYVE causes congenital cataract in human and zebrafish
Figures
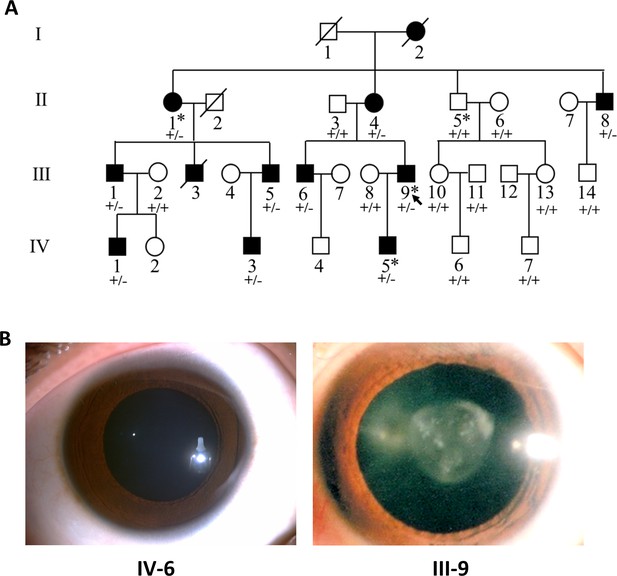
Pedigree structure and ocular manifestations of the cataract family.
(A) Pedigree of the family with congenital cataract. Squares denote males and circles denote females; Symbols crossed by a line indicate deceased individuals. Filled symbols indicate affected individuals, while open symbols indicate unaffected individuals. All affected family members had bilateral congenital cataract. The arrow denotes the proband. The individuals marked with an asterisk (∗) are analyzed by whole-exome sequencing. Genotypes of the PIKFYVE variant (p.G1943E) are indicated below each symbol (+, wild-type allele; −, p.G1943E variant allele). (B) Slit-lamp photographs showing the transparent lens of an unaffected individual (IV-6) and the nuclear pulverulent cataract in the left eye of the proband (III-9).
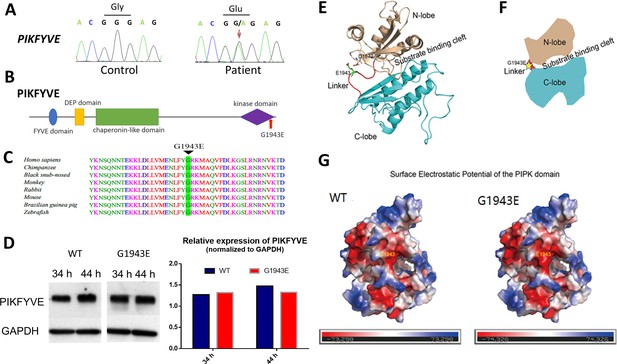
The PIKFYVE variant identified from the congenital cataract family.
(A) Sanger sequencing chromatogram showing the cDNA sequences from a healthy control and a cataract patient. The heterozygous c.5828G>A missense variant in the patient is indicated by the red arrow. (B) A schematic diagram showing the human PIKFYVE domains. The p.G1943E variant in the PIPK domain is indicated by the red arrow. (C) Protein sequence alignment of PIKFYVE orthologs in vertebrates. The black triangle denotes the conserved glycine at position 1943. (D) Western blot analysis of PIKFYVEWT and PIKFYVEG1943E expression in HEK293T cells that were transiently transfected with either pCS2(+)-CMV-PIKFYVEWT or pCS2(+)-CMV-PIKFYVEG1943E. The protein levels were normalized by GAPDH expression. Experiments were repeated three times. (E) Predicted structure model of the p.G1943E variant form of PIKFYVE PIPK domain generated by the PHYPRE2 server (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/~phyre2/html/). N-lobe, C-lobe, and the hinge linker are shown in gold, cyan, and red, respectively. The variant residue E1943 is shown in sticks and labeled with green. The negatively charged residue D1872 close to E1943 side chain is also shown in sticks. (F) A schematic demonstrating the organization of PIKFYVE PIPK domain. N-lobe, C-lobe, and the hinge linker are shown in gold, cyan, and red, respectively. The position of the p.G1943E variant is labeled with a yellow star. (G) Surface electrostatic potential comparison of the PIPK domain of PIKFYVE between wild-type (WT) and p.G1943E variant. The electrostatic potentials are presented as heatmaps from red to blue, and the electrostatic potential scales are shown in the lower panel. See Figure 2—source data 1 for details.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Raw data for intensity of bands in Figure 2D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71256/elife-71256-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Raw data for the full raw unedited blots in Figure 2D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71256/elife-71256-fig2-data2-v1.pdf
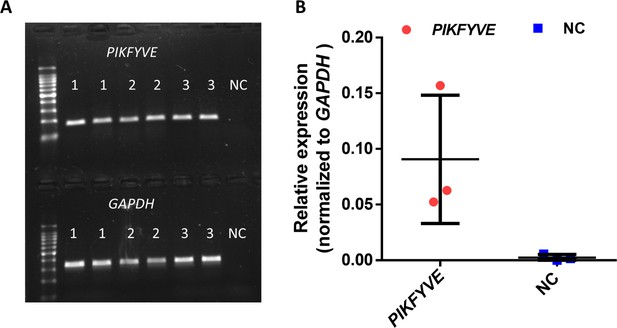
Expression of PIKFYVE in human lens capsule.
(A) RT-PCR results of lens capsules from three individuals. NC represents negative control without cDNA. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR shows the relative expression of PIKFYVE compared with GAPDH.
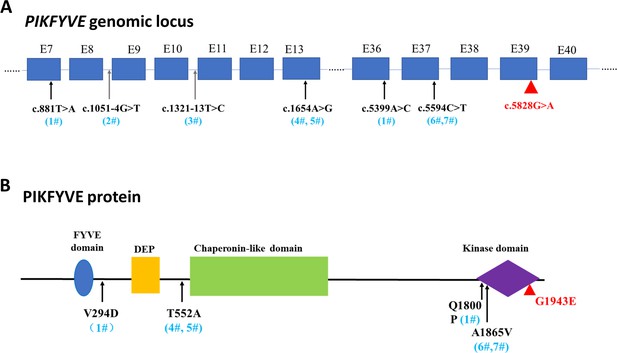
A schematic diagram showing the distribution of PIKFYVE variants.
(A) The genomic loci of identified variants of PIKFYVE from sporadic cataract patients. (B) The amino acid changes of identified variants and their positions in PIKFYVE protein.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data for the clinical manifestation of seven patients with PIKFYVE variants in Figure 2—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71256/elife-71256-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
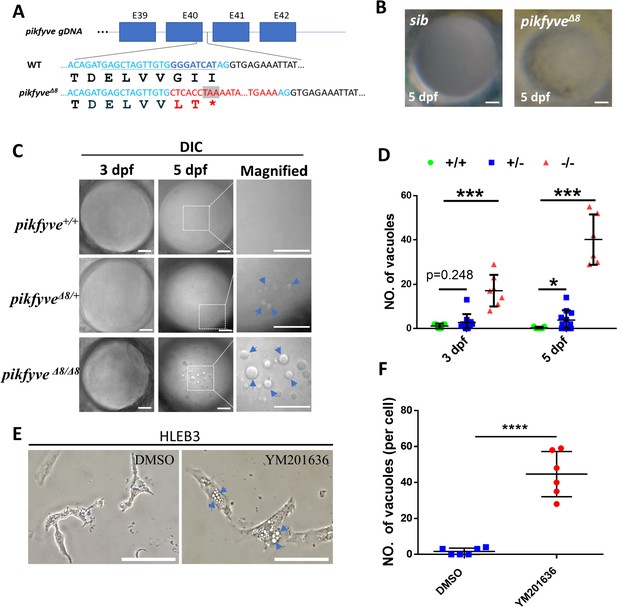
Disruption of the PIPK domain of Pikfyve in zebrafish caused early-onset cataract.
(A) A schematic diagram showing the generated pikfyveΔ8 mutant allele. The underlined base pairs are the sgRNA target. The deleted base pairs are shown in dark blue while inserted ones are shown in red. The stop codon introduced in the mutant form is shown in the grey box. (B) Representative images showing the lens of sibling and pikfyveΔ8 mutants at 5 dpf. (C) Representative differential interference contrast (DIC) images showing the lens of pikfyve+/+, pikfyve+/Δ8, and pikfyveΔ8/Δ8 embryos at 3 dpf and 5 dpf. The scale bars represent 10 μm in (B) and (C). (D) Quantification of vacuole number in the lens of pikfyve+/+, pikfyve+/Δ8, and pikfyveΔ8/Δ8 embryos at 3 dpf (n=7 for pikfyve+/+; n=10 for pikfyve+/Δ8; n=7 for pikfyveΔ8/Δ8) and 5 dpf (n=7 for pikfyve+/+; n=11 for pikfyve+/Δ8; n=6 for pikfyveΔ8/Δ8). (E) Representative images of HLEB3 cells treated with DMSO or PIKFYVE inhibitor YM201636 for 4 hr. The scale bars represent 25 μm. (F) Quantification of the vacuole numbers in (E). ****, p<0.0001, Student’s t-test. All experiments were repeated three times. See Figure 3—source data 1 for details.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw data for quantification in Figure 3D and F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71256/elife-71256-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
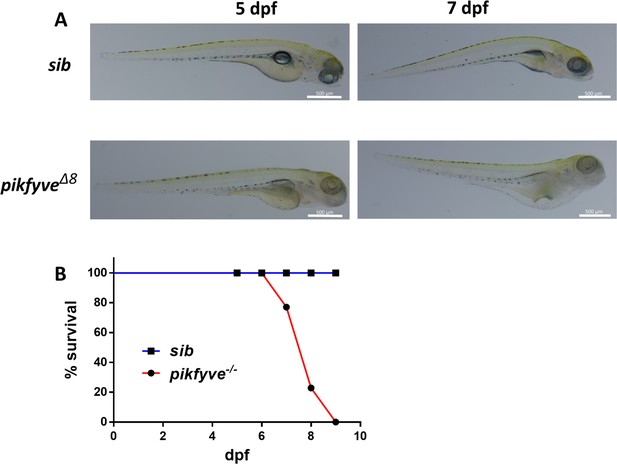
Characterization of pikfyve-deficient zebrafish mutants.
(A) Gross morphology of 5-dpf and 7-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutants. The scale bars represent 500 μm. (B) Survival rate of pikfyveΔ8 mutants (n=48) and siblings (n=50).
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for quantification in Figure 3—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71256/elife-71256-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx

Ectopic overexpression of PIKFYVEG1943E failed to induce cataract defect in zebrafish.
(A) Schematic view of constructs in which the WT and G1943E variant form of PIKFYVE were expressed under the control of the ubiquitously expressed ubiquitin promoter. (B) Representative images showing the lens of 5-dpf WT, Tg(ubi:PIKFYVEEWT) and Tg(ubi:PIKFYVEG1943E) zebrafish embryos. The scale bars represent 20 μm. All experiments were repeated three times.
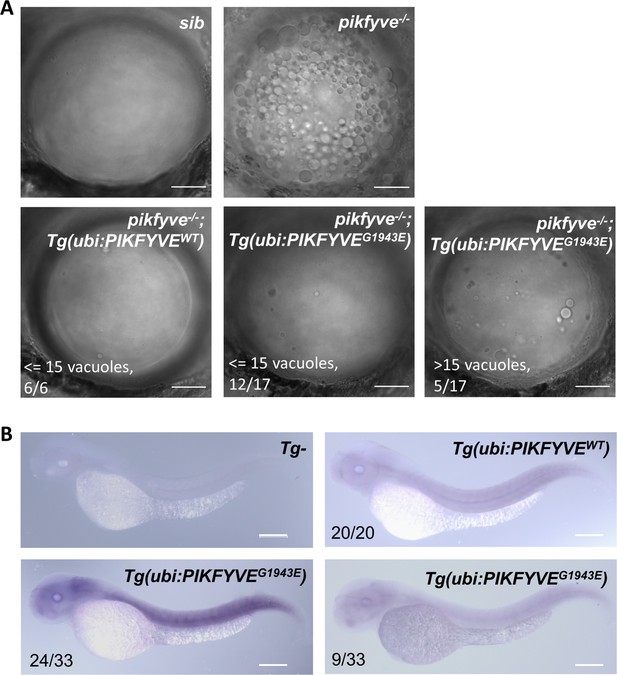
The G1943E variant form of PIKFYVE is less efficient to rescue the vacuole defect in pikfyve-deficient zebrafish mutants.
(A) Representative images showing the lens of 5-dpf siblings, pikfyveΔ8, pikfyveΔ8;Tg(ubi:PIKFYVEWT), and pikfyveΔ8;Tg(ubi:PIKFYVEG1943E) zebrafish. The scale bars represent 20 μm. (B) Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) analysis of human PIKFYVE transcripts in 2-dpf Tg(ubi:PIKFYVEWT) and Tg(ubi:PIKFYVEG1943E) zebrafish. The scale bars represent 200 μm. See Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1 for details.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Raw data for quantification in Figure 3—figure supplement 3B, C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71256/elife-71256-fig3-figsupp3-data1-v1.xlsx
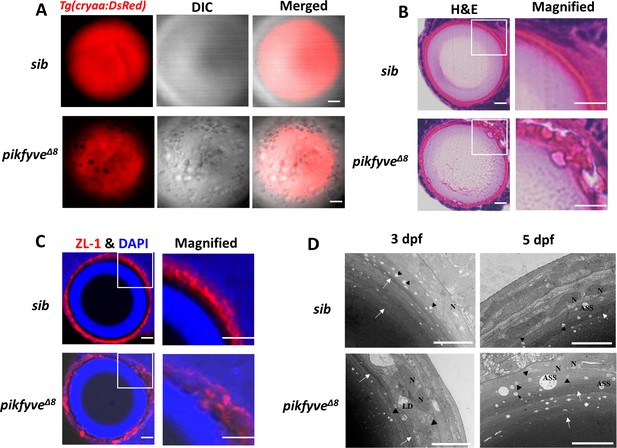
Detailed characterization of cataract phenotypes in pikfyveΔ8 mutants.
(A) Confocal imaging of the lens of 5-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutants in Tg(cryaa:DsRed) transgenic background. (B) Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of 5-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutant zebrafish lens after cryostat section. (C) ZL-1 antibody and DAPI staining of 5-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutant zebrafish lens. (D) Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of the lens of siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutants at 3 dpf and 5 dpf. ASS, autophagy lysosome; LD, lipid droplet; N, nucleus. All results were confirmed in three different individuals. All the scale bars represent 10 μm.
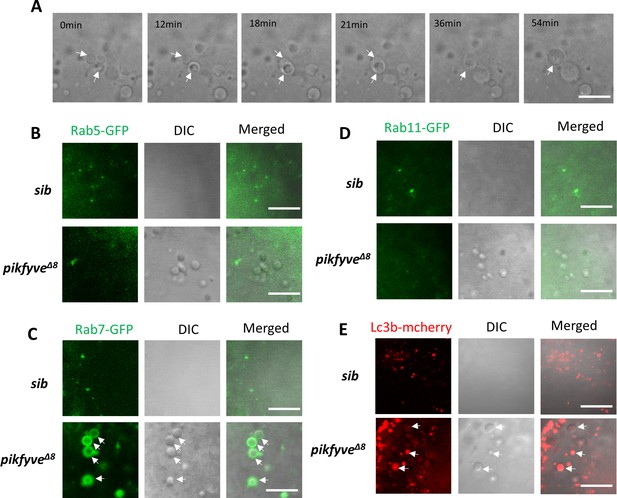
Characterization of vacuoles in pikfyveΔ8 mutants.
(A) Time-lapse imaging indicating the dynamic changes of vacuole formation in the lens of 4-dpf pikfyveΔ8 mutants. White arrows indicate the fusion process of two small vacuoles. (B) Representative images showing the lens of 3.5-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutants injected with gfp-rab5c mRNA. (C) Representative images showing lens of 3.5-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutants injected with gfp-rab7 mRNA. (D) Representative images showing lens of 3.5-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutants injected with gfp-rab11a mRNA. (E) Representative images showing lens of 3.5-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutants injected with mcherry-lc3b mRNA. All experiments were repeated three times. All the scale bars represent 10 μm.
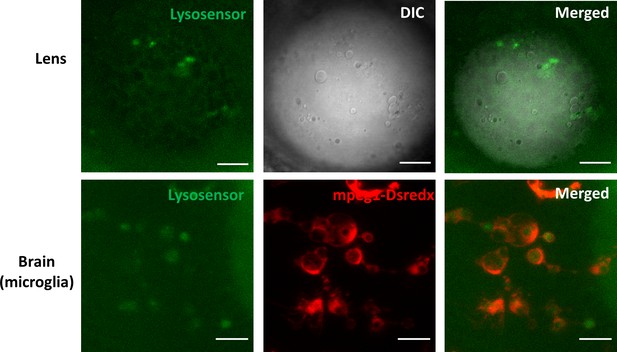
Characterization of lysosomes in microglia and lens of pikfyveΔ8 mutant zebrafish.
Confocal images of the lens and microglia of 4-dpf pikfyveΔ8 mutants in Tg(mpeg1:dsredx) background after LysoSensor staining. The results were confirmed in more than three different individuals. The scale bars represent 20 μm.
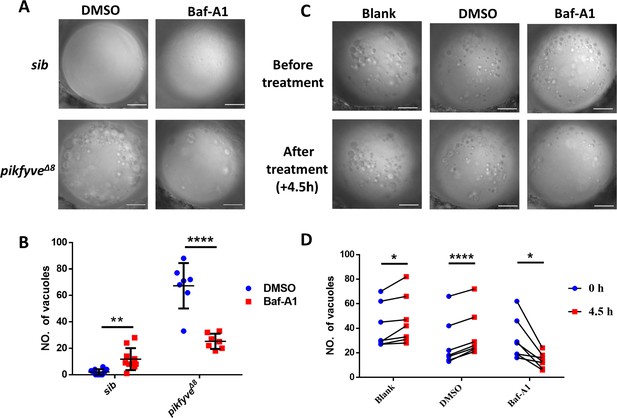
Baf-A1 partially rescued the vacuole defect in the lens of pikfyveΔ8 mutant zebrafish.
(A) Representative confocal images of the lens of 4-dpf pikfyveΔ8 mutants treated with DMSO or Baf-A1 for 4.5 hr. (B) Quantification of the vacuole numbers in the lens of 4-dpf siblings and pikfyveΔ8 mutant embryos treated with DMSO or Baf-A1 (n=10 for sibling groups; n=7 for mutant groups). (C) Confocal images of the lens of 4-dpf pikfyveΔ8 mutants with no treatment or after 4.5 hr treatment with DMSO or Baf-A1. (D) Quantification of the vacuole numbers in (C) (n=6 for each group). All experiments were repeated three times. All the scale bars represent 20 μm. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001, Student’s t-test. See Figure 6—source data 1 for details.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Raw data for quantification in Figure 6B and D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71256/elife-71256-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
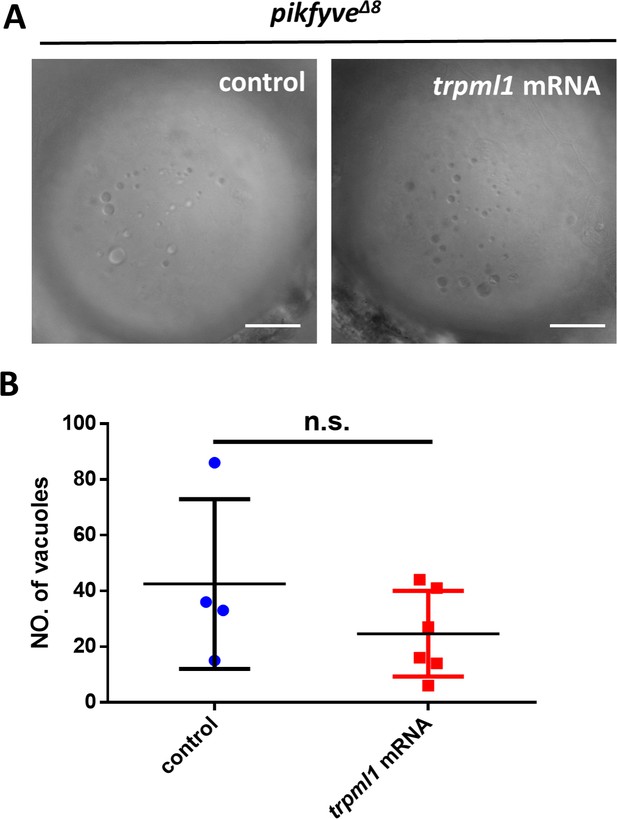
Overexpression of trpml1 failed to rescue the lens defects in pikfyve Δ8 mutants.
(A) Confocal images of the lens of 4-dpf pikfyveΔ8 mutants and pikfyveΔ8 mutants injected with trpml1 mRNA. The scale bars represent 20 μm. (B) Quantification of the vacuole number in the lens of 4-dpf pikfyveΔ8 mutants and pikfyveΔ8 mutants injected with trpml1 mRNA. n.s., not significant, p>0.05, Student’s t-test. See Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1 for details.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for quantification in Figure 6—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/71256/elife-71256-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
Clinical characteristics of living patients in the cataract family.
| Patient | Gender | Age at diagnosis (years) | BCVA before surgery (OD, OS) | Cataract type (OU) | Surgery (Y/N) | BCVA after surgery (OD, OS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅱ-1 | F | 9 | – | – | Y | 20/160, 20/125 |
| Ⅱ-4 | F | 12 | 20/40, 20/32 | Nuclear pulverulent | N | NA |
| Ⅱ-8 | M | 4 | 20/100, LP | Nuclear pulverulent | Y | 20/40, FC |
| Ⅲ-1 | M | 47 | 20/25, 20/20 | Peripheral cortical punctate | N | NA |
| Ⅲ-5 | M | 6 | 20/40, 20/40 | Nuclear pulverulent | Y | 20/20, 20/20 |
| Ⅲ-6 | M | 7 | 20/40, 20/50 | Nuclear pulverulent | Y | 20/16, 20/16 |
| Ⅲ-9 | M | 6 | 20/40, 20/66 | Nuclear pulverulent | Y | 20/28, 20/25 |
| Ⅳ-1 | M | 22 | 20/20, 20/20 | Peripheral cortical punctate | N | NA |
| Ⅳ-3 | M | 3 | 20/30, 20/25 | Nuclear pulverulent | N | NA |
| Ⅳ-5 | M | 2 | 20/125, 20/125 | Nuclear and Y-sutural | N | NA |
-
BCVA: best corrected visual acuity; OD: eye, oculus dexter; OS: eye, oculus sinister; OU: eye, oculus uterque; Y: yes; N: no; F: female; M: male; LP: light perception; FC: finger counting; —: unknown; NA: not applicable.
Candidate variants identified from whole-exome sequencing in the cataract family.
| Gene | SNP ID | Chromosome position (bp; hg19) | cDNA change | Amino acid change | MAF(gnomAD) | PolyPhen | GERP | CADD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIKFYVE | rs771244880 | chr2:209217490 | c.5828G>A | p.G1943E | 0.00002 | 0.999 | 5.09 | 26.00 |
| NPHS1 | rs114849139 | chr19:36330456 | c.2869C>G | p.V957L | 0.001 | 0.987 | 4.27 | 14.34 |
| FPR1 | rs78488639 | chr19:52249959 | c.289G>T | p.L97M | 0.008 | 0.795 | 2.55 | 10.70 |
-
MAF: minor allele frequency; gnomAD: genome aggregation database; PolyPhen: polymorphism phenotyping; GERP: evidence of evolutionary conservation; CADD: combined annotation dependent depletion.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (Homo sapiens) | HEK293T | Laboratory cell bank of Shenzhen PKU-HKUST Medical Center | Initially ordered from ATCC by colleagues in HKUST | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HLEB3 | ATCC | ATCC CRL-11421, RRID:CVCL_6367 | |
| Strain, strain background (Danio rerio) | pikfyveΔ8 mutant | This paper | Maintained in Shenzhen PKU-HKUST Medical Center | |
| Strain, strain background (D. rerio) | Tg(ubi:PIKFYVEWT) | This paper | Maintained in Shenzhen PKU-HKUST Medical Center | |
| Strain, strain background (D. rerio) | Tg(ubi:PIKFYVEG1943E) | This paper | Maintained in Shenzhen PKU-HKUST Medical Center | |
| Strain, strain background (D. rerio) | Tg(cryaa:DsRed;il-1b:GFP-F) | doi.10.1242/dmm.014498 | ||
| Chemical compound, drug | YM201636 | Selleck, China | S1219 | 800 nM for 4 hr |
| Chemical compound, drug | bafilomycin A1 | MedChemExpress, NJ | HY-100558 | 1 μM for 4.5 hr |
| Antibody | Anti-PIKFYVE antibody (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam, UK | Cat# ab137907 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-GAPDH antibody (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam, UK | Cat# ab9485, RRID:AB_307275 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (goat polyclonal) | Abcam, UK | Cat# ab205718, RRID:AB_2819160 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Lens Fiber Cell Marker antibody [ZL-1] (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam, UK | Cat# ab185979 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-Mouse-555 secondary antibody (donkey polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA | Cat# A-31570, RRID:AB_2536180 | IF (1:400) |
| Sequence-based reagent (H. sapiens) | Human PIKFYVE genotyping fwd | This paper | PCR primer | TTTTGACCTTCTCTTGATTAGAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent (H. sapiens) | Human PIKFYVE genotyping rev | This paper | PCR primer | AAATATGGCCTAGTAACCAAAGTTAAA |
| Sequence-based reagent (H. sapiens) | Human PIKFYVE cDNA cloning fwd | This paper | PCR primer | ATGGCCACAGATGATAAGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent (H. sapiens) | Human PIKFYVE cDNA cloning rev | This paper | PCR primer | TCAGCAATTCAGACCCAAGCCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent (H. sapiens) | Human PIKFYVE qPCR fwd | This paper | PCR primer | CGTCCCCAACACTGGACTCTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent (H. sapiens) | Human PIKFYVE qPCR rev | This paper | PCR primer | CCCTGGCCTCCTTCTGCTCTCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent (H. sapiens) | Human GAPDH qPCR fwd | This paper | PCR primer | CGAGATCCCTCCAAAATCAA |
| Sequence-based reagent (H. sapiens) | Human GAPDH qPCR rev | This paper | PCR primer | GTCTTCTGGGTGGCAGTGAT |
| Sequence-based reagent (D. rerio) | Zebrafish pikfyve genotyping fwd | This paper | PCR primer | GAGAACCTGCTCAAACTGGTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent (D. rerio) | Zebrafish pikfyve genotyping rev | This paper | PCR primer | AGATTTGACCACCATCTCCAGC |





