Retinoic acid signaling mediates peripheral cone photoreceptor survival in a mouse model of retina degeneration
Figures
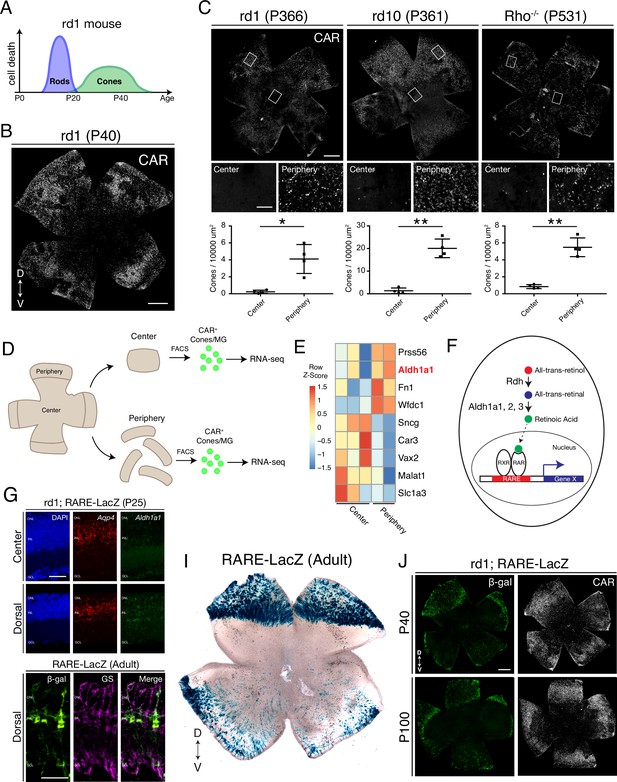
Cones in the rd1 mouse model survive long-term in regions with active RA signaling.
(A) Schematic of the timeline of rod and cone photoreceptor death in the rd1 mouse model. (B) rd1 retinal flatmount IHC against Cone Arrestin (CAR) at P40. (C) Retinal flatmount IHC against CAR for rd1, rd10, and Rho-/- mouse models at P366, P361, and P531, respectively (top images). Center and peripheral insets used for cone quantification (middle images). Number of CAR+ cones/10,000 um2 (n = 4 each) in the center and periphery for rd1 (Student’s two-tailed T test, p = 0.0206), rd10 (Student’s two-tailed T test, p = 0.0036), and Rho-/- (Student’s two-tailed T test, p = 0.0041). (D) Schematic of the strategy for cone-specific bulk RNA sequencing. Central and peripheral CD1 (non-degenerating strain) retinal tissues were collected, and CAR+ cones (and contaminating MG) were FACS purified for downstream RNA sequencing. (E) A heatmap representing relative expression levels of differentially expressed genes (adjusted P-value < 0.05) between central and peripheral retina. (F) Simplified schematic of the RA signaling pathway. (G) SABER smFISH against Aqp4, a pan MG marker, and Aldh1a1 in P25 rd1; RARE-LacZ dorsal and central retinal sections. (H) IHC against B-gal and GS, a MG marker, in adult RARE-LacZ retinal sections. (I) LacZ staining on adult RARE-LacZ flatmount. (J) IHC against B-gal and CAR in P40 (top row) and P100 (bottom row) rd1; RARE-LacZ flatmounts. D, Dorsal; V, Ventral; ONL, Outer Nuclear Layer; INL, Inner Nuclear Layer; GCL, Ganglion Cell Layer. Scale bars; 500 µm (B, C, J), 50 µm (G, H). All results are expressed as the Mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
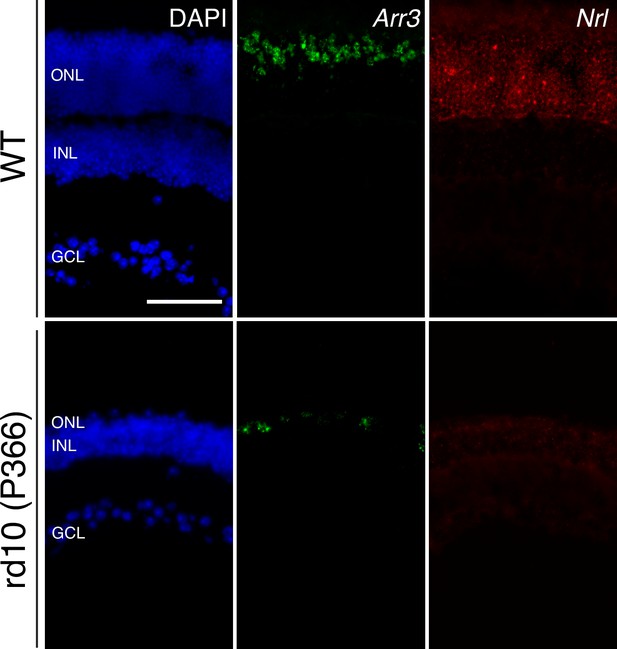
Long-term cone survival despite complete rod loss.
Representative images of smFISH against Arr3 (middle panels) and Nrl (right panels), cone and rod markers, respectively, in WT (top panels) and P366 rd10 (bottom panels) retinas, counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar; 50 µm.
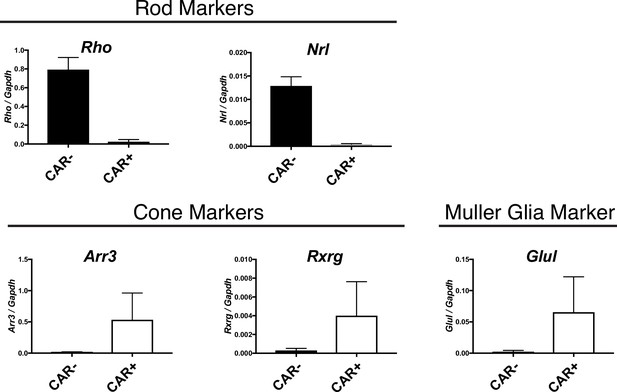
Cone and MG enrichment in CAR+ FACS-isolated cells.
Relative expression of rod (Rho, Nrl), cone (Arr3, Rxrg), and MG (Glul) markers in CAR+ and CAR- FACS-isolated populations from CD1 mice as detected by ddPCR.
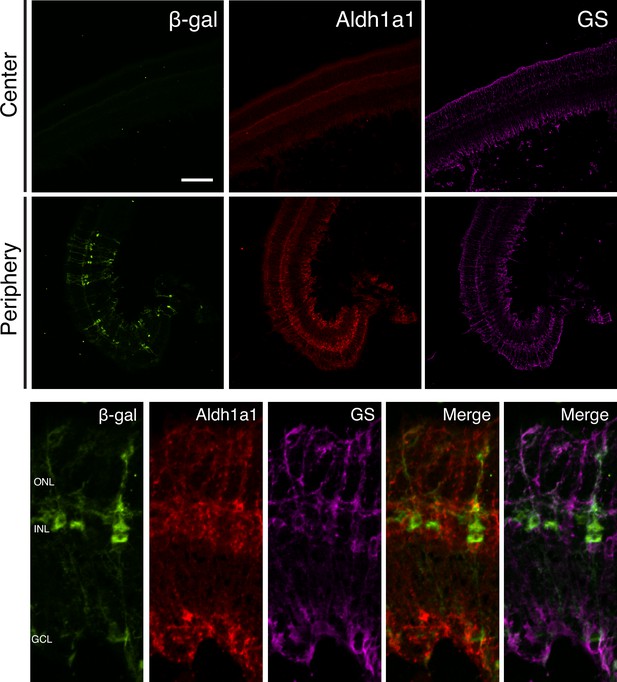
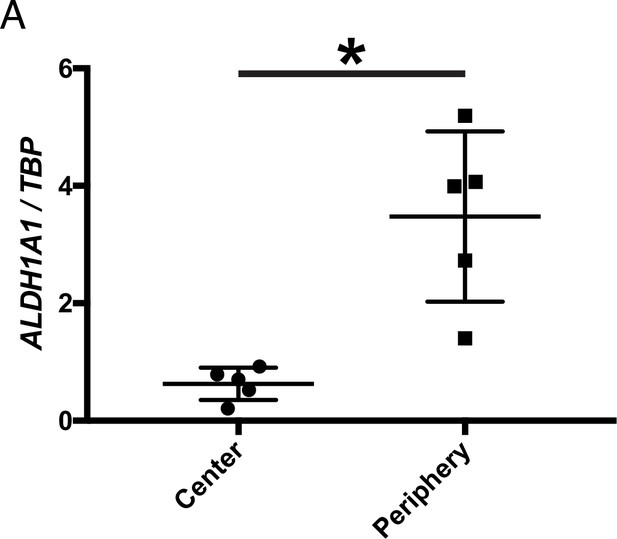
Aldh1a1 is expressed and RA signaling is active in peripheral MG.
IHC against B-gal, Aldh1a1, and GS in adult RARE-LacZ (non-degenerating) retinas showing the central (top panels) and peripheral (bottom panels) regions. Scale bar; 100 µm.
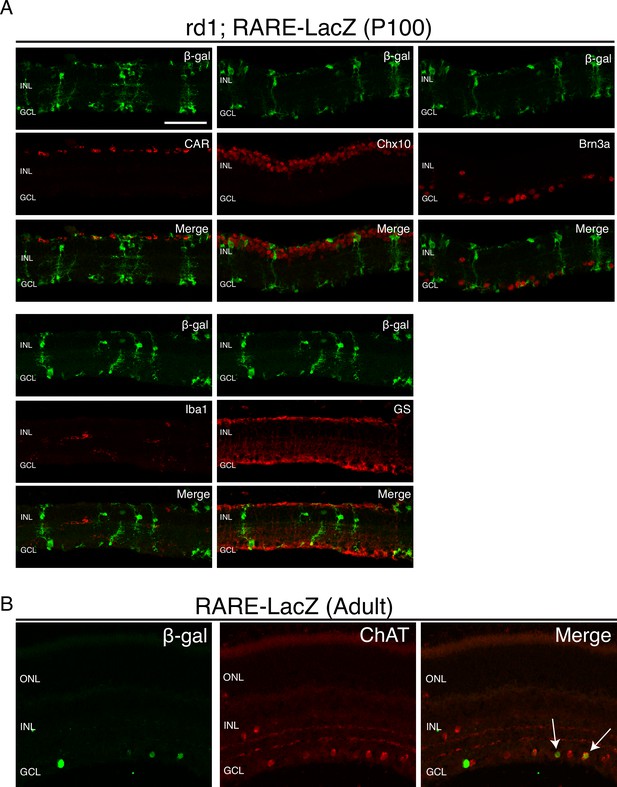
RA signaling activity is detected only in MG and a subset of ChAT+ amacrine cells.
IHC against B-gal and retina cell type specific markers, including CAR (cones), Chx10 (bipolar cells and MG), Brn3a (RGCs), Iba1 (microglia), GS (MG), and ChAT (amacrine cells) in P100 rd1; RARE-LacZ retinas. Scale bar; 50 µm.
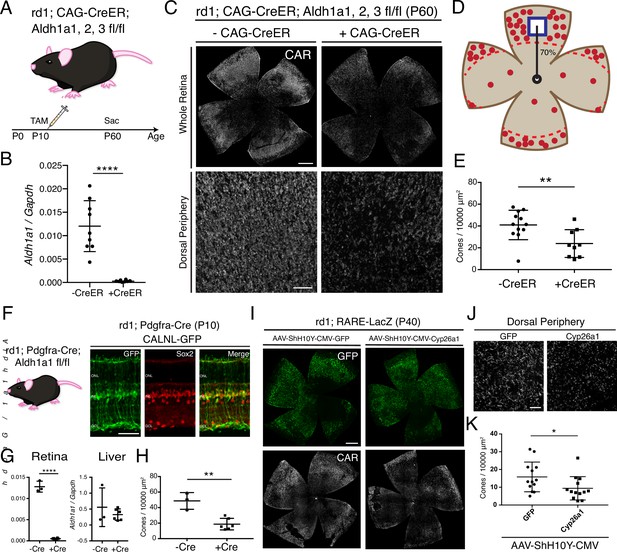
RA is necessary for peripheral cone survival.
(A) Schematic of the experimental design. Aldh Flox mice were injected with tamoxifen to create a conditional knockout (cKO) of the RA synthetic enzymes at P10, and the retinas were harvested at P60. (B) Relative expression level of Aldh1a1 in retinas with or without CAG-CreER (-Cre: n = 9,+ Cre: n = 8, Student’s two-tailed T test, p < 0.0001). (C) IHC against CAR in P60 Aldh Flox flatmounts showing the entire retina (top row) and the dorsal periphery (bottom row) with or without CAG-CreER. (D) Schematic of the area of cone quantification in the dorsal retina. Red dots represent surviving cones, and the blue box is the area of quantification. (E) Quantification of CAR+ cones in the sampled area of Aldh Flox retinas with or without CAG-CreER (-Cre: n = 12,+ Cre: n = 9, Student’s two-tailed T test, p = 0.0086). (F) Validation of MG-specific Aldh1a1 cKO mouse line. IHC against GFP and Sox2 in P10 rd1; Pdgfra-Cre retinas electroporated with a Cre-dependent plasmid, CALNL-GFP. (G) Relative expression level of Aldh1a1 in retinas and liver with or without Pdgfra-Cre (Retina: -Cre: n = 3,+ Cre: n = 6, Student’s two-tailed T test, p < 0.0001; Liver: -Cre: n = 3,+ Cre: n = 6, Student’s two-tailed T test, p = 0.3893). (H) Quantification of CAR+ cones in the sampled area of Aldh Flox retinas with or without Pdgfra-Cre (-Cre: n = 3,+ Cre: n = 6, Student’s two-tailed T test, p = 0.0016). (I) IHC against GFP (top row) and CAR (bottom row) in P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ flatmounts resulting from infection with AAV-ShH10Y-CMV-GFP (left column) or AAV-ShH10Y-CMV-Cyp26a1+ AAV-ShH10Y-CMV-GFP (right column). (J) Insets of the dorsal peripheral regions in both groups. (K) Quantification of CAR+ cones in the sampled area of infected retinas (GFP: n = 13, Cyp26a1: n = 13, Mann-Whitney test, p = 0.0441). ONL, Outer Nuclear Layer; INL, Inner Nuclear Layer; GCL, Ganglion Cell Layer. Scale bars; 500 µm (C top panels, I), 50 µm (F), 100 µm (C bottom panels, J). All results are expressed as the Mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.
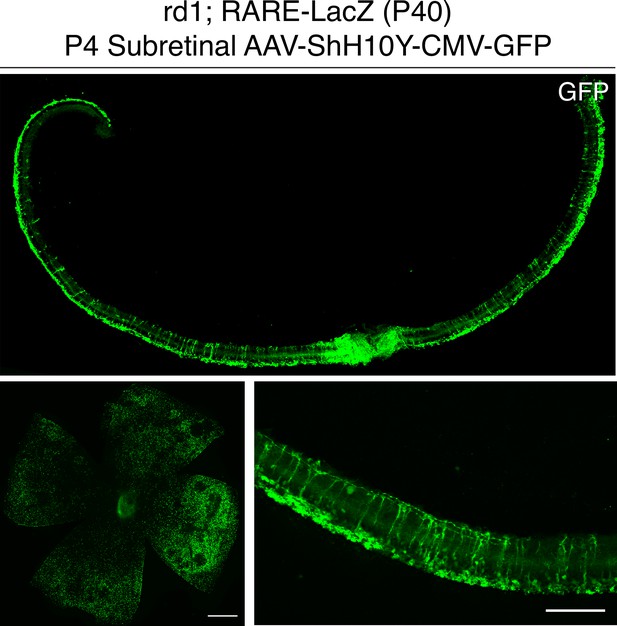
P4 subretinal injection of AAV-ShH10Y-CMV-GFP leads to retina-wide infection of MG and photoreceptors.
IHC against GFP in sections and flatmounts of P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ retinas infected with AAV-ShH10Y-CMV-GFP after P4 subretinal injection. Scale bars; 500 µm (left panel), 100 µm (right panel).
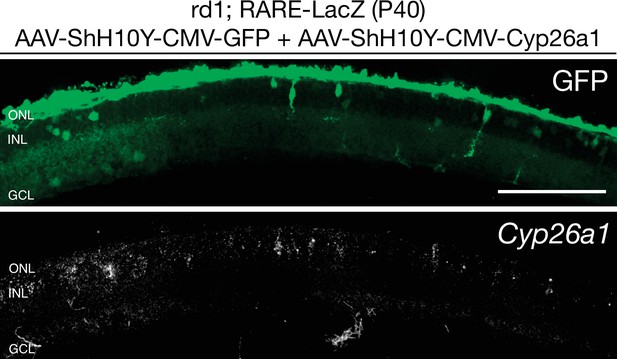
Cyp26a1 is overexpressed upon infection with AAV-ShH10Y-CMV-Cyp26a1.
smFISH against Cyp26a1 using SABER FISH in P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ retina sections infected with AAV-ShH10Y-CMV-Cyp26a1 and AAV-ShH10Y-CMV-GFP. Scale bar; 100 µm.
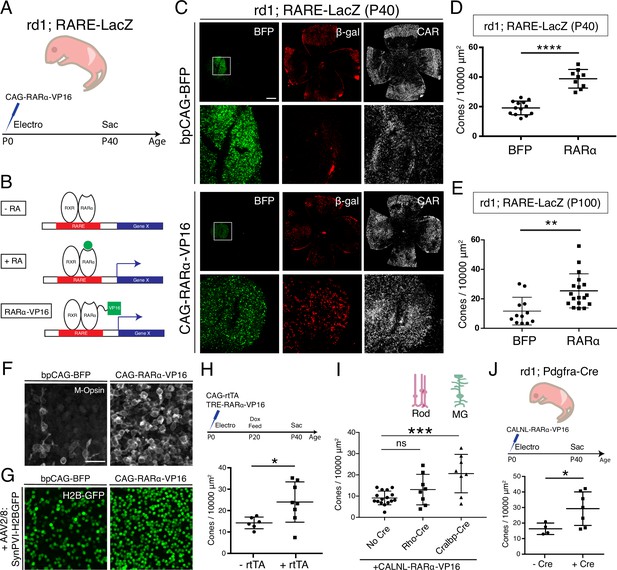
Constitutive RA signaling is sufficient for cone survival in the central retina.
(A) Schematic of the experimental design. Retinas of rd1; RARE-LacZ mice were electroporated with bpCAG-BFP with or without the CAG-RARa-VP16 construct at P0 or P1 and harvested at P40. (B) Schematic of RA-mediated transcriptional activation and RARa-VP16-mediated constitutive activation. Without RA, the RARa-RXR dimer, bound to genomic RAREs, repress downstream transcription. With RA, the dimer activates transcription of downstream genes, which includes the RA degradation enzyme, Cyp26a1, creating a strong negative feedback. With the introduction of RARa-VP16, transcription of genes downstream of RAREs is activated despite the lack of RA. (C) IHC against BFP (left column), B-gal (middle column), and CAR (right column) in P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ whole retinal flatmounts (top rows) and BFP+ insets (bottom rows) with overexpression of bpCAG-BFP with or without CAG-RARa-VP16. (D) Cone quantification in BFP+ central retina of P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ mice electroporated with bpCAG-BFP with or without CAG-RARa-VP16 (BFP: n = 13, RARa: n = 9, Student’s two-tailed T test, p < 0.0001). (E) Cone quantification in BFP+ central retina of P100 rd1; RARE-LacZ mice electroporated with bpCAG-BFP with or without CAG-RARa-VP16 (BFP: n = 12, RARa: n = 18, Mann-Whitney test, p = 0.0010). (F) Representative images of IHC against M-Opsin (Opn1mw) in BFP+ central retina of P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ mice electroporated with bpCAG-BFP with or without CAG-RARa-VP16. (G) Representative images of IHC against GFP in BFP+ central retina of P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ mice electroporated with bpCAG-BFP with or without CAG-RARa-VP16 and injected with AAV8-SynPVI-H2BGFP. (H) Schematic of the experimental design (top). Retinas of rd1; RARE-LacZ mice were electroporated with TRE-RARa-VP16 with or without CAG-rtTA. Doxycycline was administered from P20 – P40, at which time point the retinas were harvested. Cone quantification in BFP+ central retina of P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ mice electroporated with with TRE-RARa-VP16 with or without CAG-rtTA (-rtTA: n = 6, RARa: n = 8, Student’s two-tailed T test, p = 0.0311). (I) Cone quantification in BFP+ central retina of P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ mice electroporated with CALNL-RARa-VP16 with or without Rho-Cre or Cralbp-Cre (No Cre: n = 16, Rho: n = 8, Cralbp: n = 8, One-way ANOVA, F = 9.372, p = 0.0007; Tukey’s multiple comparison test, No Cre vs. Rho: p = 0.3111, No Cre vs. Cralbp: p = 0.0005, Cralbp vs. Rho: p = 0.0511). (J) Schematic of the experimental design (top). Retinas of rd1; Pdgfra-Cre mice were electroporated with CALNL-RARa-VP16 and harvested at P40. Cone quantification in BFP+ central retina of P40 rd1; Pdgfra-Cre electroporated with CALNL-RARa-VP16 (-Cre: n = 4,+ Cre: n = 7, Student’s two-tailed T test, p = 0.0488). Scale bars; 500 µm (C), 25 µm (F). All results are expressed as the Mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
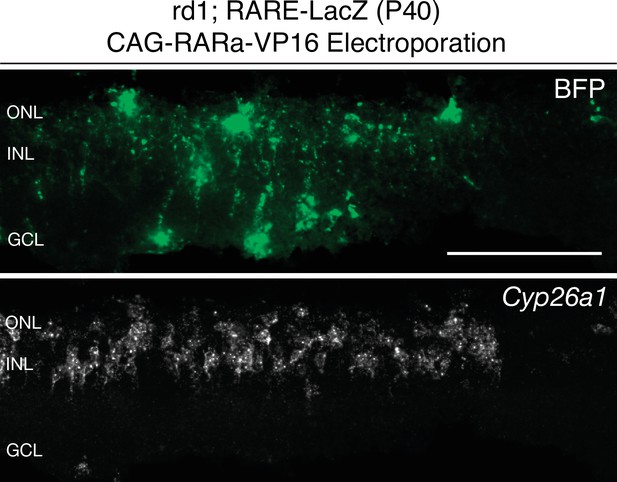
Cyp26a1 expression is upregulated upon RARa-VP16 overexpression.
smFISH against BFP and Cyp26a1 using SABER in P40 rd1; RARE-LacZ retina sections electroporated with CAG-RARa-VP16. Scale bar; 100 µm.
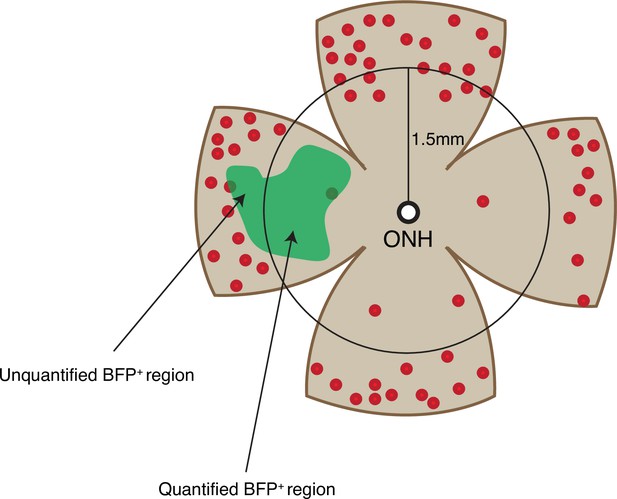
Cone quantification strategy in gain-of-function experiments.
Schematic of the area of cone quantification in the dorsal retina. Red dots represent surviving cones, and the green region is the area of electroporation. A circle with a radius of 1.5 mm was used to crop the central retina to ensure that the naturally surviving peripheral cones were excluded. Only the cones in the central BFP+ region were counted.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | RARE-LacZ | Jackson Laboratories | 008477 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | CAG-CreER | Jackson Laboratories | 004682 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Pdgfra-Cre | Jackson Laboratories | 013148 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Aldh1a1, 2, 3 Flox/Flox | PMCID: PMC5363406 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Rho-Cre | PMCID: PMC1764220 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Cralbp-Cre | PMCID: PMC1764220 | ||
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CAG-RARa-VP16 | This Study | Expression of RARa-VP16 from CAG promoter | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CALNL-RARa-VP16 | This Study | Cre-dependent expression of RARa-VP16 from CAG promoter | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | TRE-RARa-VP16 | This Study | Doxycycline-dependent expression of RARa-VP16 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | CAG-rtTA | This Study | Expression of rtTA from CAG promoter | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | AAV-CMV-Cyp26a1 | This Study | AAV expression plasmid encoding Cyp26a1 from CMV promoter | |
| Antibody | (Rabbit polyclonal) anti-Cone Arrestin | Millipore Sigma | AB15282 | (1:3000) |
| Antibody | (Chicken polyclonal) anti-B-galactosidase | Aves Labs | BGL1010 | (1:3000) |
| Antibody | (Goat polyclonal) anti-B-galactosidase | AbD Serotec | 4600–1409 | (1:3000) |
| Antibody | (Mouse monoclonal) anti-Brn3a | Millipore Sigma | MAB1585 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | (Rabbit polyclonal) anti-Iba1 | GeneTex | GTX100042 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | (Mouse monoclonal) anti-Glutamine Synthetase | Millipore Sigma | MAB302 | (1:3000) |
| Antibody | (Goat polyclonal) anti-ChAT | Millipore Sigma | AB144P | (1:500) |
| Antibody | (Chicken polyclonal) anti-GFP | Aves Labs | GFP-1020 | (1:3000) |
| Antibody | (Mouse monoclonal) anti-Sox2 | R&D Systems | AF2018 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | (Rabbit polyclonal) anti-Opn1mw | Millipore Sigma | AB5405 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | (Goat polyclonal) anti-Aldh1a1 | Abcam | 9,883 | (1:1000) |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mm Arr3 RNAscope Probe | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | 486,551 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mm Nrl RNAscope Probe | Advanced Cell Diagnostics | 475,011 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Genotyping and ddPCR primers and oligonucleotide sequences for SABER FISH probes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/76389/elife-76389-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/76389/elife-76389-transrepform1-v1.pdf