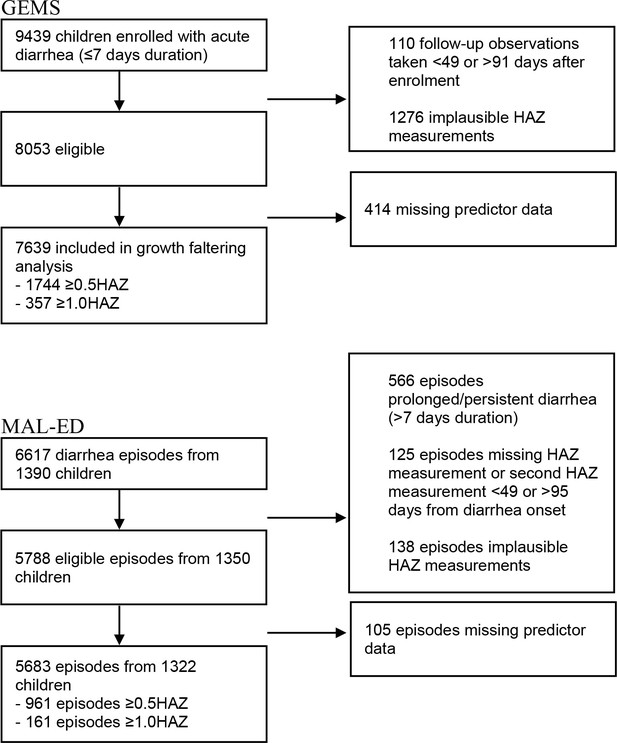
Derivation and external validation of clinical prediction rules identifying children at risk of linear growth faltering
Figures
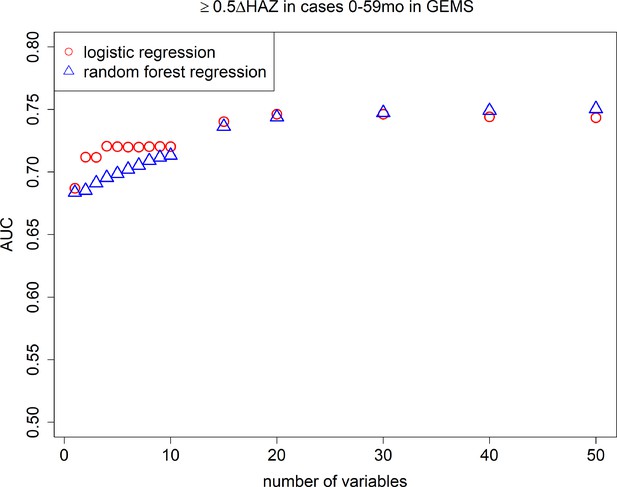
Area under the curves (AUCs).
Cross-validated AUC achieved by number of predictive variables included in random forest regression and logistic regression models predicting growth faltering (≥0.5 decrease in height-for-age z-score [HAZ]) in children 0–59 months of age presenting with diarrhea in the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS).
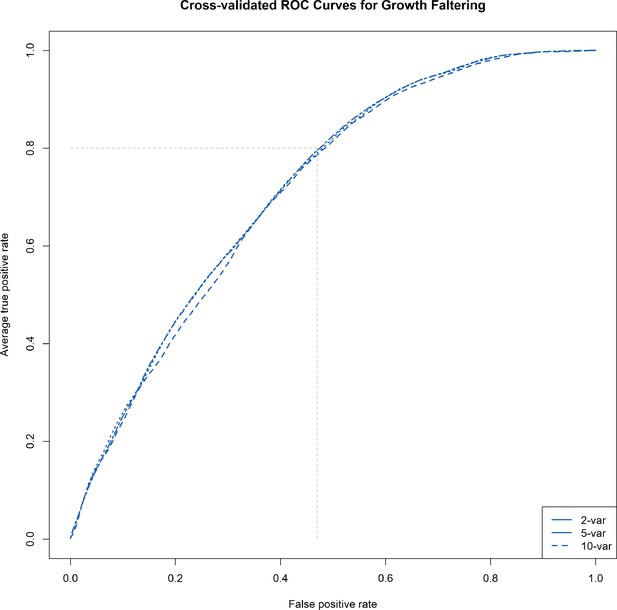
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves: average ROC curves from the cross-validated logistic regression models predicting growth faltering with 2, 5, and 10 predictors.
The faded dashed lines represent specificity (1 − false positive rate) achievable with a sensitivity (true positive rate) of 0.80 for prediction of the outcome.
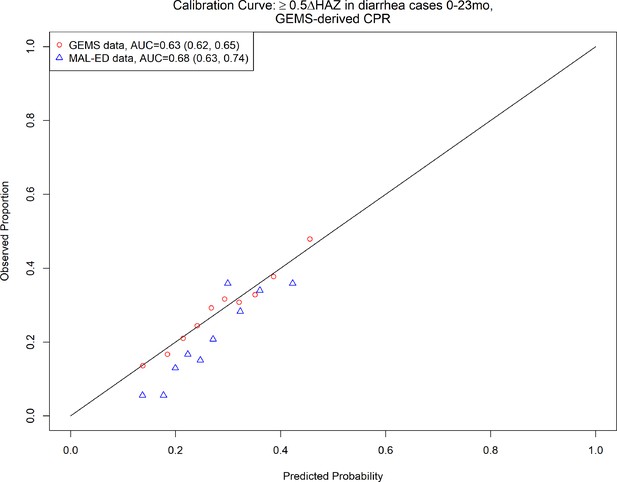
2-Variable clinical prediction rule (CPR) for growth faltering: calibration curve and discriminative ability of 2-varaible (age, height-for-age z-score [HAZ] at enrollment) model predicting growth faltering (≥0.5 decrease in HAZ) in children presenting for acute diarrhea in LMICs.
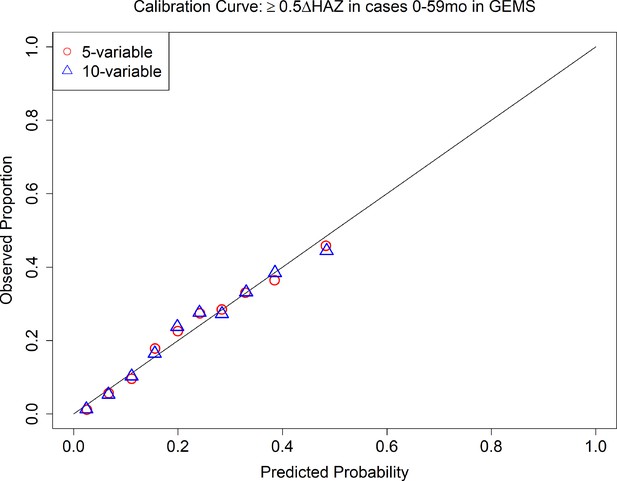
Calibration curve of 5- and 10-variable model predicting growth faltering (≥0.5 decrease in height-for-age z-score [HAZ]) in children 0–59 months of age presenting for acute diarrhea in the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS).
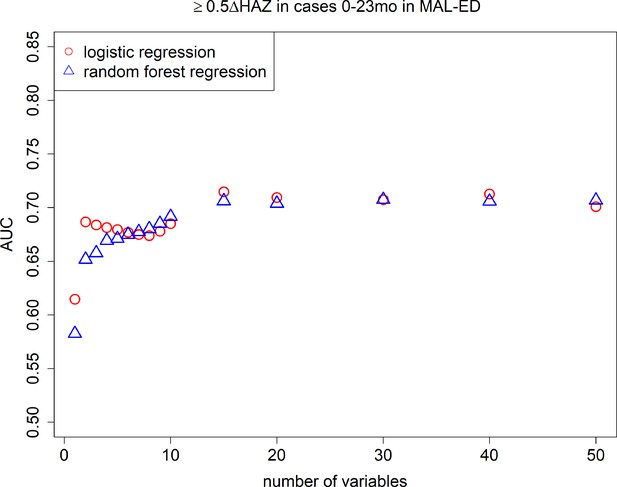
Area under the curves (AUCs): cross-validated AUC achieved by number of predictive variables included in random forest regression and logistic regression models predicting growth faltering (≥0.5 decrease in height-for-age z-score [HAZ]) in children 0–23 months of age presenting with diarrhea in the MAL-ED (the Etiology, Risk Factors, and Interactions of Enteric Infections and Malnutrition and the Consequences for Child Health and Development) study.
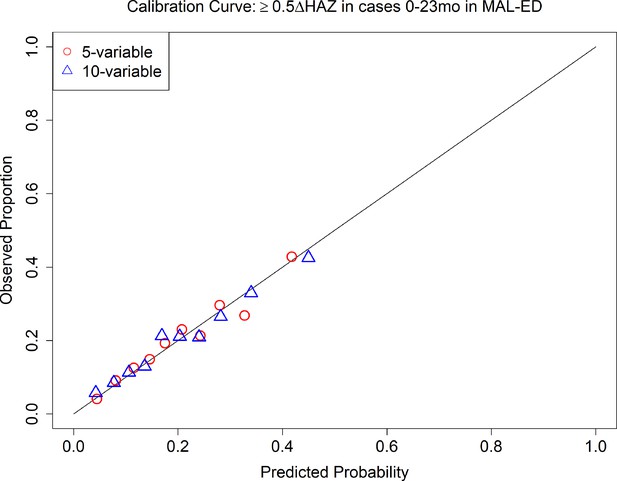
Calibration curves of 5- and 10-variable model predicting growth faltering (≥0.5 decrease in height-for-age z-score [HAZ]) in children 0–23 months of age presenting for acute diarrhea in the MAL-ED (the Etiology, Risk Factors, and Interactions of Enteric Infections and Malnutrition and the Consequences for Child Health and Development) study.
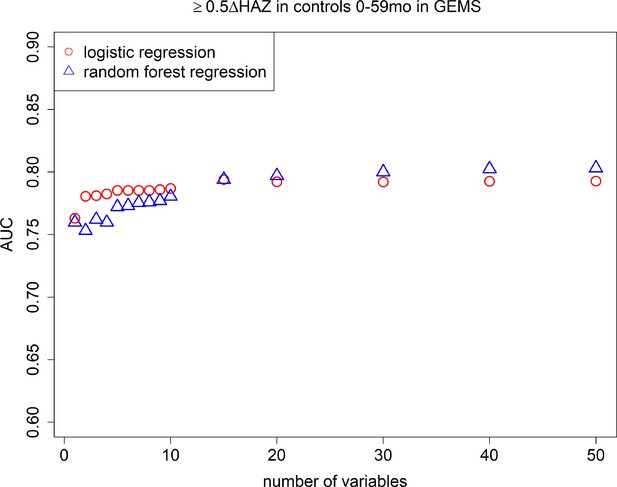
Area under the curves (AUCs): cross-validated AUC achieved by number of predictive variables included in random forest regression and logistic regression models predicting growth faltering (≥0.5 decrease in height-for-age z-score [HAZ]) in children 0–59 months of age without diarrhea in the Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS).
Tables
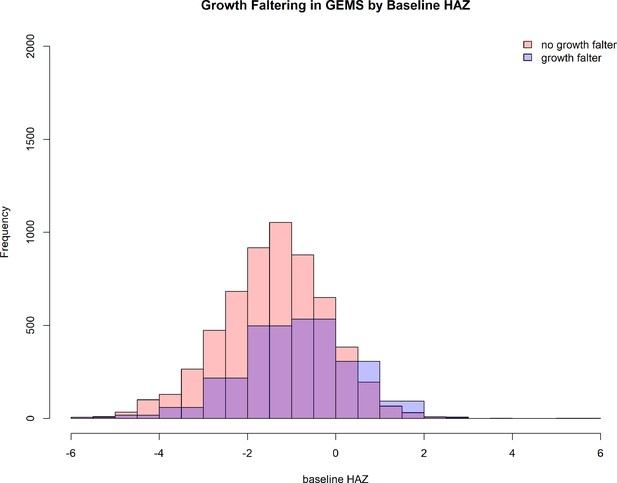
Growth faltering.
Variable importance ordering and cross-validated average overall area under the curve (AUC) and AUC by patient subset and 95% confidence intervals for a 5 (bold) and 10 (italicized) variable logistic regression model for predicting growth faltering in children in 7 LMICs(Low- and middle-income countries) derived from Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS) data (≥0.5 decrease in height-for-age z-score [HAZ] in children with acute diarrhea).
| GEMS | MAL-ED | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient subset | 0–59 months (main text model) | 0–59 months (limit to only those NOT stunted at beginning (HAZ ≥−2) 5659/7639 (74.1%)) | 0–59 months limited to only those NOT stunted at beginning outcome is ANY stunting at follow-up (HAZ <−2) | 0–23 months (for external validation) | Healthy controls | 0–23 months |
| AUCs | 0.72 (0.72, 0.72) | 0.71 (0.70, 0.72) | 0.90 (0.89, 0.91) | 0.64 (0.63, 0.65) | 0.79 (0.78, 0.79) | 0.67 (0.67, 0.68) |
| 0.72 (0.72, 0.72) | 0.71 (0.70, 0.72) | 0.90 (0.89, 0.90) | 0.64 (0.64, 0.64) | 0.79 (0.79, 0.79) | 0.68 (0.67, 0.69) | |
| 1 | Age (months) | Age (months) | HAZ | HAZ | Age (months) | HAZ |
| 2 | HAZ | HAZ | Age | Age (months) | HAZ | Age (days) |
| 3 | Respiratory rate | Respiratory rate | Respiratory rate | Temperature | Respiratory rate | Total days breastfeeding |
| 4 | Temperature | Temperature | Temperature | Respiratory rate | Temperature | Total days in all diarrheal episodes to date |
| 5 | Num. people living in household | Num. people living in household | Num. people living in household | Num. people living in household | Num. people living in household | Mean number of people per room |
| 6 | Num. rooms used for sleeping | Num. rooms used for sleeping | Num. days of diarrhea at presentation | Num. rooms used for sleeping | Breastfed | Days with diarrhea so far in this episode |
| 7 | Num. days of diarrhea at presentation | Num. days of diarrhea at presentation | Num. other households that share same fecal waste facility | Num. days of diarrhea at presentation | Num. rooms used for sleeping | Maternal education (years) |
| 8 | Num. other households that share same fecal waste facility | Breastfed | Num. rooms used for sleeping | Num. other households that share same fecal waste facility | Num. children <60 months live in household | Days since last diarrhea episode |
| 9 | Breastfed | Num. other households that share same fecal waste facility | Num. children <60 months live in household | Num. children <60 months live in household | Caregiver education | People sleeping in house |
| 10 | Num. children <60 months live in household | Num. children <60 months live in household | Caregiver education | Caregiver education | Num. other households share latrine | Max loose stools in this episode |
Calibration intercept and slope.
| Number of predictor variables | GEMS 0–59 monthsIntercept (95% CI) | Slope (95% CI) | GEMS 0–23 months (for external validation)Intercept (95% CI) | Slope (95% CI) | MAL-ED 0–23 months Rederivationintercept (95% CI) | Slope (95% CI) | GEMS-derived model applied to MAL-ED dataIntercept (95% CI) | Slope (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.9 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.82, 1.2) | −1.0 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.97 (0.62, 1.3) | 9.6 × 10−3 (−0.32, 0.32) | 1.0 (0.35, 1.7) | ||
| 2 | 3.6 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.84, 1.2) | −1.1 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.98 (0.70, 1.3) | 1.1 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 1.0 (0.51, 1.5) | −0.32 (−0.54, −0.11) | 1.5 (1.0, 2.1) |
| 3 | 3.6 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.84, 1.2) | −1.2 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.97 (0.70, 1.2) | 1.1 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 0.99 (0.51, 1.5) | ||
| 4 | 4.1 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.84, 1.2) | −1.2 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.97 (0.71, 1.2) | 1.1 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 0.97 (0.49, 1.5) | ||
| 5 | 4.2 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.83, 1.2) | −1.2 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.96 (0.70, 1.2) | 1.1 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 0.95 (0.48, 1.5) | ||
| 6 | 4.2 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.83, 1.2) | −1.2 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.96 (0.70, 1.2) | 1.2 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 0.94 (0.47, 1.5) | ||
| 7 | 4.3 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.83, 1.2) | −1.2 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.96 (0.70, 1.2) | 1.2 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 0.92 (0.47, 1.4) | ||
| 8 | 4.4 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.83, 1.2) | −1.2 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.95 (0.69, 1.2) | 1.2 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 0.92 (0.47, 1.4) | ||
| 9 | 4.7 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.83, 1.2) | −1.2 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.95 (0.69, 1.2) | 1.2 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 0.91 (0.47, 1.4) | ||
| 10 | 4.8 × 10−3 (−1.2 × 10−1, 1.3 × 10−1) | 1.0 (0.83, 1.2) | −1.2 × 10−2 (−0.14, 0.12) | 0.93 (0.69, 1.2) | 1.2 × 10−2 (−0.33, 0.33) | 0.89 (0.46, 1.4) |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78491/elife-78491-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf
-
Supplementary file 1
Additional methodological details and results of sensitivity analyses.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78491/elife-78491-supp1-v2.pdf