Activation of the CaMKII-Sarm1-ASK1-p38 MAP kinase pathway protects against axon degeneration caused by loss of mitochondria
Figures
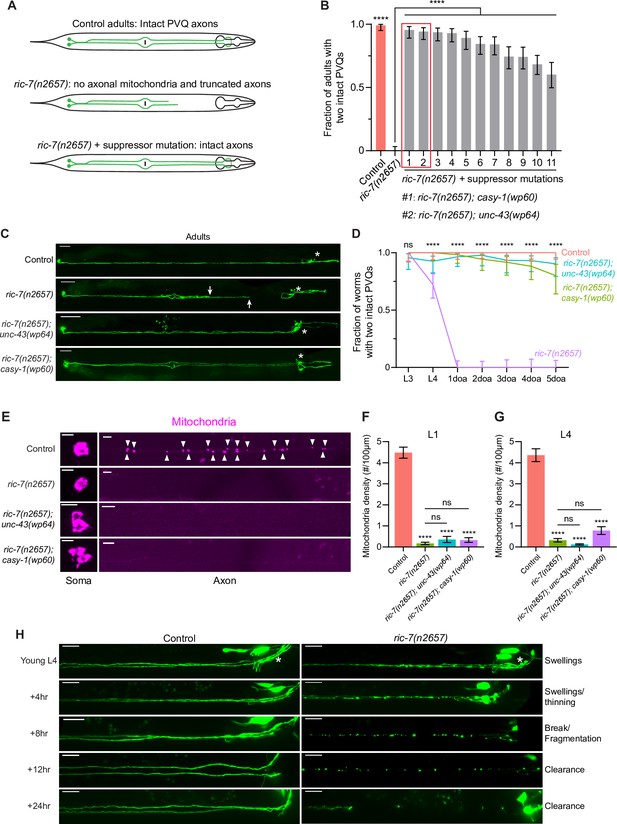
An unbiased screen identifies suppressors of spontaneous axon degeneration caused by loss of mitochondria.
(A) Diagrams of PVQ neurons in control, ric-7(n2657), and ric-7(n2657) + suppressor animals. Throughout this study, PVQ neurons are visualized with oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], and mitochondria in PVQ are visualized with sra-6p::mito::TagRFP. (B) Axon degeneration modifiers identified in unbiased forward genetic screen. Graph shows proportion of 3-day-old adult (3doa) animals without degeneration in either PVQ neuron. Leftmost bars show control (99% animals without degeneration) and ric-7(n2657) (0% animals without degeneration). Remaining bars show strains that are all ric-7(n2657) mutants and that also carry an independent mutation that suppresses degeneration. The top two suppressor mutants, ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) and ric-7(n2657); unc-43(wp64), are highlighted. Bars show proportion and 95% confidence intervals (CIs), N > 74 for all strains. ****p<0.0001, compared to ric-7(n2657), Fisher’s exact test. (C) Suppression of axon degeneration by mutations in CaMKII/unc-43 and calsyntenin/casy-1. Representative images of control, ric-7(n2657), ric-7(n2657); unc-43(wp64), and ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) 2–3doa. Arrows indicate the tips of degenerated axons. Asterisks indicate the head neurons—these are co-labeled by the GFP reporter but are not the subject of this study. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Quantification of suppression of axon degeneration. PVQ degeneration is analyzed from the L3 stage to 5-day-old adult (5doa) in control and suppressor mutants. Graph shows proportion and 95% CI. N = 44–74 for each timepoint. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, Chi-square test. (E) Suppressors of degeneration do not restore axonal mitochondria. Images of mitochondria in PVQ neurons in control, ric-7(n2657), and suppressor mutants at L4. Arrowheads indicate mitochondria in axons. Scale bar, 5 μm. (F, G) Quantification of mitochondria density in control, ric-7(n2657), and suppressor mutants at L1 and L4 stages. Bars show mean and SEM. N = 16, 26, 63, 53 for L1s and N = 54, 52, 50, 70 for L4s. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to control except where indicated, one-way ANOVA, Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons. (H) Axon degeneration in the absence of mitochondria is progressive. Images of axon morphology in a single control and a single ric-7(n2657) animal at timepoints during the L4-1doa transition. Asterisk indicates the nerve ring. Scale bar, 10 μm.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Axon degeneration and mitochondria density in control and suppressor mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
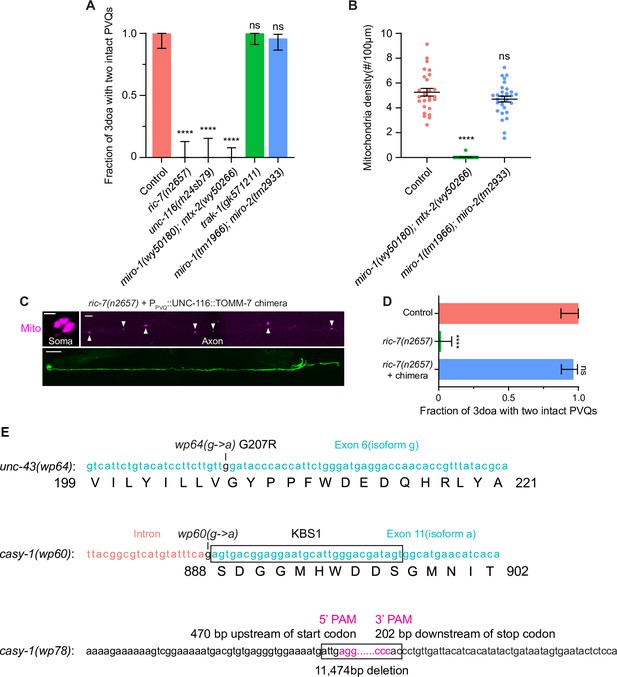
Complete loss of axonal mitochondria leads to degeneration and key allele information.
(A) Axon degeneration in mutants of the mitochondria transport machinery. Quantification of axon degeneration in control (N = 28), ric-7(n2657) (N = 26), unc-116(rh24sb79) (N = 21), miro-1(wy50180); mtx-2(wy50266) (N = 45), trak-1(gk571211) (N = 39), and miro-1(tm1966); miro-2(tm2933) (N = 50) 3-day-old adult (3doa). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test. (B) Mitochondria density in control (N = 27), miro-1(wy50180); mtx-2(wy50266) (N = 22), and miro-1(tm1966); miro-2(tm2933) (N = 30) L4 animals. Mean ± SEM. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, one-way ANOVA, Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons. (C) Images of restored axonal mitochondria and suppressed degeneration in a ric-7(n2657) mutant that expresses the UNC-116::TOMM-7 chimera in PVQ. Scale bar, 5 µm for mitochondria and 50 µm for whole animal. (D) Axon degeneration in ric-7(n2657) is due to loss of axonal mitochondria. Quantification of axon degeneration in control (N = 27), ric-7(n2657) (N = 57), and ric-7(n2657) with the UNC-116::TOMM-7 chimera in PVQ (N = 56). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test. (E) Detailed molecular information of key unc-43 and casy-1 alleles.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Axon degeneration and mitochondria density in mutants that affect mitochondria transport.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
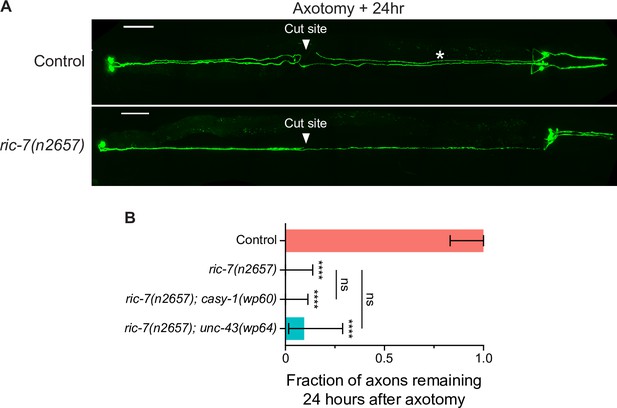
casy-1(wp60) and unc-43(wp64) do not suppress enhanced injury-induced axon degeneration (after laser axotomy) in ric-7(n2657).
(A) Representative images of laser axotomy-induced axon degeneration in PVQ in control and ric-7(n2657) animals. Asterisk indicates the remaining distal axon segment after axotomy. (B) Quantification of the presence of the distal axon segments 24 hr after axotomy in control (N = 19), ric-7(n2657) (N = 24), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) (N = 30), and ric-7(n2657); unc-43(wp64) (N = 21) animals. Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to control except where indicated, Fisher’s exact test.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Axotomy-induced axon degeneration in ric-7, ric-7; casy-1 and ric-7; unc-43 gof animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
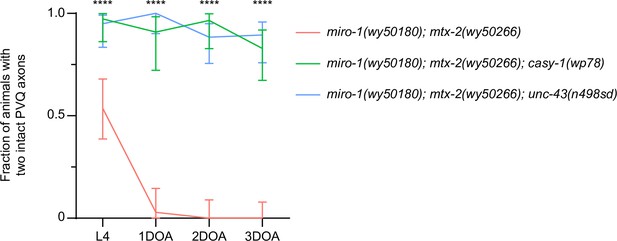
casy-1(wp78) and unc-43(n498sd) suppress axon degeneration in miro-1(wy50180); mtx-2(wy50266) mutants.
Quantification of axon degeneration in miro-1(wy50180); mtx-2(wy50266) (N = 35–45), miro-1(wy50180); mtx-2(wy50266); casy-1(wp78) (N = 22–37) and miro-1(wy50180); mtx-2(wy50266); unc-43(n498sd) (N = 35–43). Graph shows proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, chi-square test.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Axon degeneration in miro-1; mtx-2, miro-1; mtx-2; casy-1 and miro-1; mtx-2; unc-43 gof animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig1-figsupp3-data1-v1.xlsx
Active CaMKII/UNC-43 suppresses axon degeneration cell-autonomously through the conserved Sarm1/TIR-1-ASK1/NSY-1 MAPK pathway.
(A) Active CaMKII/UNC-43 functions cell-autonomously to suppress degeneration. Quantification of axon degeneration in 3-day-old adult (3doa) animals. Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657) (N = 36), ric-7(n2657); unc-43(wp64) (N = 35), ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd) (N = 31), ric-7(n2657); unc-43(e408) (N = 35), ric-7(n2657) + PPVQ::WT UNC-43 (N = 43) and ric-7(n2657) + PPVQ::constitutively active (CA) UNC-43 (N = 39). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, **p<0.01, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657) except where indicated, Fisher’s exact test. (B) Images of axon morphology in a single ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd) animal at timepoints during the L4-1doa transition. Arrowheads indicate axon swellings. Scale bar, 10 µm. (C) Loss of kinesin-1/unc-116 results in axon degeneration that is suppressed by active CaMKII/unc-43. Quantification of axon degeneration from the L3 stage to 1-day-old adults (1doa). Genotypes and number of animals: unc-116(rh24sb79) (N = 50–73), and unc-116(rh24sb79); unc-43(n498sd) (N = 38–55). Graph shows proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to unc-116(rh24sb79), Fisher’s exact test. (D) Endogenous CaMKII/UNC-43 localization. Images of native and tissue-specific fluorescence (NATF)-tagged CaMKII/UNC-43 in PVQ cell bodies and distal axons adjacent to the nerve ring in control, ric-7(n2657), and ric-7(n2657) + PPVQ::UNC-116::TOMM-7 in L3 stage animals. Scale bar, 5 µm. (E) Normalized NATF-tagged CaMKII/UNC-43 intensities (arbitrary units) in PVQ cell bodies and distal axons in control, ric-7(n2657) and ric-7(n2657) + PPVQ::UNC-116::TOMM-7 in L3 stage animals. Violin plots with median and quantiles are shown. ****p<0.0001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns, not significant, compared to control except where indicated, one-way ANOVA, Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons. (F) The UNC-43-TIR-1-MAPK pathway and conservation in mammals. (G) The TIR-1-NSY-1-SEK-1-PMK-3-CEBP-1 pathway is required to suppress axon degeneration in activated CaMKII/unc-43 mutants. Quantification of axon degeneration in 1doa. Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd) (N = 35), ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd); tir-1(qd4) (N = 37), ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd); nsy-1(ok593) (N = 33), ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd), pmk-1(km25) (N = 33), ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd), pmk-3(ok169) (N = 27), and ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd), cebp-1(tm2807) (N = 48). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd), Fisher’s exact test. (H) Sarm1/TIR-1 protects against degeneration in the context of lack of axonal mitochondria. Quantification of axon degeneration in 3doa. Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657) (N = 24), ric-7(n2657); tir-1(qd4) (N = 30), ric-7(n2657); tir-1(ok2859) (N = 25) and ric-7(n2657) + PPVQ::WT TIR-1 (N = 35). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657), Fisher’s exact test.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Axon degeneration in mutants in the CaMKII-Sarm1-MAPK pathway and endogenous CaMKII abundance.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
The GFP1-10 control and the casy-1::gfp11x7 control for the native and tissue-specific fluorescence (NATF) approach.
(A) The PPVQ::GFP1-10 construct alone has no detectable fluorescence. Asterisk indicates the approximate location of PVQ cell bodies. (B) The NATF tag does not disrupt the function of calsyntenin/casy-1 in axon degeneration. Quantification of axon degeneration in ric-7(n2657) (N = 36) and ric-7(n2657); casy-1(syb3311[casy-1::gfp11x7]) (N = 63) 3-day-old adult (3doa). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
The gfp11x7 insertion at the casy-1 locus does not affect axon degeneration.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
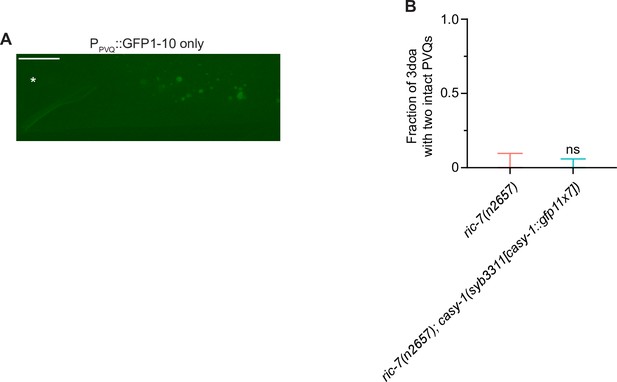
Overexpressing worm NMNATs does not suppress degeneration in ric-7(n2657).
Quantification of axon degeneration in ric-7(n2657) (N = 26), ric-7(n2657) + PPVQ::NMAT-1 (N = 30) and ric-7(n2657) + PPVQ::NMAT-2 (N = 33) 3-day-old adult (3doa). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Axon degeneration in ric-7 animals that overexpress NMATs in PVQ.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig2-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
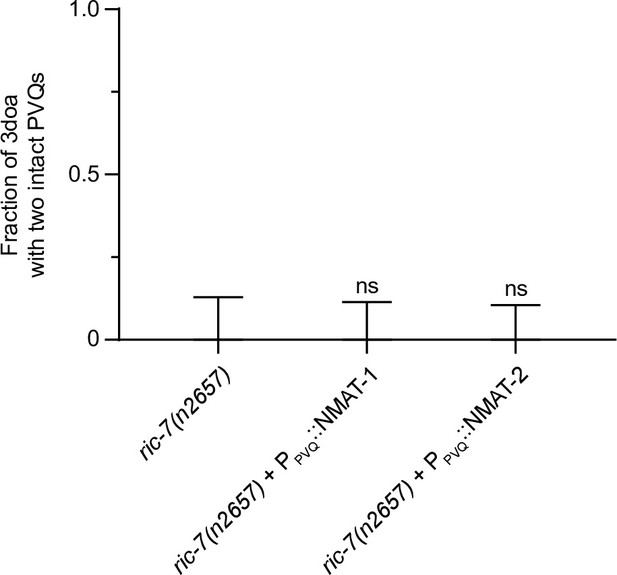
Calsyntenin/CASY-1 promotes axon degeneration cell-autonomously.
(A) The three C. elegans CASY-1 isoforms. SP, signal peptide; LG/LNS, laminin G-like; TM, transmembrane domain; KBS, kinesin-binding site. (B) Loss of calsyntenin/casy-1 suppresses degeneration due to loss of axonal mitochondria. Quantification of axon degeneration in 3-day-old adult (3doa). Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657) (N = 25), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) (N = 22), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) (N = 30), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) + the casy-1 fosmid WRM0622dH03 (N = 32), and ric-7(n2657); casy-1(tm718) (N = 49). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, =not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657), Fisher’s exact test. (C) Loss of calsyntenin/casy-1 arrests degeneration before axon severing. Images of axon morphology in a ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) animal during the L4-1doa transition. Arrowheads indicate axon swellings. Scale bar, 10 µm. (D) Structure-function analysis of CASY-1. Left, six CASY-1 fragments expressed in PVQ in ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) animals. Right, quantification of axon degeneration in 3doa. Number of animals in experiments, respectively: 23, 76, 97, 80, 30, 47, and 56. Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) with no transgene, Fisher’s exact test. Transgenic fragments #1–4 restore degeneration to ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) mutants. (E) Overexpression of calsyntenin/casy-1 enhances axon degeneration due to loss of axonal mitochondria. Quantification of axon degeneration in L4 stage animals. Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657) (N = 51), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) (N = 44), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) + PPVQ::CASY-1C (N = 43), and casy-1(wp60) + PPVQ::CASY-1C (N = 34). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657), Fisher’s exact test.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Axon degeneration in casy-1 loss-of-function and overexpression animals.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
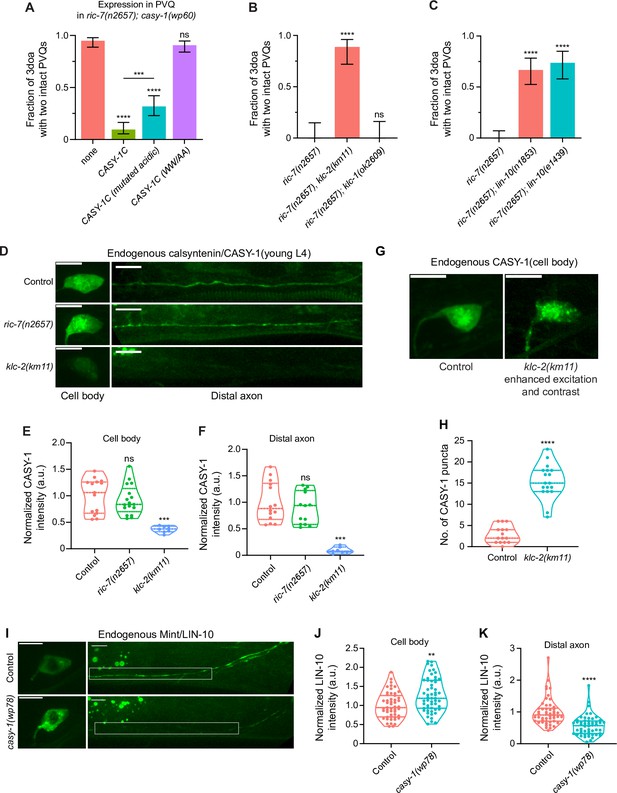
Calsyntenin/CASY-1 functions as a kinesin adaptor for Mint/LIN-10 to promote axon degeneration.
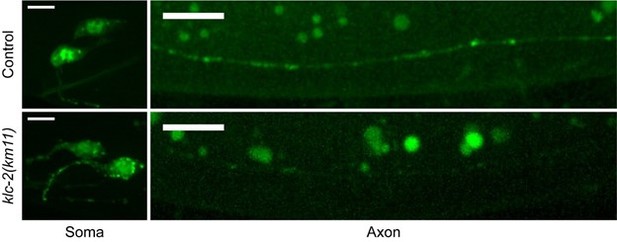
(A) Kinesin binding is required for calsyntenin’s function in axon degeneration. Quantification of axon degeneration in 3-day-old adult (3doa). All animals have the ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) background. Transgenes and number of animals: none (control) (N = 100); WT CASY-1C (N = 114); CASY-1C with mutated acidic residues (N = 88); CASY-1C with the WW/AA mutation (N = 118). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) with no transgene except where indicated, Fisher’s exact test. Transgenic CASY-1C with the WW/AA mutation does not restore degeneration to ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp60) mutants. (B) Loss of kinesin light chain klc-2 suppresses axon degeneration. Quantification of axon degeneration in 3doa. Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657) (N = 22), ric-7(n2657), klc-2(km11) (N = 27), and ric-7(n2657); klc-1(ok2609) (N = 20). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. **** p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657), Fisher’s exact test. (C) Loss of Mint/lin-10 suppresses axon degeneration. Quantification of axon degeneration in 3doa. Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657) (N = 50), ric-7(n2657); lin-10(n1853) (N = 48), and ric-7(n2657); lin-10(e1439) (N = 38). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, compared to ric-7(n2657), Fisher’s exact test. (D) Images of native and tissue-specific fluorescence (NATF)-tagged calsyntenin/CASY-1 in PVQ cell bodies and distal axons in control, ric-7(n2657), and klc-2(km11) animals at early L4 stage. Scale bar, 5 µm. (E, F) Loss of kinesin light chain klc-2 alters calsyntenin abundance. Normalized NATF-tagged CASY-1 intensities (arbitrary units) in PVQ cell bodies and distal axons. Violin plots with median and quantiles are shown. *** p<0.001, ns, not significant, compared to control, one-way ANOVA, Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons. (G) Calsyntenin accumulates in cell body puncta in animals that lack kinesin light chain klc-2. Images of NATF-tagged CASY-1 in PVQ cell bodies in control and klc-2(km11) at early L4 stage. Excitation and contrast are enhanced in klc-2(km11) animals. Scale bar, 5 µm. (H) Number of NATF-tagged CASY-1 puncta in PVQ cell bodies. Violin plots with median and quantiles are shown. ****p<0.0001, compared to control, Mann–Whitney test. (I) Images of NATF-tagged Mint/LIN-10 in PVQ cell bodies and distal axons in control and casy-1(wp78) animals at L4 stage. Boxes highlight the distal axon region for quantifications in (K). Scale bar, 5 µm. (J, K) Mint/LIN-10 is depleted from distal axon in animals that lack calsyntenin. Normalized NATF-tagged LIN-10 intensities (arbitrary units) in PVQ cell bodies and distal axons. Violin plots with median and quantiles are shown. ****p<0.0001, **p<0.01, compared to control, Mann–Whitney test.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Axon degeneration in CASY-1/KLC/LIN-10 mutants and endogenous CASY-1 and LIN-10 localization.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
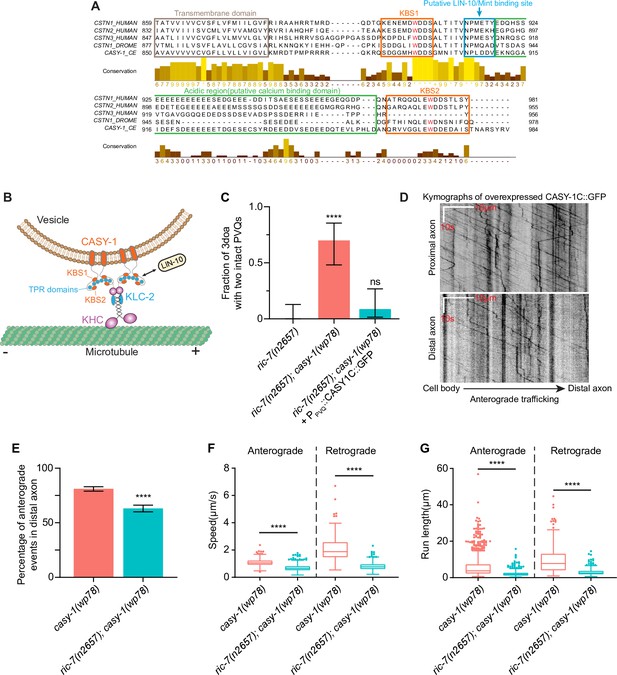
Functional domains in the CASY-1 ICD and quantification of CASY-1C traffic.
(A) Sequence alignment of the transmembrane and intracellular portion of C. elegans, Drosophila, and human calsyntenins. The two tryptophan residues critical for kinesin light chain (KLC) binding are highlighted in red. (B) Model of how CASY-1 functions as a kinesin adaptor that transports cargoes such as Mint/LIN-10. KHC, kinesin heavy chain; TPR, tetratricopeptide repeat. (C) GFP-tagged CASY-1C functions in axon degeneration. Quantification of axon degeneration in ric-7(n2657) (N = 26), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) (N = 20), and ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) + PPVQ::CASY-1C::GFP (N = 23) 3-day-old adult (3doa). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test. (D) Representative kymographs of trafficking of overexpressed CASY-1C::GFP in PVQ axons in casy-1(wp78) animals. (E) Percentage of anterograde events of overexpressed CASY-1C::GFP in distal axons in casy-1(wp78) (N = 1729) and ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) (N = 957) animals at L4. Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, Fisher’s exact test. (F) Speeds of CASY-1 vesicles in distal axons in casy-1(wp78) and ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) (nontruncated axons) at L4. N = 1125 for casy-1(wp78) anterograde, 604 for ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) anterograde, 262 for casy-1(wp78) retrograde, and 353 for ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) retrograde. Box plots with whiskers are shown. ****p<0.0001, unpaired t-test. (G) Run lengths of CASY-1 vesicles in distal axons in casy-1(wp78) and ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) (nontruncated axons) at L4. N = 1125 for casy-1(wp78) anterograde, 604 for ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) anterograde, 262 for casy-1(wp78) retrograde, and 353 for ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) retrograde. Box plots with whiskers are shown. ****p<0.0001, unpaired t-test.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Quantification of CASY-1 vesicle trafficking.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
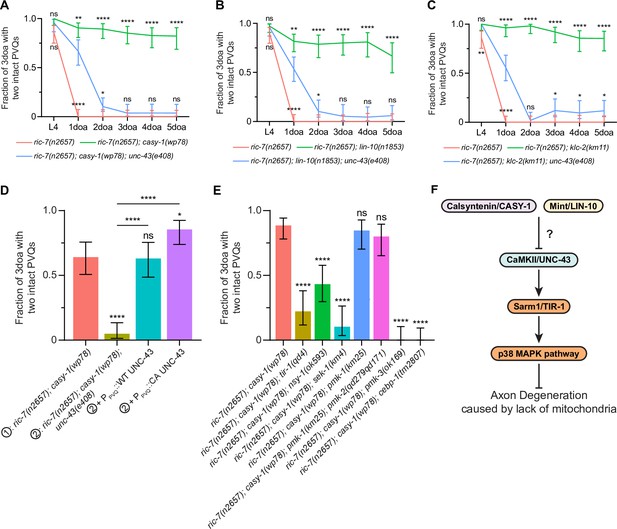
Loss of calsyntenin/CASY-1 or Mint/LIN-10 suppresses axon degeneration by activating the CaMKII-Sarm1-ASK1 MAPK pathway.
(A–C) Axon protection conferred by loss of calsyntenin/casy-1 requires CaMKII (A), Mint (B), and kinesin (C). Quantification of axon degeneration from L4 to 5-day-old adult (5doa). Number of animals: 45–77 (A), 33–75 (B), and 42–60 (C) animals. Graphs show proportion and 95% CI. **** p<0.0001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns, not significant, compared to the triple mutant (blue curve) at each timepoint, Fisher’s exact test. (D) CaMKII/unc-43 is required cell-autonomously to suppress axon degeneration in calsyntenin/casy-1 mutants. Quantification of axon degeneration in 3-day-old adult (3doa). Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) (N = 53), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78); unc-43(e408) (N = 61), and ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78); unc-43(e408) + PPVQ::WT UNC-43 (N = 46) or constitutively active (CA) UNC-43 (N = 55). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, *p<0.05, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) except where indicated, Fisher’s exact test. (E) The TIR-1-NSY-1-MAPK pathway is required to suppress axon degeneration in calsyntenin/casy-1 mutants. Suppression of protection against axon degeneration in ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) (N = 61) by tir-1(qd4) (N = 36), nsy-1(ok593) (N = 44), sek-1(km4) (N = 29), pmk-1(km25) (N = 39), pmk-1(km25); pmk-2(qd279qd171) (N = 40), pmk-3(ok169) (N = 33), and cebp-1(tm2807) (N = 37). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78), Fisher’s exact test. (F) Diagram of regulation of axon degeneration by the calsyntenin-Mint-CaMKII-Sarm1-ASK1 p38 MAPK pathway.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Epistatic analysis of mutants in the CASY-1-CaMKII-Sarm1-p38 MAPK pathway.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
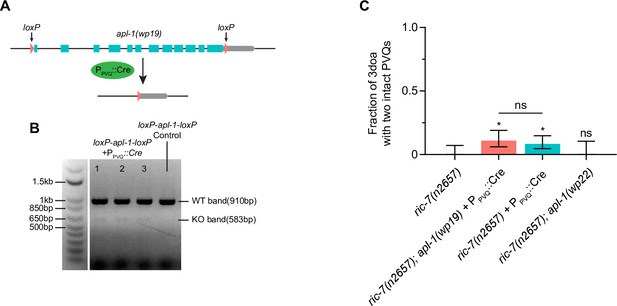
APL-1 mutations do not suppress spontaneous degeneration in ric-7(n2657).
(A) Schematic of the Cre-loxP method to knock out the entire apl-1 gene in PVQ. (B) Gel image showing the KO bands in three individual animals that express Cre in PVQ. The loxP control without Cre expression only shows the WT band. (C) Quantification of axon degeneration in ric-7(n2657) (N = 50), ric-7(n2657); apl-1(wp19)+ PPVQ::Cre (N = 91), ric-7(n2657) + PPVQ::Cre (N = 119), and ric-7(n2657); apl-1(wp22) (N = 33) 3-day-old adult (3doa). Mean and 95% CI are plotted. Bars show proportion and 95% CI. *p<0.05, ns, not significant, compared to ric-7(n2657) except where indicated, Fisher’s exact test.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Gel images of APL-1 genotyping. Three extrachromosomal array lines (oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; apl-1(wp19) X + sra-6p::nCre) were generated from one microinjection and genotyped for APL KO in PVQ. 15 worms from line 1, 8 worms from line 2, and 8 worms from line 3 were genotyped. The KO band (583 bp) can be seen in most worms from line 1 but not in worms from line 2 or line 3, probably due to expression levels and mosaicism. Line 1 was then integrated to generate XE2634(oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; apl-1(wp19) X; wpIs146[sra-6p::nCre + odr-1p::RFP]), which was used for analysis of axon degeneration. Control is XE2415(oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; apl-1(wp19) X). Blank is no worm input. The cropped image of control and last three worms from line 1 is shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 1B, with enhanced contrast.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Axon degeneration in apl-1 mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig5-figsupp1-data2-v1.xlsx
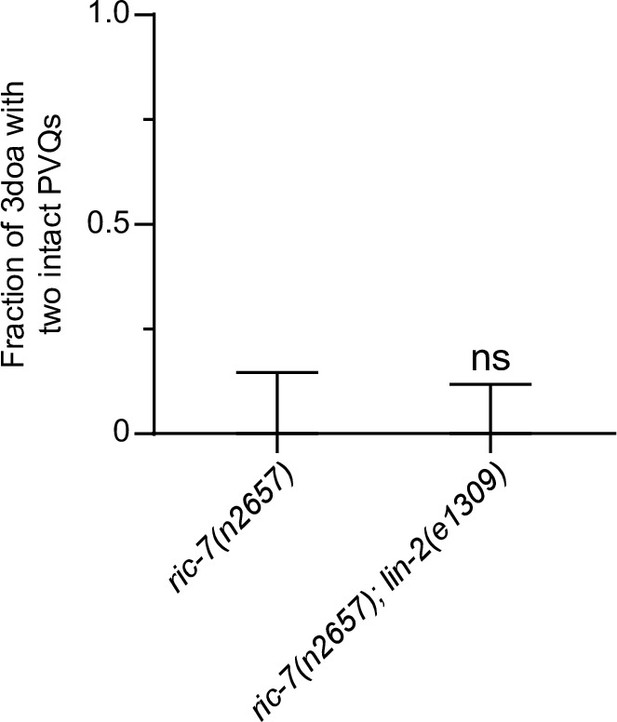
The lin-2 lof allele e1309 does not suppress PVQ degeneration in ric-7(n2657).
Quantification of suppression of axon degeneration. N = 25 for ric-7(n2657) and N = 32 for ric-7(n2657); lin-2(e1309). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Axon degeneration in the ric-7; lin-2 mutant.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig5-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
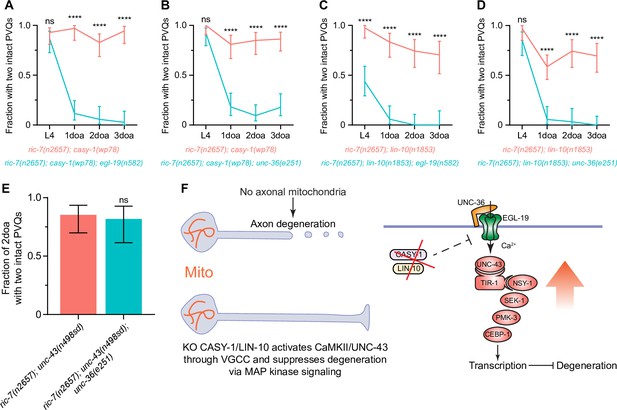
Loss of calsyntenin/CASY-1 or Mint/LIN-10 activates CaMKII/UNC-43 through the L-type voltage-gated calcium channel (VGCC) to suppress axon degeneration.
(A–D) Axon protection conferred by loss of calsyntenin/casy-1 or Mint/lin-10 requires VGCC subunit egl-19 (A, C) and VGCC subunit unc-36 (B, D). Quantification of axon degeneration from L4 to 3-day-old adult (3doa). Number of animals = 23–58. Graphs show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001 at each timepoint, ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test. (E) Axon protection conferred by activation of CaMKII does not requires VGCC subunit unc-36. Quantification of axon degeneration in 2-day-old adult (2doa). Genotypes and number of animals: ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd) (N = 34) and ric-7(n2657); unc-43(n498sd); unc-36(e251) (N = 22). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test. (F) Integrated model of how loss of calsyntenin/casy-1 and Mint/lin-10 suppresses axon degeneration caused by the absence of mitochondria.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Epistatic analysis between egl-19/unc-36 and casy-1/lin-10.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
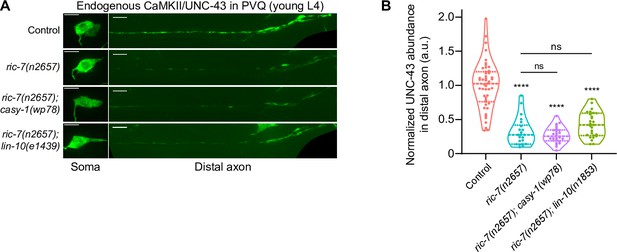
CaMKII/UNC-43 abundance in distal axons is not restored in ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) and ric-7(n2657); lin-10(e1439) animals.
(A) Images of native and tissue-specific fluorescence (NATF)-tagged CaMKII/UNC-43 in PVQ cell bodies and distal axons in L4 stage animals. Genotypes: control, ric-7(n2657), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78), and ric-7(n2657); lin-10(e1439). Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) Normalized NATF-tagged CaMKII/UNC-43 intensity (arbitrary units) in PVQ distal axons in control, ric-7(n2657), ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78), and ric-7(n2657); lin-10(e1439) animals at L4. Violin plots with median and quantiles are shown. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, compared to control except where indicated, one-way ANOVA, Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Endogenous CaMKII abundance in distal axon in control and suppressor mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.xlsx
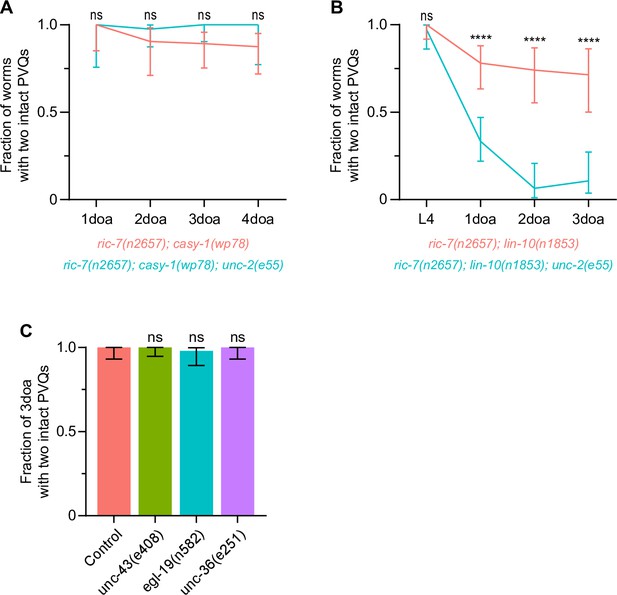
Voltage-gated calcium channel (VGCC) subunit unc-2 does not mediate axon protection, and loss of CaMKII/unc-43, VGCC subunit egl-19 or VGCC subunit unc-36 does not result in axon degeneration.
(A, B) Effect of the loss-of-function (lof) mutation, unc-2(e55), on the protection against degeneration in ric-7(n2657); casy-1(wp78) (N = 13–41) and ric-7(n2657); lin-10(n1853) (N = 21–51) animals. Graphs show proportion and 95% CI. ****p<0.0001, ns, not significant, Fisher’s exact test. (C) Quantification of axon degeneration in control (N = 52), unc-43(e408) (N = 69), egl-19(n582) (N = 49), unc-36(e251) (N = 52) 3-day-old adult (3doa). Bars show proportion and 95% CI. ns, not significant, compared to control, Fisher’s exact test.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Epistatic analysis between unc-2 and cays-1/lin-10 and degeneration in unc-43, egl-19 and unc-36 single mutants.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/73557/elife-73557-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v1.xlsx
Overexpressed CASY-1C accumulates on punctated structures in PVQ cell bodies and is at very low level in axons in klc-2(km11) mutants.
Same imaging conditions and contrasts. Scale bar = 10 μm.

Endogenous EGL-19 in PVQ is visualized by the NATF approach.
For the distal axon, the z projections are focused either on the axon before it joins the nerve ring or the nerve ring itself. White lines indicate the distal part of the PVQ axon or the axon bundles in the nerve ring. Asterisks indicate head neurons. Scale bar = 10 μm.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical compound, drug | Levamisole hydrochloride | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | Cat# sc-205730 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Proteinase K | Sigma | Cat# 3115879001 | |
| Other | Polybead Microspheres 0.05 μm | Polysciences | Cat# 08691 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Gateway LR Clonase II Enzyme mix | Invitrogen | Cat# 11791020 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | 1 kb DNA Ladder | Promega | Cat# G571A | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease V3 | IDT | Cat# 1081058 | |
| RNA | tracrRNA | IDT | Cat# 1072532 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ethyl methanesulfonate | Sigma | Cat# M0880 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit | QIAGEN | Cat# 27106 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase | NEB | Cat# M0530L | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nonidet P-40 | americanBIO | Cat# AB01425 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TWEEN 20 | Sigma | Cat# P5927 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Gelatin | MP Biomedicals | Cat# 901771 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | β-Mercaptoethanol | Sigma | Cat# M3148-25ML | |
| Chemical compound, drug | UltraPure phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol | Invitrogen | Cat# 15593031 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium acetate, 3 M solution, pH5.2 | americanBIO | Cat# AB13168-01000 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Nuclease-free water | americanBIO | Cat# AB02123-00500 | |
| Genetic reagent (Caenorhabditis elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V | CGC | XE2047 | |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V | This study | XE2046 | Control; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; wpEx369[sra-6p::mito::TagRFP+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2263 | Mito marker; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; wpEx369[sra-6p::mito::TagRFP+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2264 | Mito marker: Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II | This study | XE2209 | casy-1 lof suppressor; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(wp64) II | This study | XE2210 | unc-43 gof suppressor; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp78) II; wpEx370[sra-6p::casy-1c::GFP+ sra-6p::TagRFP+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2265 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | casy-1(wp78) II; wpEx370[sra-6p::casy-1c::GFP+ sra-6p::TagRFP+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2266 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(wp64) IV; wpEx369[sra-6p::mito::TagRFP+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2618 | Mito marker; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx371[sra-6p::mito::TagRFP+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2269 | Mito marker; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx374[sra-6p::casy-1a::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2274 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx375[sra-6p::casy-1b::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2275 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx376[sra-6p::casy-1c::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2276 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx379[sra-6p::casy-1a no KBS::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2277 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra::gfp], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx407[sra-6p::casy-1c_delta_extracellular::SL2::mCherry+ myo-2p::mCherry]; | This study | XE2355 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx380[sra-6p::casy-1 cytoplasmic domain::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2278 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; casy-1(wp60) II | This study | XE2374 | casy-1(wp60) suppressor; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx376[sra-6p::casy-1c::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2544 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; wpEx438[sra-6p::casy-1c mutated acidic region::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2547 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra::gfp], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60) II; wpEx431[sra-6p::casy-1(WW-AA)::SL2::mCherry+ myo-2p::mCherry] | This study | XE2504 | casy-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; wpEx381[sra-6p::unc-116::GFP::tomm-7+ sra-6p::mito::TagRFP+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2279 | Kinesin-mito chimera; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657), klc-2(km11) V | This study | XE2350 | klc-2 suppressor; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; klc-1(ok2609) IV | This study | XE2290 | klc-1 mutant; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; tir-1(qd4) III | This study | XE2308 | tir-1 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; tir-1(ok2859) III | This study | XE2309 | tir-1 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(tm718) II | This study | XE2294 | casy-1(tm718); Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2262 | casy-1(wp78) suppressor; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2260 | casy-1 KO; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp60); wpEx397[WRM0622dH03+ myo-2p::mCherry] | This study | XE2313 | casy-1 fosmid rescue; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(n498sd) IV | This study | XE2419 | unc-43(n498sd) suppressor; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(e408) IV | This study | XE2423 | unc-43 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2244 | casy-1 KO; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; lin-10(n1853) I | This study | XE2428 | lin-10 suppressor; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(e408) IV; casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2429 | unc-43 lof; casy-1; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2441 | PVQ::GFP1-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; lin-10(n1853) I; unc-43(e408) IV | This study | XE2508 | unc-43 lof; lin-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; lin-10(e1439) I | This study | XE2490 | lin-10 suppressor; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; unc-43(e408) IV | This study | XE2580 | unc-43 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(e408) IV; casy-1(wp78) II + wpEx430[sra-6p::unc-43g + myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2496 | WT unc-43 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(e408) IV; casy-1(wp78) II + wpEx432[sra-6p::unc-43g T284D::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2506 | Constitutively active unc-43 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; lin-10(e1439) I; unc-43(e408) IV | This study | XE2530 | unc-43 lof; lin-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-2(e55) X; casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2546 | unc-2; casy-1; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(wp106[unc-43::gfp11x7]) IV; wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] II | This study | XE2564 | Endogenous UNC-43; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(wp106[unc-43::gfp11x7]) IV; wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry], casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2565 | Endogenous UNC-43; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | unc-43(wp106[unc-43::gfp11x7]) IV; wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] II | This study | XE2567 | Endogenous UNC-43; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | ric-7(n2657) V; lin-10(e1439) I; unc-43(wp106[unc-43::gfp11x7]) IV; wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] II | This study | XE2605 | Endogenous UNC-43; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(wp106[unc-43::gfp11x7]) IV; wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] II; wpEx450[sra-6p::unc-116::tomm-7+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2649 | Endogenous UNC-43 with forced transport of mito; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | casy-1(syb3311[casy-1::gfp11x7]) II | This study | PHX3311 | casy-1::gfp11x7 KI; Generated by SunyBiotech |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657), klc-2(km11) V; unc-43(e408) | This study | XE2575 | unc-43 lof; klc-2; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | casy-1(syb3311[casy-1::gfp11x7]), wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] II | This study | XE2593 | Endogenous casy-1; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | casy-1(syb3311[casy-1::gfp11x7]), wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] II; ric-7(n2657) V | This study | XE2594 | Endogenous CASY-1; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | casy-1(syb3311[casy-1::gfp11x7]), wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] II; klc-2(km11) V | This study | XE2595 | Endogenous CASY-1; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-2(e55) X; lin-10(n1853) I | This study | XE2585 | unc-2 lof; lin-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | lin-10(wp109[lin-10::gfp11x7]) I; wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] II | This study | XE2586 | Endogenous LIN-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | lin-10(wp109[lin-10::gfp11x7]) I; wpIs141[sra-6p::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mcherry] casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2587 | Endogenous LIN-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; egl-19(n582) IV; casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2606 | egl-19 lof; casy-1; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; egl-19(n582) IV; lin-10(n1853) I | This study | XE2607 | egl-19 lof; lin-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-36(e251) III; casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2608 | unc-36 lof; casy-1; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-36(e251) III; lin-10(n1853) I | This study | XE2609 | unc-36 lof; lin-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(syb3311[casy-1::gfp11x7]) II | This study | XE2610 | casy-1 gfp11x7 KI; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; apl-1(wp19) X | This study | XE2415 | apl-1(wp19); Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; apl-1(wp19) X; wpIs146[sra-6p::nCre+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2634 | apl-1 KO; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; wpIs146[sra-6p::nCre+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2698 | Cre control; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; apl-1(wp22) X | This study | XE2489 | apl-1(wp22); Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; egl-19(n582) IV | This study | XE2640 | egl-19 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; unc-36(e251) III | This study | XE2641 | unc-36 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(n498sd) IV; unc-36(e251) III | This study | XE2648 | unc-36 lof; unc-43 gof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(n498sd) IV; tir-1(qd4) III | This study | XE2652 | tir-1 lof; unc-43 gof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(n498sd) IV; nsy-1(ok593) II | This study | XE2653 | nsy-1 lof; unc-43 gof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(n498sd), pmk1(km25) IV | This study | XE2655 | pmk-1 lof; unc-43 gof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp78) II; tir-1(qd4) III | This study | XE2656 | tir-1 lof; casy-1 KO; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp78), nsy-1(ok593) II | This study | XE2657 | nsy-1 lof; casy-1 KO; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp78) II; sek-1(km4) X | This study | XE2658 | sek-1 lof; casy-1 KO; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; casy-1(wp78) II; pmk-1(km25) IV | This study | XE2659 | pmk-3 lof; casy-1 KO; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; wpEx453[sra-6p::unc-43g T284D::SL2::mcherry+ myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2661 | Constitutively active unc-43 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; wpEx452[sra-6p::unc-43g + myo-2p::mcherry] | This study | XE2662 | Constitutively active unc-43 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; unc-116(rh24sb79) III | This study | XE2411 | unc-116 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; unc-116(rh24sb79) III; unc-43(n498sd) IV | This study | XE2717 | unc-116 lof; unc-43 gof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(wp106[unc-43::gfp11x7]) IV; wpEx475[sra-6p::unc-116::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mCherry] | This study | XE2752 | Endogenous UNC-43 with forced transport of mitochondria; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; unc-43(wp106[unc-43::gfp11x7]) IV; wpEx475[sra-6p::unc-116::GFP1−10+ myo-2p::mCherry] | This study | XE2753 | Endogenous UNC-43 with forced transport of mitochondria; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; miro-1(wy50180) IV; mtx-2(wy50266) III | This study | XE2839 | miro-1 lof; mtx-2 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; trak-1(gk571211) I | This study | XE2840 | trak-1 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; miro-1(tm1966) IV; miro-2(tm2933) X | This study | XE2349 | miro-1 lof; miro-2 lof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; mtx-2(wy50266) III; miro-1(wy50180) IV; casy-1(wp78) II | This study | XE2840 | miro-1 lof; mtx-2 lof; casy-1 KO; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; mtx-2(wy50266) III; miro-1(wy50180), unc-43(n498sd) IV; | This study | XE2878 | miro-1 lof; mtx-2 lof; unc-43 gof; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; wpEx499[sra-6p::nmat-1::SL2::mCherry+ myo-2p::mCherry] | This study | XE2910 | nmat-1 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP], ric-7(n2657) V; wpEx500[sra-6p::nmat-2::SL2::mCherry+ myo-2p::mCherry] | This study | XE2911 | nmat-2 OE; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; mtx-2(wy50266) III; miro-1(wy50180) IV; wpEx369[sra-6p::mito::TagRFP+ odr-1p::RFP] | This study | XE2883 | miro-1 lof; mtx-2 lof with mito marker; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans N2 hermaphrodite) | oyIs14[sra-6p::GFP] V; miro-1(tm1966) IV; miro-2(tm2933) X; wpEx501[sra-6p::mito::TagRFP+ myo-2p::mCherry] | This study | XE2912 | miro-1 lof; miro-2 lof with mito marker; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1a CDS::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD1 | PVQ::casy-1a; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1b CDS::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD2 | PVQ::casy-1b; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1c CDS::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD3 | PVQ::casy-1c; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1a no KBS CDS::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD4 | PVQ::casy-1a no KBS; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1 cytoplasmic CDS::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD5 | PVQ::casy-1 cytoplasmic domain; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1 CDS no ECD::SL2::mCherry | This study | pYW135 | PVQ::casy-1 with out ECD; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::mito::tagRFP | This study | pCD6 | PVQ::mito marker; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::unc-116::gfp::tomm7 | This study | pCD7 | PVQ::mito-gfp-chimera; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::unc-43g WT | This study | pCD8 | PVQ::WT unc-43 isoform g; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::unc-43g T286D::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD9 | PVQ::CA unc-43; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::GFP1-10 | This study | pCD10 | PVQ::GFP1-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::unc-116::tomm-7 | This study | pCD11 | PVQ::mito-chimera; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1c CDS-WWAA::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD12 | PVQ::casy-1c with the WW/AA mutation; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1c CDS::mutated acidic region::SL2::mCherry | This study | pYW184 | PVQ::casy-1c with mutated acidic residues; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::casy-1c::GFP | This study | pYW86 | PVQ::casy-1c::GFP; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::Cre | This study | pCD13 | PVQ::Cre; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pRF4::rol-6(su1006) | Mello et al., 1991 | pRF4 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::wt tir-1a::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD14 | PVQ::WT tir-1 isoform a; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::unc-116::gfp1-10 | This study | pCD15 | PVQ::kinesin-gfp1-10; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::nmat-1::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD27 | PVQ::nmat-1; Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | sra-6p::nmat-2::SL2::mCherry | This study | pCD28 | PVQ::nmat-2: Generated in the Hammarlund lab |
| Software, algorithm | Fiji 1.53c | NIH | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/download.html | |
| Software, algorithm | MetaMorph, version 7.10.2.240 | Molecular Devices | https://mdc.custhelp.com/app/products/detail/p/13 | |
| Software, algorithm | Prism, version 8 | GraphPad | https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Galaxy | Afgan et al., 2016 | https://usegalaxy.org/ | |
| Software, algorithm | MiModD | Maier and Baumeiste, 2016 | http://mimodd.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html | |
| Software, algorithm | Bowtie2-2.3.4.2 | Langmead and Salzberg, 2012 | http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/bowtie2/index.shtml | |
| Software, algorithm | ApE | M.Wayne Davis | https://jorgensen.biology.utah.edu/wayned/ape/ | |
| Software, algorithm | Jalview, version 2.11.1.2 | Waterhouse et al., 2009 | http://www.jalview.org/getdown/release/ |
List of key oligonucleotides for CRISPR.
| Name | Sequence | Source |
|---|---|---|
| crRNA(20 bp immediately 5' to the PAM sequence) | ||
| casy-1(wp78) 5' | gtgagggtggaaaatgattg | IDT |
| casy-1(wp78) 3' | tgtgatgtaatcaacagggt | IDT |
| unc-43-gfp11x7 | gagaaaaataggcataaaga | IDT |
| casy-1-gfp11x7#1 | agaacgagcgttcgttgaga | SunyBiotech |
| casy-1-gfp11x7#2 | tgtcgttggaggtcttgagt | SunyBiotech |
| lin-10-gfp11x7 | ataaacaatcaaatgtattg | IDT |
| Genotyping primers | ||
| casy-1(wp78) | f: gaataagaatgagaagacccgctgc; r1: ctccttgcagattgattattggcgc; r2: aaggagtgaaaaggacagtatgaagacg | IDT |
| unc-43-gfp11x7 | f: tcagaaacggagaagctcatacccg; r1: tcatgtagtaccatatggtcgcgtcc; r2: ccatatatctgagagaatgggacaag | IDT |
| casy-1-gfp11x7 | f: aaattccttcaggcatgttg; r: gaaggagtgaaaaggacagt | IDT |
| lin-10-gfp11x7 | f: tcgcagttgcacatgacaggtgag; r: attcacattagggcgcactttctgg | IDT |
| Others | ||
| 7XGFP11 template | tcaggaggccgtgaccacatggtccttcatgagtatgtaaa tgctgctgggattacaggtggctctggaggtagagatcatat ggttctccacgaatacgttaacgccgcaggcatcactggcgg tagtggaggacgcgaccatatggtactacatgaatatgtcaatg cagccggaataaccggagggtccggaggccgggatcacat ggtgctgcatgagtatgtgaacgcggcgggtataactggtggg tcgggcggacgagaccatatggtgcttcacgaatacgtaaacg cagctggcattactggcggatcaggtggcagggatcacatggt actccatgagtacgtgaacgctgctggaatcacaggcggtagcgg cggtcgggaccatatggtcctgcacgaatatgtcaatgctg ccggtatcaccggcggcaag | IDT |
| GFP1-10 template | atgtccaaaggagaagaactgtttacgggtgttgtgccaatttt ggttgaactcgatggtgatgtcaacggacataagttctcagtg agaggcgaaggagaaggtgacgccaccattggaaaattg actcttaaattcatctgtactactggtaaacttcctgtaccatgg ccgactctcgtaacaacgcttacgtacggagttcagtgcttttc gagatacccagaccatatgaaaagacatgacttttttaagtc ggctatgcctgaaggttacgtgcaagaaagaacaatttcgttc aaagatgatggaaaatataaaactagagcagttgttaaattt gaaggagatactttggttaaccgcattgaactgaaaggaacag attttaaagaagatggtaatattcttggacacaaactcgaatacaa ttttaatagtcataacgtatacatcactgctgataagcaaaagaac ggaattaaagcgaatttcacagtacgccataatgtagaagatgg cagtgttcaacttgccgaccattaccaacaaaacacccctattgg agacggtccggtacttcttcctgataatcactacctctcaacacaaa cagtcctgagcaaagatccaaatgaaaaataa | IDT |





