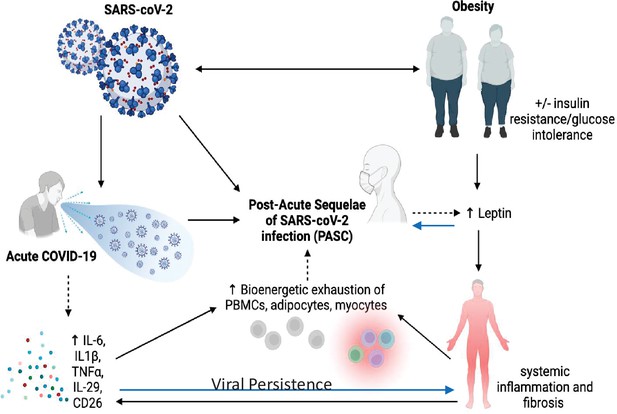
Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A metabolic perspective
Figures
Tables
Table 1
Risk of new onset metabolic dysfunction (T2D/hyperglycemia for post-SARS-CoV-2 patients).
| Author | Study type | HR or OR (95% CI), comments |
|---|---|---|
| Aminian et al | Longitudinal COVID + 2800 pts | 1.39 (1.13–1.71), for future Dx testing |
| Leong et al | Mendelian Random UKBio | 1.14 (1.07–1.21), BMI and COVID-19 + severe |
| Xie et al | Cohort Study 180,000 VA Records | 1.40 (1.36–1.44), incident DM of COVID-19+ |
| Fernández-de-Las-Peñas | Case Control 299 | 1.06 (0.92–1.24), not significant DM risk |
| Barrett et al. | Two Retrospective Cohorts Record IQVIA, HealthVerity Covid+ | 2.66 (1.98–356) for DM (claims data)*1.31 (1.20–1.44) for DM (claims data) |
| Montefusco | Prospective 551 pts hospitalized | 46% of COVID-19 + pts hyperglyc at 2 months |
-
*
CDC MMWR report.
Download links
A two-part list of links to download the article, or parts of the article, in various formats.
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A metabolic perspective
eLife 11:e78200.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.78200