Contribution of Trp63CreERT2-labeled cells to alveolar regeneration is independent of tuft cells
Figures
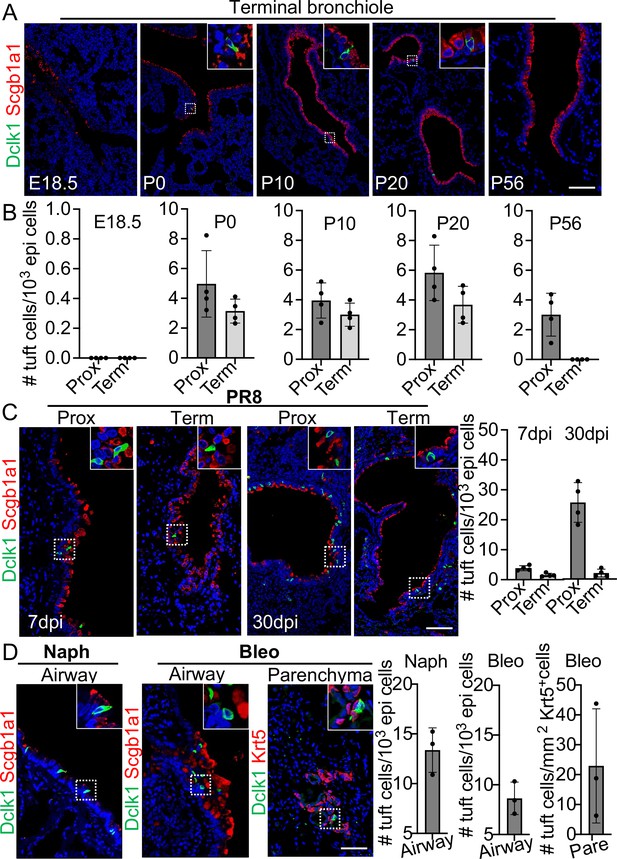
Tuft cells in homeostasis and their expansion in response to severe injuries.
(A) Tuft cells are present in the distal airways at P0, P10, P20 but not P56. n=4 for each group. (B) Quantification of tuft cells from panel (A). (C) Tuft cells expand in the large airway and are ectopically present in the terminal airways following viral infection. (D) Tuft cells expand in the airways following naphthalene and bleomycin challenge and are ectopically present in parenchyma following bleomycin challenge. Scale bars, 50 μm.
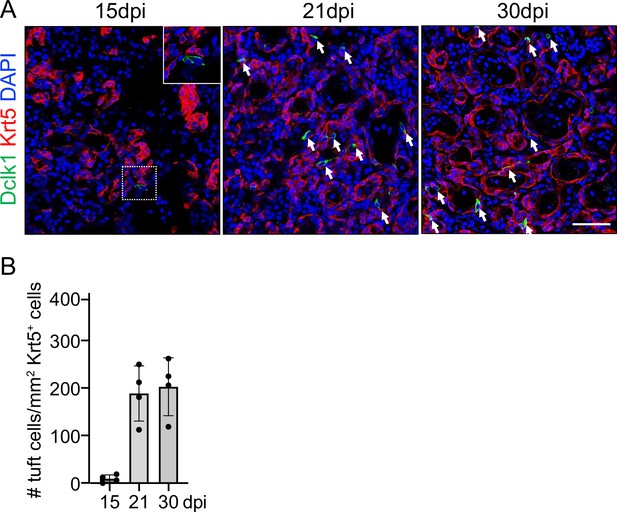
Ectopic tuft cells appear after viral infection.
(A) Time course analysis of ectopic tuft cells in the lung parenchyma following viral infection. (B) Quantification of tuft cells in ectopic basal cells areas of lung parenchyma. Scale bars, 50 μm.
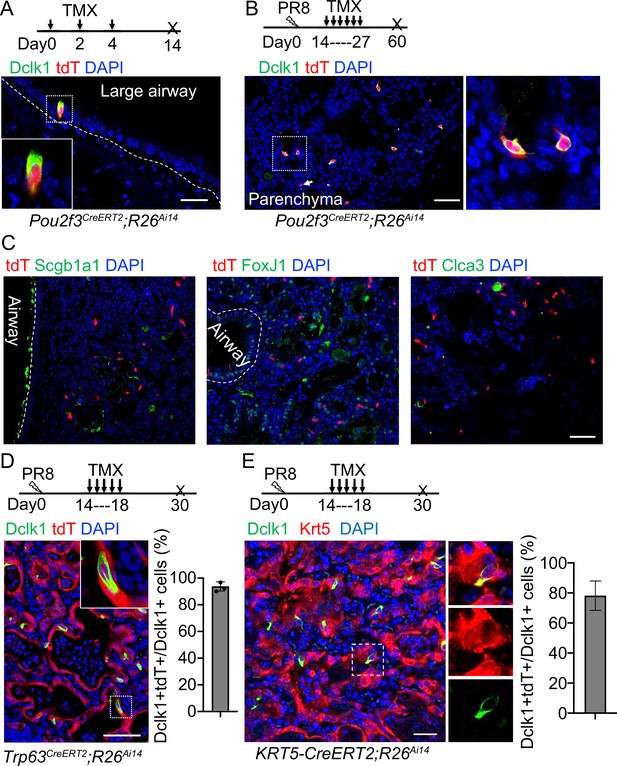
Tuft cells in the parenchyma are derived from ectopic basal cells (EBCs) following H1N1 PR8 viral infection.
(A) Pou2f3CreERT2;R26Ai14 mouse line specifically labels Dclk1+ tuft cells in the large airways at homeostasis. (B) Lineage tracing of Pou2f3+ cells in the parenchyma after PR8 virus infection. Arrow indicates a tdT+Dclk1- cell. (C) Lineage labeled tuft cells do not contribute to other cell lineages, including Scgb1a1+ club cells, FoxJ1+ ciliated cells and Clca3+ goblet cells. (D) Lineage tracing confirms that tuft cells are derived from EBCs in the lung parenchyma of Trp63CreERT2;R26Ai14 mice following PR8 infection. (E) Lineage tracing shows about 80% of tuft cells are derived from EBCs in the lung parenchyma of KRT5-CreERT2;R26Ai14 mice following PR8 infection. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. Scale bars, 20 μm (A) and 50 μm (B to G).
Tuft cells in the lung parenchyma are derived from ectopic basal cells (EBCs).
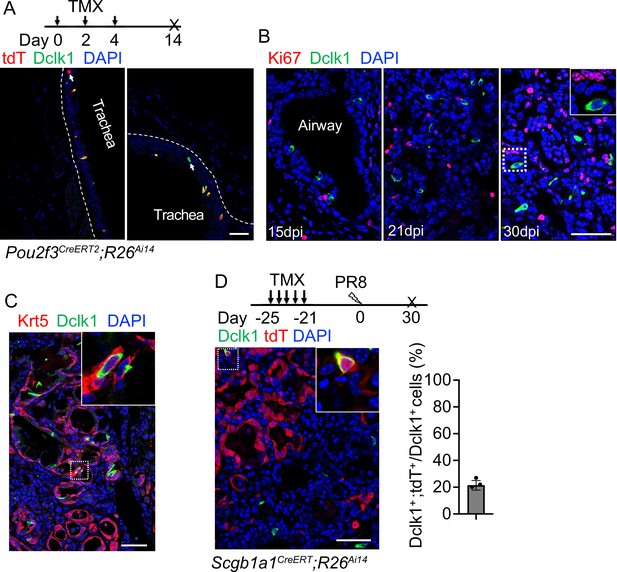
(A) Lineage tracing shows heterogeneity of tuft cells in the trachea of Pou2f3CreERT2;R26Ai14 mice. Note that some lineage labeled cells do not express Dclk1 (arrowhead in left panel). (B) Tuft cells do not proliferate when examined at days 15, 21, and 30 post-infection. (C) ~5% of tuft cells within EBCs co-express Krt5 and Dclk1. (D) Lineage labeled cells contribute to ~21% ectopic tuft cells in the lung parenchyma of Scgb1a1CreERT;R26Ai14 mice. Scale bars, 50 μm.
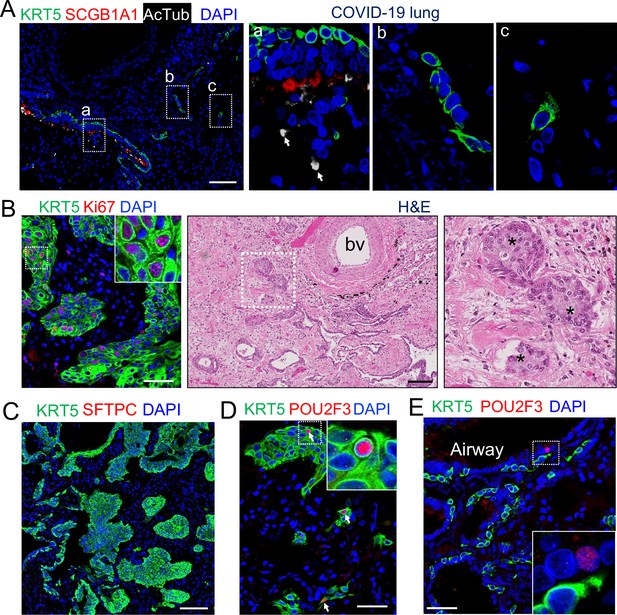
EBCs likely give rise to tuft cells in the parenchyma of COVID-19 lungs.
(A) SARS-CoV-2 infection causes the loss of club and ciliated cells (arrows in a), exposing the underlying basal cells (B) in the small airways. Note the detached basal cells (C). (B) EBCs proliferate in the parenchyma of COVID-19 lungs. H&E staining shows the presence of EBC clusters in COVID-19 lungs. (C) Representative clusters of EBCs are present in COVID-19 lungs. (D) Tuft cells within EBCs express both KRT5 and the tuft cell marker POU2F3. (E) Solitary tuft cells without KRT5 expression are present in the airways of COVID-19 lung. Abbreviation: bv, blood vessel. Scale bars, 100 μm (A, B and C) and 50 μm (D and E).
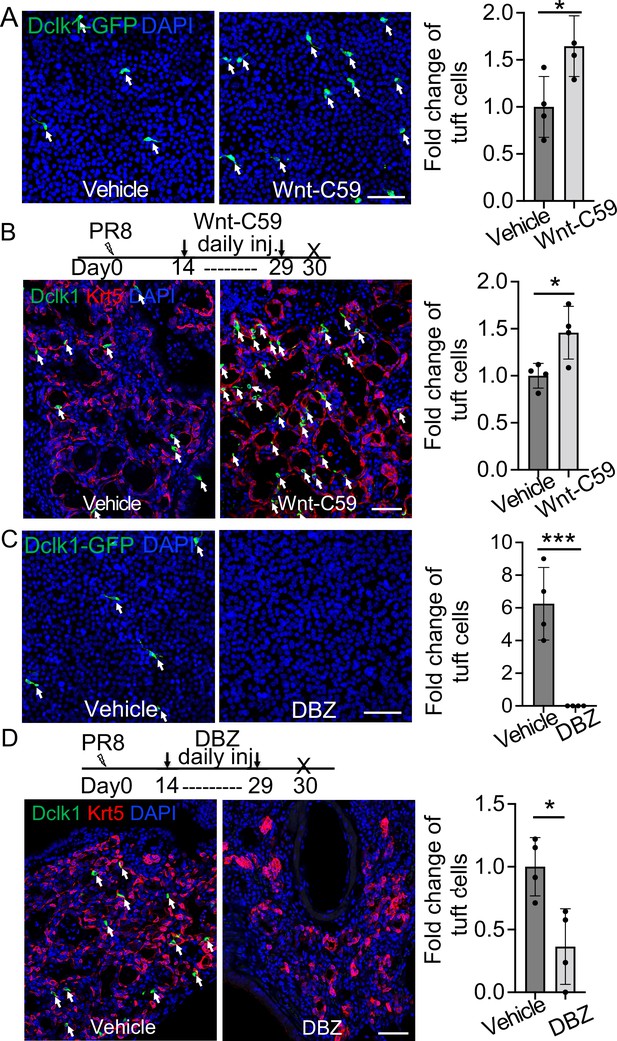
Wnt inhibition promotes EBC differentiation into tuft cells while Notch inhibition has an opposite effect.
(A) Treatment with the WNT signaling inhibitor Wnt-C59 promotes tuft cell differentiation of Dclk1-GFP basal cells in ALI culture. (B) Wnt-C59 treatment increases the number of tuft cells in the lung parenchyma following viral infection. (C) Treatment with the Notch signaling inhibitor DBZ completely blocks tuft cell differentiation of Dclk1-GFP basal cells in ALI culture. (D) Daily injection of DBZ following PR8 infection dramatically reduces tuft cell derivation in the lung parenchyma. n=4 per group. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001; statistical analysis by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars, 50 μm.
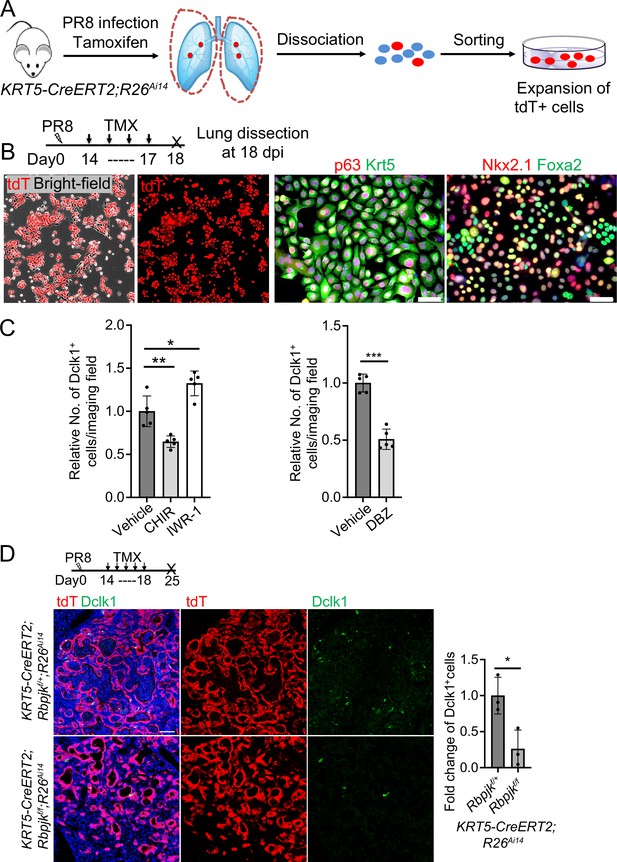
Isolation and expansion of Krt5+ EBCs from the lungs of Trp63CreERT2; R26Ai14 mice that were infected with PR8 virus.
(A) Schematic illustration depicts the methodology. (B) Lineage labeled EBCs are expanded and characterized. (C) Quantification of Dclk1+ cells derived from EBCs at various conditions (Vehicle, 2 μM CHIR99021, 5 μM IWR-1, and 2 μM DBZ) in air-liquid interface (ALI) culture. (D) Ablation of Notch effector Rbpjk in EBCs blocks differentiation of tuft cells from EBCs. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. * p<0.05, ** pP<0.01, *** pP<0.001; statistical analysis by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars, 50 μm.
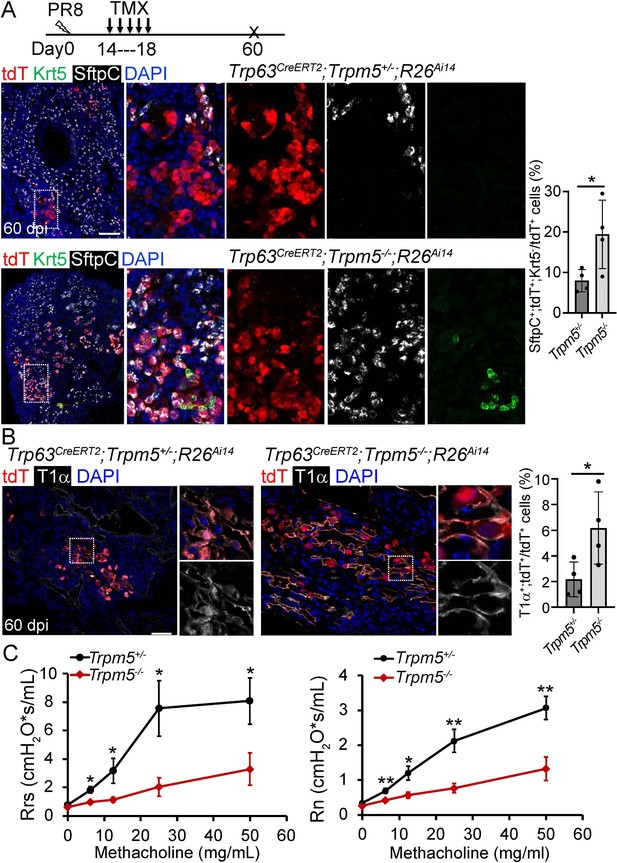
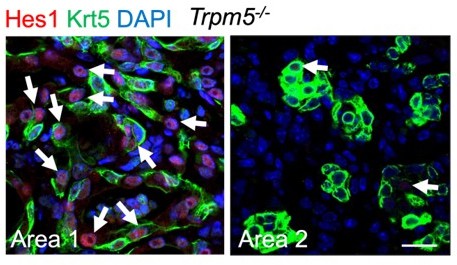
Increased generation of Trp63CreERT2 labeled alveolar epithelium in Trpm5 null mutants following PR8 infection.
(A) Trpm5 deletion leads to the increased presence of tdT+SftpC+Krt5- cells in the lung parenchyma at 60 dpi. (B) Increased tdT-labeled AT1 cells in the mutant lungs as compared to controls at 60 dpi. (C) Whole lung airway resistance improves in Trpm5-/- mice following viral infection (left panel). Central airway resistance is also reduced following viral infection (right panel). n=7 for WT group, n=9 for Trpm5-/- group. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. *p<0.05, **p<0.01; statistical analysis by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars, 100 μm (A), 20 µm (B).
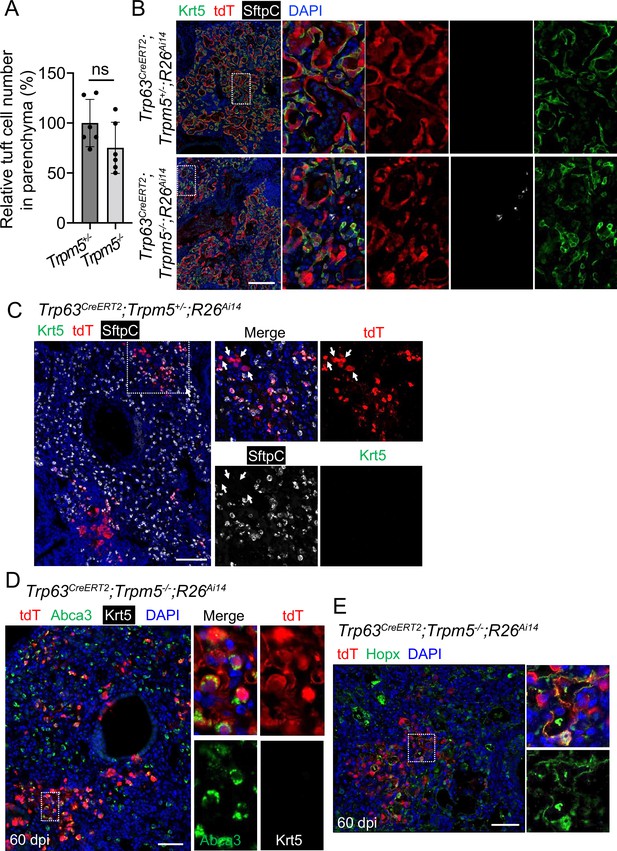
Increased Trp63CreERT2 labeled AT1 and AT2 cells in virus-infected Trpm5-/- mice.
(A) Quantification of tuft cells within EBCs areas established in the lung parenchyma of Trpm5+/- and Trpm5-/- mutants at 30 dpi. (B) Extensive Krt5+ EBCs in the lung parenchyma of controls (Trp63CreERT2;Trpm5+/-;R26Ai14) and mutants (Trp63CreERT2;Trpm5-/-;R26Ai14) at 60 dpi. (C) Clusters of lineage-labeled AT2 cells. Note some lineage-labeled cells are SftpC- (arrowheads). Also note the same image in Figure 5A. (D) Staining with Abca3 confirms the presence of lineage labeled AT2 cells in Trp63CreERT2;Trpm5-/-;R26Ai14 mutants at 60 dpi. (E) Lineage tracing confirms that the presence of lineage labeled AT1 (Hopx+) in the parenchyma of Trp63CreERT2;Trpm5-/-;R26Ai14 mutants. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. ns: not significant; statistical analysis by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bars, 100 µm (B), 50 μm (C and D) and 20 µm (E).
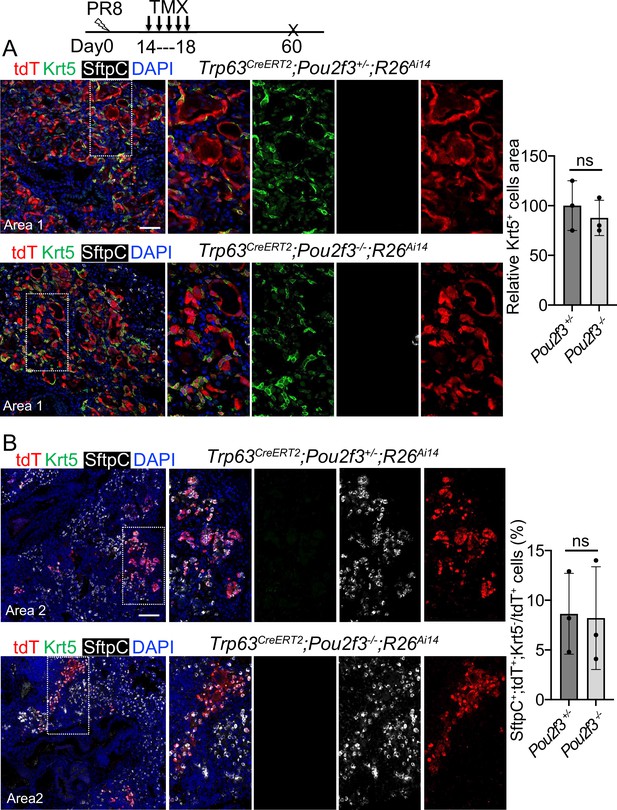
A complete loss of tuft cell does not increase the generation of Trp63CreERT2 labeled alveolar cells following PR8 infection.
(A) Extensive Krt5+SftpC- EBCs are present in the parenchyma of control (Trp63CreERT2;Pou2f3+/-;R26Ai14) and mutant (Trp63CreERT2;Pou2f3-/-;R26Ai14) lungs when examined at 60 dpi following PR8 infection. (B) Representative areas show Trp63CreERT2 labeled AT2 cells in both control and mutant lungs. Ns: not significant; statistical analysis by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Scale bar, 50 μm (A), 100 µm (B).
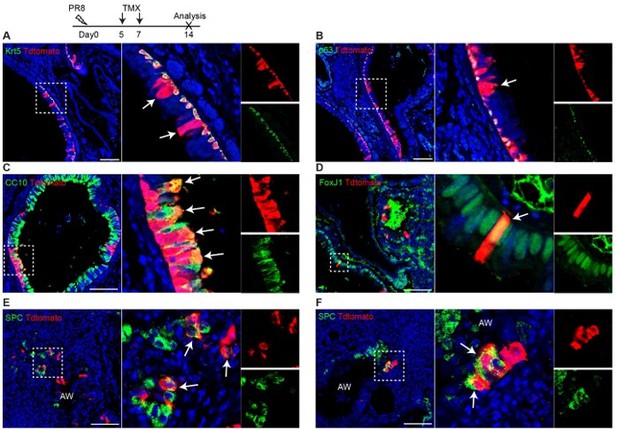
Trp63-CreERT2 lineage labeled cells in the airways but not alveoli when Tamoxifen was induced at day 5 and 7 after PR8 H1N1 viral infection. Trp63-CreERT2;R26-tdT mice were infected with PR8 at 250 pfu and Tmx were delivered at a dose of 0.25 mg/g bodyweight by oral gavage. Lung samples were collected and analyzed at 14 dpi. Stained antibodies are as indicated. Scale bar: 100 µm.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Trp63CreERT2 | Lee et al., 2014b; Lee et al., 2014a PMID:25210499 | Dr. Jianming Xu (Baylor College of Medicine) | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Tg(KRT5-CreERT2) | Rock et al., 2009 PMID:19625615 | Dr. Brigid Hogan (Duke University); A transgenic mouse strain in which human KRT5 promoter drives CreERT2 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Scgb1a1CreERT | Rawlins et al., 2009 PMID:19497281 | MGI:3849566 | Dr. Brigid Hogan (Duke University) |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Pou2f3CreERT2 | McGinty et al., 2020 PMID:32160525 | MGI:6755141 | Dr. Jakob von Moltke (University of Washington) |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Tg(Trpm5-GFP) | Clapp et al., 2006 PMID:16573824 | 16573824 | Dr. Tod Clapp (Colorado State University) |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Trpm5-/- | Damak et al., 2006 PMID:16436689 | Dr. Robert Margolskee (Mount Sinai) | |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Pou2f3-/- | Matsumoto et al., 2011 PMID:21572433 | MGI:5140071 | Dr. Keiko Abe (The University of Tokyo) |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | Rbpjkloxp/loxp | Han et al., 2002 PMID:12039915 | MGI:3583755 | Dr. Tasuku Honjo (Kyoto University) |
| Genetic reagent (Mus musculus) | B6.Cg-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm14(CAG-tdTomato)Hze/J | Madisen et al., 2010 PMID:20023653 | MGI: 4436847 | Jackson Laboratories (#007914, R26Ai14) |
| Antibody | Anti-Dclk1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab31704 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | Anti-CC10 (E-11) (Mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc-365992 | 1:200; Scgb1a1 |
| Antibody | Anti-SCGB1A1 (Rat monoclonal) | R&D | MAB4218 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-Krt5 (Chicken polyclonal) | BioLegend | 905901 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-Krt5 (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab17130 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-Krt5 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab53121 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-p63 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Genetex | GTX102425 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | Anti-p63 (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab735 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | Anti-Acetylated tubulin (Mouse monoclonal) | Sigma | T7451 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-TTF1 (Rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | ab76013 | 1:500; Nkx2.1 |
| Antibody | Anti-FOXA2 (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | ab60721 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | Anti-POU2F3 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Sigma | HPA019652 | 1:200 |
| Antibody | Anti-ABCA3 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Seven Hills | WRAB-70565 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Anti-Hop (E-1) (Mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz | sc-398703 | 1:100; Hopx |
| Antibody | Anti- Prosurfactant Protein C (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab90716 | 1:500; SftpC |
| Antibody | Anti-Pro-SP-C (Rabbit polyclonal) | Seven Hills | WRAB-9337 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Anti-tdTomato (Goat polyclonal) | Biorbyt | orb182397 | 1:1000 |
| Antibody | Anti-Pdpn (Syrian hamster monoclonal) | DSHB | 8.1.1 c | 1:500; T1α |
| Antibody | Anti- Green Fluorescent Protein (Chicken polyclonal) | Fisher (Aves Lab) | GFP1020 | 1:200; GFP |
| Antibody | Anti-Ki-67 (Rat monoclonal) | Invitrogen | 14-5698-82 | 1:50 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 488 Donkey Anti-Chicken (Donkey polyclonal) | Jackson Immuno Research | 703-546-155 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 488 Donkey Anti-Mouse (Donkey polyclonal) | Jackson Immuno Research | 715-545-151 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Cy5 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Rat IgG (Donkey polyclonal) | Jackson Immuno Research | 712-175-150 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Cy3 AffiniPure Donkey Anti-Mouse IgM (Donkey polyclonal) | Jackson Immuno Research | 715-165-140 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 488 Donkey anti-Rat IgG (Donkey polyclonal) | Invitrogen | A21208 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 555 Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG (Donkey polyclonal) | Invitrogen | A31572 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 555 Donkey anti-Goat IgG (Donkey polyclonal) | Invitrogen | A21432 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 555 Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (Donkey polyclonal) | Invitrogen | A31570 | 1:500 |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 647 Goat anti-Chicken IgG (Goat polyclonal) | Invitrogen | A21449 | 1:500 |
| Chemical compound, drug | DBZ | Tocris | 4489 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Wnt-C59 | Tocris | 5148 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | CHIR99021 | Tocris | 4423 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | IWR-1 | Tocris | 3532 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dorsomorphin | Sigma | P5499 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Verteporfin | Sigma | SML0534 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | GDC-0449 | Selleckchem | S1082 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Dexamethasone | Sigma | D2915 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 3-Isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) | Sigma | I5879 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant Il-6 | Peprotech | 200–06 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant Il-4 | Peprotech | 200–13 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant Murine Il-13 | Peprotech | 210–13 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 8-Bromoadenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (8-Br-cAMP) | Sigma | B5386 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bleomycin | Fresenius Kabi | 63323013610 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Naphthalene | Sigma-Aldrich | 84679 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Small Airway Epithelial Cell Medium | Lonza | CC-3118 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Small Airway Epithelial Cell Medium | Promocell medium | C-21170 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Complete Pneumacult-ALI medium | StemCell Technology | 05001 | |
| Other | Antigen unmasking solution, Citric acid based | Vector Laboratories | H-3300 | Antigen retrieval buffer for immunostaining |
| Other | Normal donkey serum | Jackson Immuno Research | 017-000-121 | Blocking reagent for immunostaining |