Cannabinoid signaling modulation through JZL184 restores key phenotypes of a mouse model for Williams–Beuren syndrome
Figures
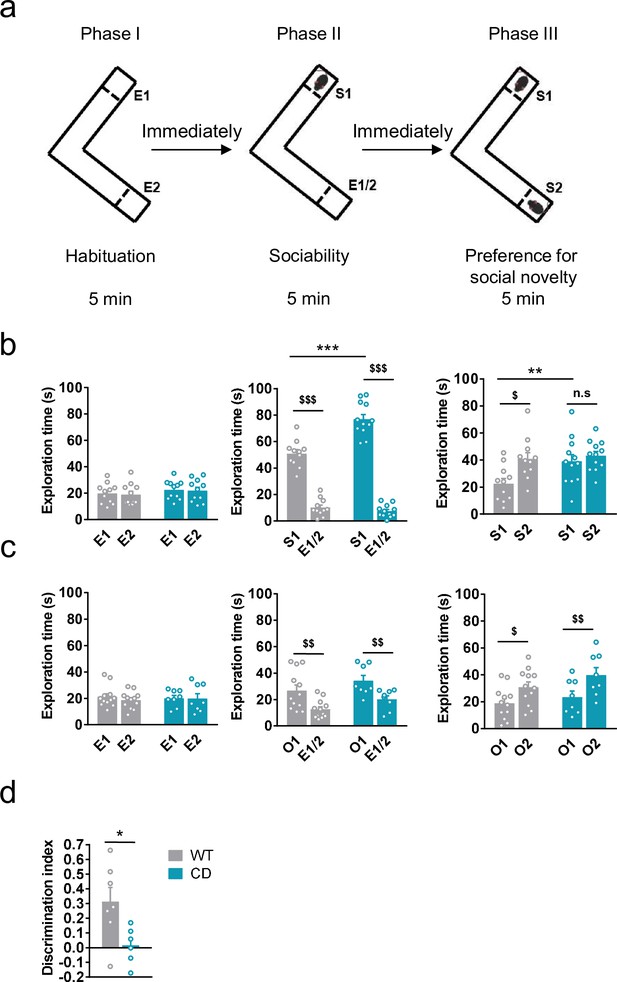
Complete deletion (CD) mice show an hypersociable phenotype, no preference for social novelty and cognitive alterations.
(a) Schematic cartoon of the sociability and preference for social novelty procedure. (b) Time spent exploring either empty compartments (E) or stranger mice (S) during the three phases of the Vsocial-maze (WT, n = 11; CD, n = 11–12). (c) Time spent exploring either empty compartments (E) or objects (O) (WT, n = 12; CD, n = 8). Statistical significance was calculated by repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) comparison. $p < 0.05; $$p < 0.01; $$$p < 0.001 (compartment effect); **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (genotype effect). (d) Discrimination index of WT and CD mice (WT, n = 7; CD, n = 6). Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05 (genotype effect). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Complete deletion (CD) mice social and cognitive alterations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig1-data1-v1.zip
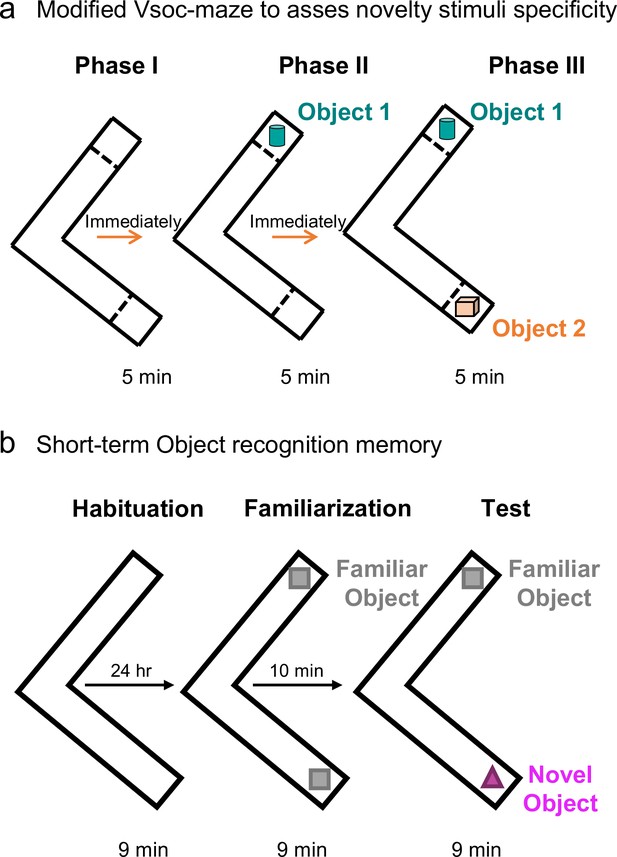
Schematic cartoon of behavioral test.
Schematic cartoon of the (a) modification of the sociability and preference for social novelty procedure using unfamiliar objects instead of unfamiliar mice and (b) and short-term object recognition memory procedure.
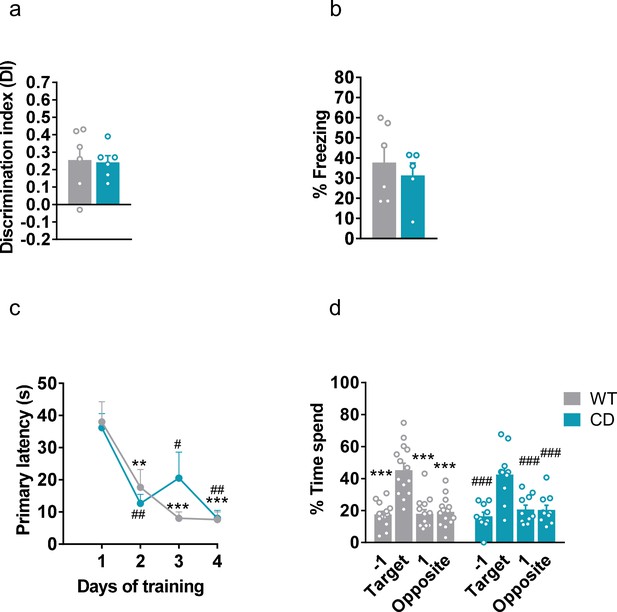
Long-term nonemotional, emotional, and spatial memory in complete deletion (CD) mice.
(a) Discrimination index in long-term novel object recognition test (WT, n=6; CD, n=6). Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. (b) Freezing (%) behaviour measured in long-term context fear conditioning paradigm (WT, n=6; CD, n=5). Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. (c) Primary latency (s) measured during Barnes maze training. Statistical significance was calculated by Newman-Keuls post hoc test following Repeated measures two-way ANOVA ** p< 0.01, *** p< 0.001 (compared to WT Day 1); # p<0.05, ## p<0.01 (compared to CD Day 1). (d) Time spend (%) in each quadrant during Barnes maze test trial (WT, n=14; CD, n=10). Statistical significance was calculated by Newman-Keuls post hoc test following Repeated measures two-way ANOVA *** p< 0.001 (compared to WT Target quadrant); ### p<0.001 (compared to CD Target quadrant). Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Long-term nonemotional, emotional, and spatial memory in complete deletion (CD) mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
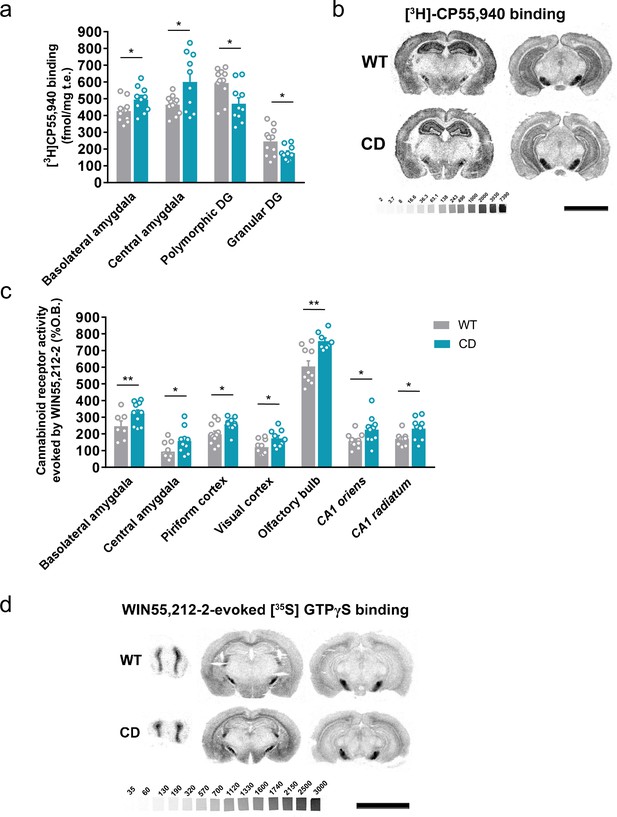
Complete deletion (CD) mice show alterations in cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) density and coupling to Gi/o proteins.
(a) [3H]CP55,940 binding of brain regions with significant changes in CD mice in comparison to WT littermates (WT, n = 11; CD, n = 10). (b) Representative images of [3H]CP55,940-binding autoradiography. (c) Brain regions showing significant changes in [35S]GTPγS binding evoked by WIN55,212–2 (10 µM) in CD mice in comparison to WT littermates (WT, n = 10–11; CD, n = 8–10), expressed as percentage of stimulation over the basal binding. (d) Representative images of WIN55,212–2-evoked [35S]GTPγS binding. [14C]-microscales used as standards in Ci/g t.e. Scale bar = 5 mm. Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; (genotype effect). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) density and coupling to Gi/o proteins in complete deletion (CD) mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig2-data1-v1.zip
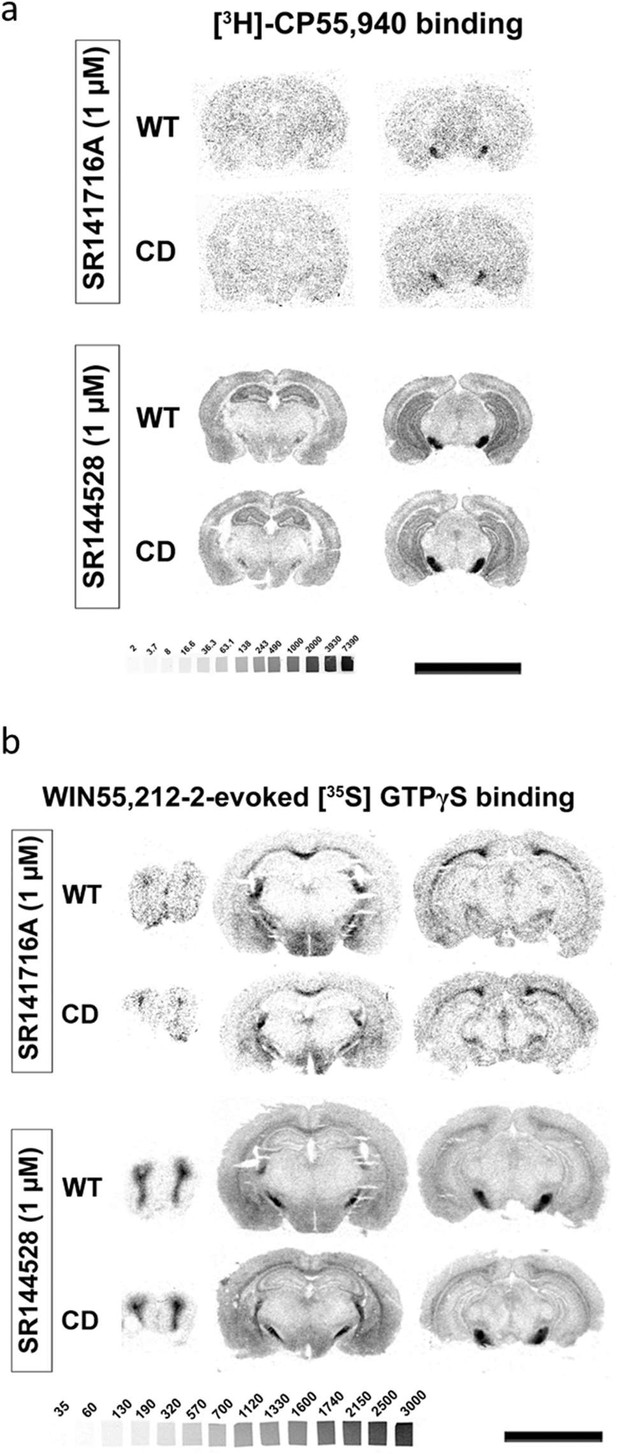
Complete deletion (CD) mice alterations in cannabinoid receptor density and activity are specific for cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R).
(a) Representative image of [3H]CP55,940 radioligand binding autoradiography. [3H]CP55,940 radioligand binding in brain slices was blocked with rimonabant but not with the CB2R antagonist SR144528. (b) Representative images of WIN55,212-2-evoked [35S]GTPγS binding. The increase in WIN55,212-2-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in brain slices was blocked in the presence of the CB1R antagonist rimonabant, but not with SR144528.
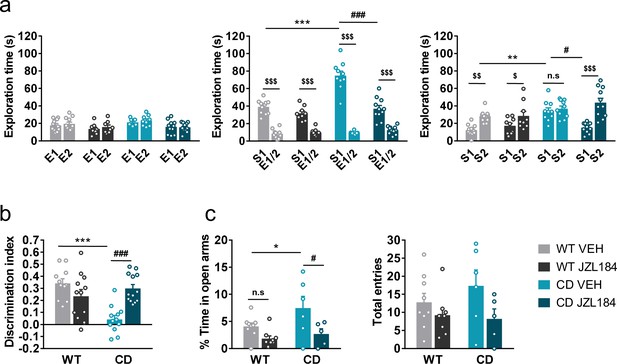
JZL184 treatment normalizes behavioral traits of complete deletion (CD) mice.
(a) Time spent exploring either empty compartments (E) or stranger mice (S) in the Vsocial-maze after 10 days of treatment with vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n = 11; WT JZL184, n = 8–9; CD VEH, n = 9–10; CD JZL184, n = 11). Statistical significance was calculated by repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) comparison. $p < 0.05; $$p < 0.01; $$$p < 0.001 (compartment effect); *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001 (genotype effect); #p < 0.05; ###p < 0.001 (treatment effect). (b) Discrimination index of WT and CD mice treated for 7 days with vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n = 11; WT JZL184, n = 12; CD VEH, n = 12; CD JZL184, n = 13). Statistical significance was calculated by Newman–Keuls post hoc test following two-way ANOVA. ***p < 0.001 (genotype effect); ###p < 0.001 (treatment effect). (c) Percentage of time spend in open arms and total entries in the elevated plus maze of WT and CD mice treated for 10 days with vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n = 9; WT JZL184, n = 9; CD VEH, n = 6; CD JZL184, n = 5). Statistical significance was calculated by Newman–Keuls post hoc test following two-way ANOVA. *p < 0.05 (genotype effect); #p < 0.05 (treatment effect). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
JZL184 treatment normalizes behavioral traits of complete deletion (CD) mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig3-data1-v1.zip
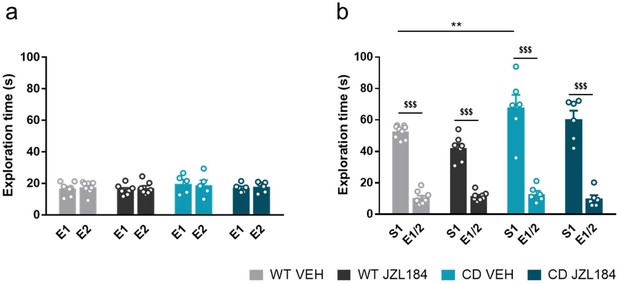
Acute administration of JZL184.
Acute administration of JZL184 does not normalise hypersociable phenotype in CD mice. (a) Time spent exploring both empty compartments (E). (b) Time spent exploring either empty compartments (E) or stranger mice (S) after one single of treatment of vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n=7-8; WT JZL184, n=7-8; CD VEH, n=5-6; CD JZL184, n=6). Statistical significance was calculated by repeated measures ANOVA comparison. $$$ p<0.001 (compartment effect); ** p<0.01 (genotype effect). Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Acute administration of JZL184.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
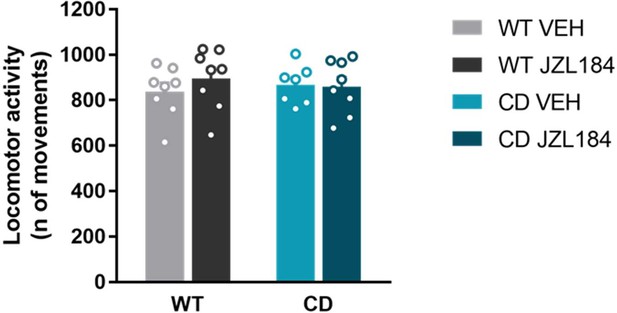
Locomotor activity after JZL184 treatment.
JZL184 treatment does not modify locomotor activity in WT and CD mice. Horizontal movements performed in locomotor activity boxes for 30 minutes by mice treated with vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n=8; WT JZL184, n=8; CD VEH, n=7; CD JZL184, n=8). Statistical significance was calculated by two-way ANOVA. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Locomotor activity after JZL184 treatment.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig3-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
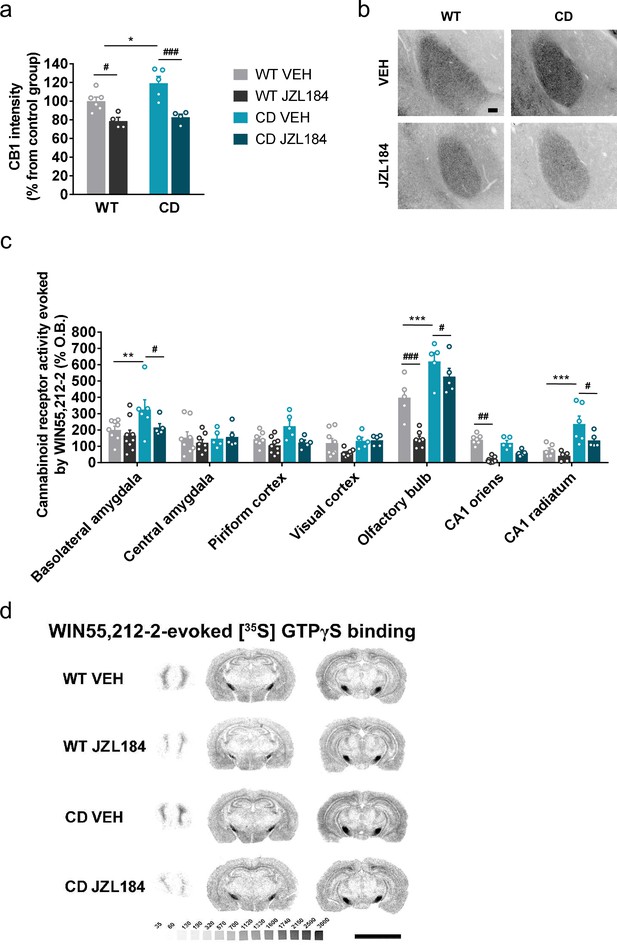
JZL184 treatment restores altered cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) density and coupling to Gi/o proteins in complete deletion (CD) mice.
(a) Quantification and (b) representative images of CB1R immunodetection in the basolateral amygdala of WT and CD mice after 10 days of treatment with vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n = 6; WT JZL184, n = 4; CD VEH, n = 5; CD JZL184, n = 4). Scale bar = 100 µm. Statistical significance was calculated by Newman–Keuls post hoc test following two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). *p < 0.05 (genotype effect); #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 (treatment effect). (c) [35S]GTPγS binding evoked by WIN55,212–2 (10 µM) after 10 days of treatment with vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n = 5–8; WT JZL184, n = 6–9; CD VEH, n = 5–6; CD JZL184, n = 5) expressed as percentage of stimulation over the basal binding. Statistical significance was calculated by Newman–Keuls post hoc test following two-way ANOVA. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (genotype effect); #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 (treatment effect). (d) Representative images of WIN55,212–2-evoked [35S]GTPγS binding. [14C]-microscales used as standards in Ci/g t.e. Scale bar = 5 mm. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
JZL184 treatment restores altered cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) density and coupling.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig4-data1-v1.zip
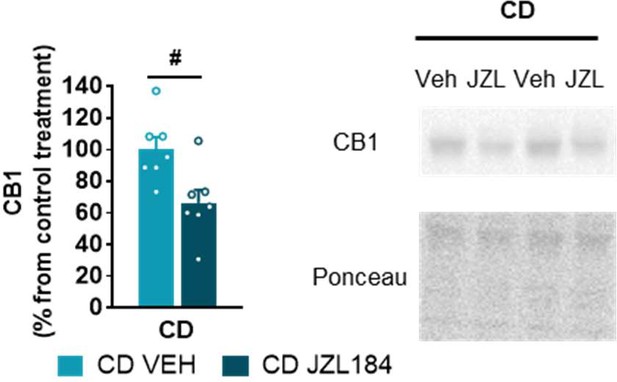
JZL184 treatment downregulates cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) protein levels in the amygdala of complete deletion (CD) mice (CD VEH, n=7; CD JZL184, n=7).
Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. # p<0.05 (treatment effect). Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
JZL184 treatment downregulates cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) protein levels in the amygdala of complete deletion (CD) mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Original blots of cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R) in the amygdala of complete deletion (CD) mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig4-figsupp1-data2-v1.pdf
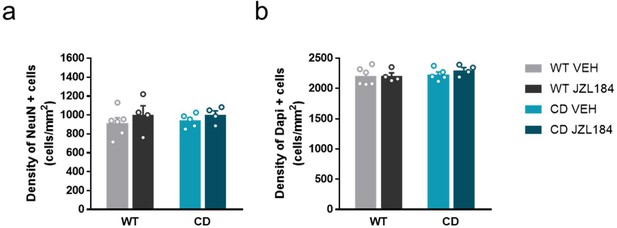
Quantification of total number of cells and neurons in basolateral amygdala.
The number of cells and neurons is not altered neither in CD mice or JZL184 treatment condition in Basolateral amygdala. (a) Density of NeuN+ and (b) Dapi + cells in basolateral amygdala measured by immunofluorescence. (WT VEH, n=6; WT JZL184, n=4; CD VEH, n=5; CD JZL184, n=4). Statistical significance was calculated by Newman-Keuls post hoc test following two-way ANOVA. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Quantification of total number of cells and neurons in basolateral amygdala.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
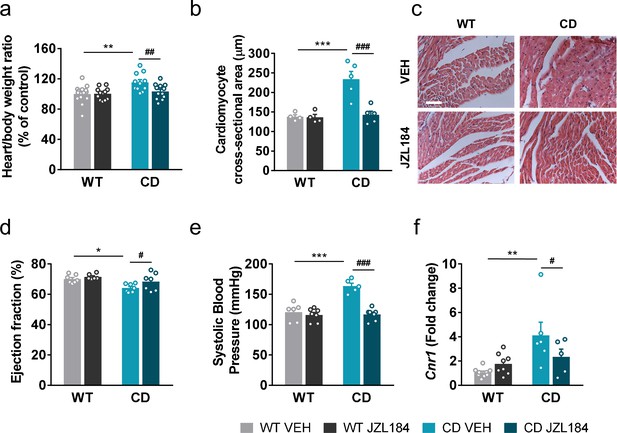
JZL184 administration regresses cardiac hypertrophy and the expression of cardiac Cnr1 alterations of complete deletion (CD) mice.
(a) Heart/body weight ratios obtained from WT and CD mice treated for 10 days with vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n = 14; WT JZL184, n = 12; CD VEH, n = 11; CD JZL184, n = 12). (b) Cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area measured from WT and CD mice after treatment (WT VEH, n = 4; WT JZL184, n = 4; CD VEH, n = 5; CD JZL184, n = 5) and (c) representative images, scale bar = 5 µm. (d) Ejection fraction (%) assessed by echocardiography from measurements performed on bidimensional images (WT VEH, n = 7; WT JZL184, n = 6; CD VEH, n = 7; CD JZL184, n = 7). (e) Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) obtained after 10 days treatment (WT VEH, n = 6; WT JZL184, n = 7; CD VEH, n = 5; CD JZL184, n = 7) (f) Cardiac mRNA levels of Cnr1 gene obtained by qPCR expressed in fold-change after the 10th day administration (WT VEH, n = 9; WT JZL184, n = 8; CD VEH, n = 6; CD JZL184, n = 5). Statistical significance was calculated by Newman–Keuls post hoc test following two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (genotype effect); #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.001 (treatment effect). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
JZL184 treatment has an impact on the cardiovascular phenotype of complete deletion (CD) mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig5-data1-v1.zip
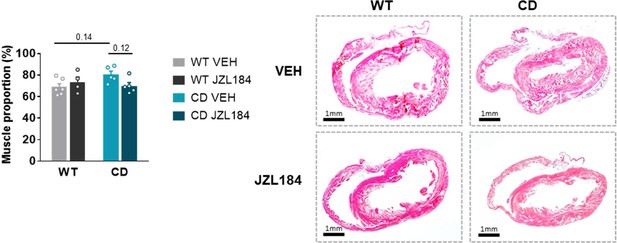
Additional heart morphology data.
Additional heart morphology data after JZL184 treatment in CD mice. Representative haematoxylin-eosin stained transverse cardiac sections and quantification of muscle proportion from WT and CD mice treated for 10 days with vehicle (VEH) or JZL184 (8 mg/kg) (WT VEH, n=6; WT JZL184, n=4; CD VEH, n=5; CD JZL184, n=5). Statistical significance was calculated by Newman-Keuls post hoc test following two-way ANOVA. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Additional heart morphology data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
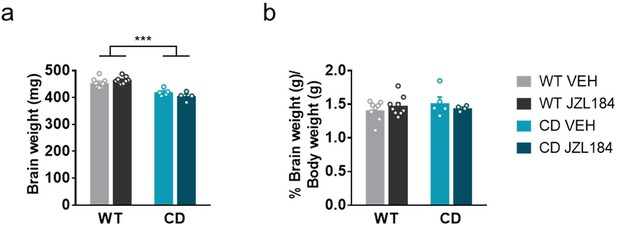
Brain weight measurements.
Brain weight (a) and proportion of brain to body weight (b) of WT and CD mice after sub-chronic treatment with vehicle or JZL184. (WT VEH, n=8; WT JZL184, n=9; CD VEH, n=5; CD JZL184, n=4). Statistical significance was calculated by two-way ANOVA. *** p<0.001 (effect of genotype). Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Brain weight measurements.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig5-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
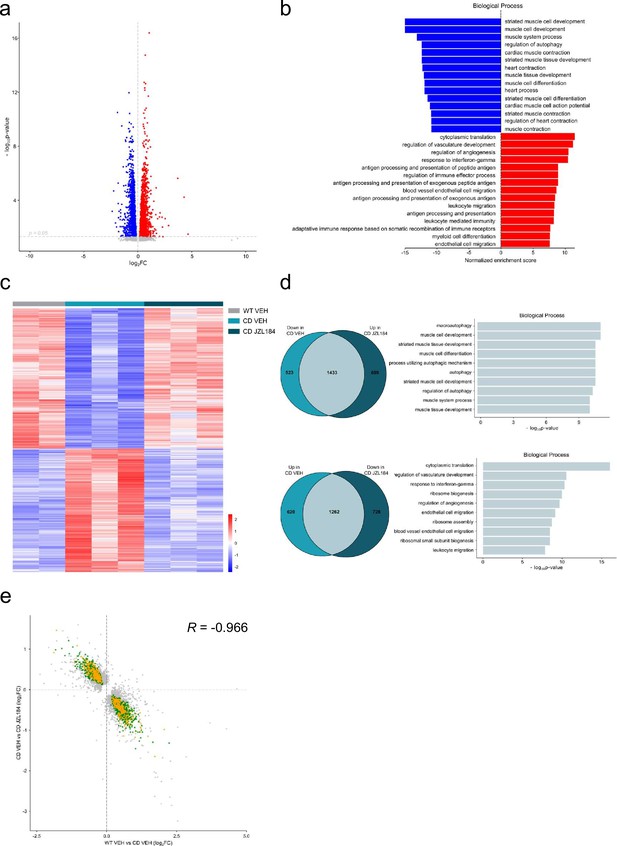
JZL184 treatment reversed alterations of the cardiac transcriptome observed in complete deletion (CD) mice.
(a) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (p < 0.05 and |log2FC| > 0) between CD and WT mice. Red indicates relative increased expression and blue indicates relative decreased expression. (b) Gene ontology enrichment analysis for both up- and downregulated genes in CD mice compared with WT. Most significant biological processes terms are represented for each group. (c) Heatmap showing the relative mRNA expression level of genes that reverted their expression in CD mice treated for 10 days with JZL184 (8 mg/kg) and CD or WT littermates treated with vehicle. (d) Venn diagrams and gene ontology enrichment analysis of genes that showed opposite differential expression in CD mice after 10 days treatment with JZL184 (8 mg/kg) compared with CD mice treated with vehicle. (e) Correlation plot of differentially expressed genes in CD mice treated for 10 days with JZL184 (8 mg/kg) and CD or WT littermates treated with vehicle. In green, genes with opposite differential expression between conditions, in orange reverted genes associated with cardiovascular function, in gray genes with no change (WT VEH, n = 2; CD VEH, n = 3; CD JZL184, n = 3).
-
Figure 6—source data 1
JZL184 treatment reverses cardiac transcriptional deficits of complete deletion (CD) mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig6-data1-v1.zip
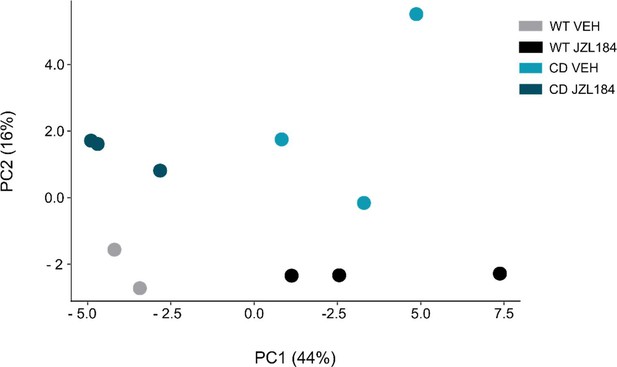
Principal component analysis (PCA).
Principal component analysis (PCA) of sample-to-sample variation in gene expression (WT VEH, n=2; WT JZL184, n=3; CD VEH, n=3; CD JZL184, n=3).
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Principal component analysis (PCA).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
Tables
Levels of endocannabinoids and related compounds in whole brain homogenates of complete deletion (CD) and WT.
(WT, n = 10; CD, n = 11). Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
| Whole brain | ||
|---|---|---|
| WT | CD | |
| 2-AG (nmol/g) | 4.96 ± 0.08 | 5.51 ± 0.29 |
| 2-LG (nmol/g) | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.03 |
| 2-OG (nmol/g) | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 0.96 ± 0.05 |
| AEA (pmol/g) | 5.57 ± 0.19 | 5.65 ± 0.32 |
| DEA (pmol/g) | 1.98 ± 0.07 | 1.93 ± 0.06 |
| DHEA (pmol/g) | 12.38 ± 0.35 | 11.63 ± 0.60 |
Levels of the two major endocannabinoids (2-AG and AEA) in brain regions relevant for social and cognitive behavior (amygdala and hippocampus) after 10 days treatment with VEH or JZL184.
(WT VEH, n = 6; WT JZL184, n = 6; CD VEH, n = 7; CD JZL184, n = 7). Statistical significance was calculated by Newman–Keuls post hoc test following two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). ###p < 0.001 (treatment effect). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
| Amygdala | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT VEH | WT JZL184 | CD VEH | CD JZL184 | |
| 2-AG (nmol/g) | 18.72 ± 4.60 | 122.96 ± 21.99### | 16.99 ± 0.86 | 128.33 ± 18.12### |
| AEA(pmol/g) | 6.89 ± 1.04 | 5.34 ± 0.53 | 6.64 ± 0.41 | 4.69 ± 0.41 |
| Hippocampus | ||||
| WT VEH | WT JZL184 | CD VEH | CD JZL184 | |
| 2-AG (nmol/g) | 9.11 ± 1.45 | 75.55 ± 14.95### | 9.01 ± 0.46 | 86.46 ± 15.25### |
| AEA (pmol/g) | 8.30 ± 0.77 | 8.26 ± 0.57 | 8.80 ± 0.63 | 7.85 ± 0.87 |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus, male) | C57BL/6J | Charles Rivers, France | C57Bl/6J | Male |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | CD | University Pompeu Fabra | (C57BL/6J background, male) | |
| Chemical compound, drug | JZL184 | Abcam | ab141592 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dimethyl sulfoxide | Scharlau Chemie | SU01531000 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Polyethylene glycol 400 | AppliChem | 142436.1611 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tween-80 | Sigma-Aldrich | P1754 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 0.9%, NaCl physiological saline | Laboratorios Ern | Vitulia | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ketamidor | Richter pharma | K1NAI027 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Xylazine hydrochloride | Sigma-Aldrich | X1251 | |
| Biological sample (Equus asinus) | Normal donkey serum | Sigma-Aldrich | D9663-10ML | 3% in PBS with 0.3% Triton X-100 |
| Antibody | Anti-CB1R (rabbit polyclonal) | Immunogenes | 1:1000 immunofluorescence | |
| Antibody | Anti-CB1R (rabbit polyclonal) | Frontier science | CB1-Rb-Af380-1 | 1:500 western blot |
| Antibody | Anti-NeuN (mouse monoclonal) | Merck Millipore | MAB377 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Anti-rabbit IgG (H+L)-AlexaFluor-555 (donkey polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-31572 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IgG (H+L)-AlexaFluor-488 (goat polyclonal) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 115-545-003 | 1:1000 |
| Commercial assay, kit | Immobilon Forte Western HRP Substrate | Merck Millipore | WBLUF0500 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Nucleospin RNA isolation kit | Macherey-Nagel | 740955-250 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | SuperScript III enzyme | Invitrogen | 12574-026 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | SybrGreen master mix | Thermo Fisher | 4309155 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers Cnr1 (CB1R) (forward) | Sigma-Aldrich | 5′-CCTGGGAAGTGTCATCTTTGT-3′ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers Cnr1 (CB1R) (reverse) | Sigma-Aldrich | 5′-GGTAACCCCACCCAGTTTGA-3′ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers Gapdh (GAPDH) (forward) | Sigma-Aldrich | 5′-TGTCGTGGAGTCTACTGGTGTCTT-3′ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers Gapdh (GAPDH) (reverse) | Sigma-Aldrich | 5′-TGGCTCCACCCTTCAAGTG-3′ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers Hprt1 (HPRT) (forward) | Sigma-Aldrich | 5′-AAGCTTGCTGGTGAAAAGGA-3′ | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Primers Hprt1 (HPRT) (reverse) | Sigma-Aldrich | 5′-TTGCGCTCATCTTAGGCTTT-3′ | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DAPI Fluoromount-G mounting media | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 00-4959-52 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 7 | GraphPad Software, Inc | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithm | STATISTICA 6.0 | StatSoft, USA | RRID:SCR_014213 | |
| Software, algorithm | Smart 3.0 videotracking software | Panlab | RRID:SCR_002852 | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA | RRID:SCR_003070 | |
| Software, algorithm | The Quantity One software v4.6.3 | Bio-Rad | RRID:SCR_014280 | |
| Software, algorithm | Salmon | PMID:28263959 | RRID:SCR_017036 | v0.7.2 |
| Software, algorithm | R | https://www.R-project.org/ | RRID:SCR_001905 | v3.6.3 |
| Software, algorithm | tximport | PMID:26925227 | RRID:SCR_016752 | v1.2.0 |
| Software, algorithm | DESeq2 | PMID:25516281 | RRID:SCR_015687 | v1.26.0 |
| Software, algorithm | clusterProfiler | PMID:22455463 | RRID:SCR_016884 | v3.14.3 |
| Chemical compound, drug | SR141716A | Tocris | 158681-13-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SR144528 | Tocris | 192703-06-3 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CP55,940 | Tocris | 83002-04-4 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | WIN55,212–2 | Sigma-Aldrich | 131543-23-2 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris–HCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 1185-53-1 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | BSA | Sigma-Aldrich | 9048-46-8 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich | 7365-45-9 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | NaCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 7647-14-5 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | MgCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | 7791-18-6 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EGTA | Sigma-Aldrich | 13368-13-3 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | GDP | Sigma-Aldrich | 43139-22-6 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | DTT | Sigma-Aldrich | 3483-12-3 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | GTPγS | Sigma-Aldrich | 10220647001 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | [3H]CP55,940 | PerkinElmer | NET1051250UC | |
| Chemical compound, drug | [35S]GTPγS | PerkinElmer | NEG030H250UC | |
| Other | β-Radiation sensitive film | Sigma-Aldrich | F5263-50EA | See autoradiography methodology |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
[3H]CP55,940 binding of all analyzed brain regions (WT, n = 11; complete deletion [CD], n = 10) in fmol/mg t.e. of cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1R).
Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (genotype effect). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-supp1-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
[35S]GTPγS binding evoked by WIN55,212–2 (10 µM) of all analyzed brain regions (WT, n = 11; complete deletion [CD], n = 10), expressed as percentage of stimulation over the basal binding.
Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (genotype effect). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-supp2-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Additional echocardiogram measurements after JZL184 treatment in complete deletion (CD) mice.
Interventricular septum diastolic (IVSd), left ventricular posterior wall thickness diastolic (LVPWd), LV end-diastolic diameter (LVDd), and left ventricular mass diastolic (Lvmass) measurement relatives to body weight (BW) (WT VEH, n = 8; WT JZL184, n = 7; CD VEH, n = 7; CD JZL184, n = 7). Statistical significance was calculated by Newman–Keuls post hoc test following two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) ***p < 0.001 (genotype effect). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-supp3-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Summary of gene expression reversion after JZL 184 administration in complete deletion (CD) mice of genes implicated in cardiac-related process.
Pathways were obtained from Reactome database and expression changes are expressed as log2 ratios of fold-changes between CD mice treated for 10 days with JZL184 (8 mg/kg) and CD or WT littermates treated with vehicle.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-supp4-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72560/elife-72560-transrepform1-v1.pdf






