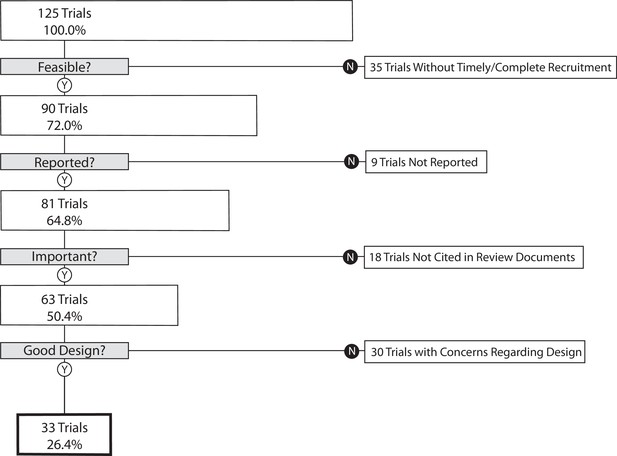
The proportion of randomized controlled trials that inform clinical practice
Figures
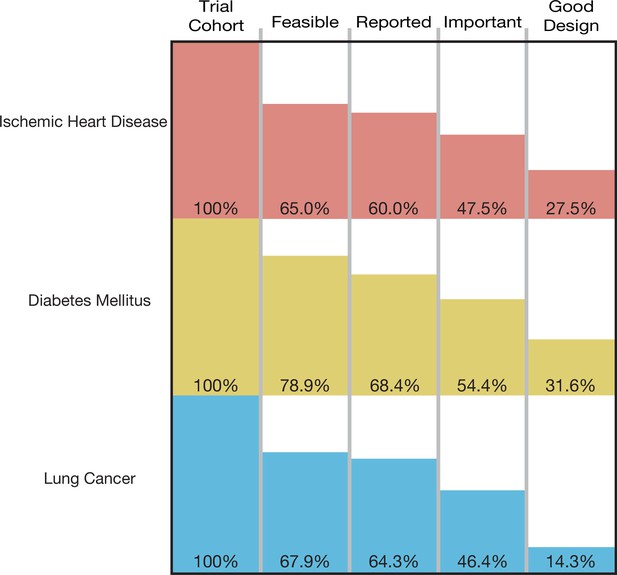
The cumulative proportion of trials meeting four conditions of informativeness by disease area.
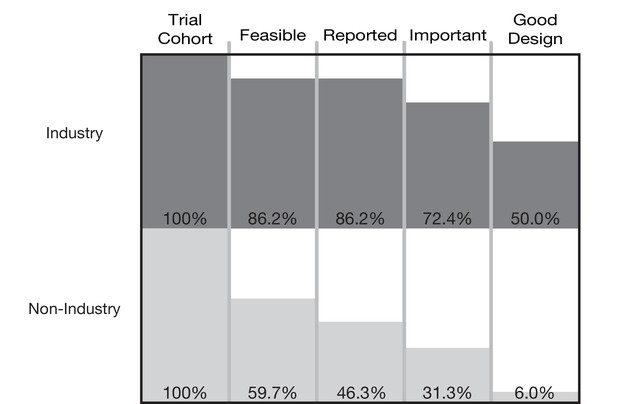
The cumulative proportion of trials meeting four conditions of informativeness by sponsor.
Of the 67 non-industry funded trials, 7 were funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health or other U.S. Federal agencies.
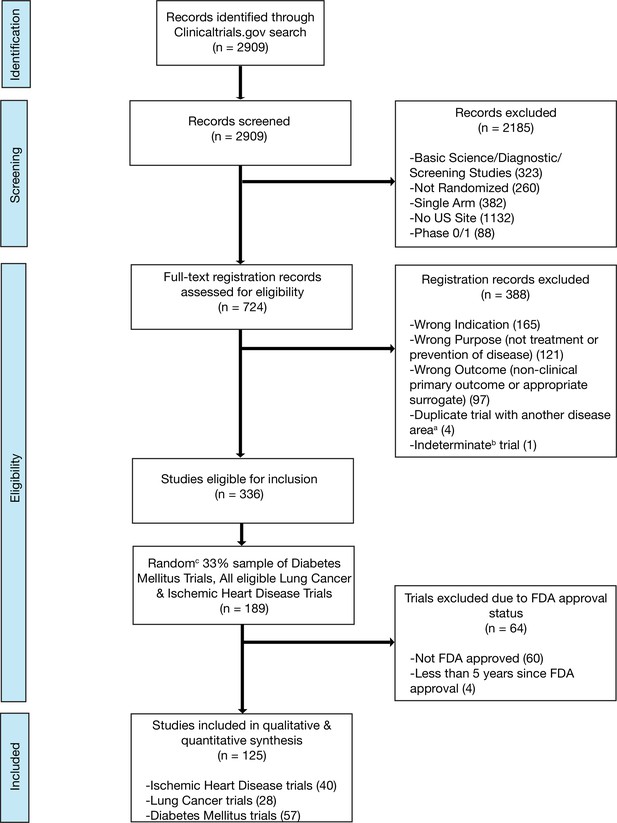
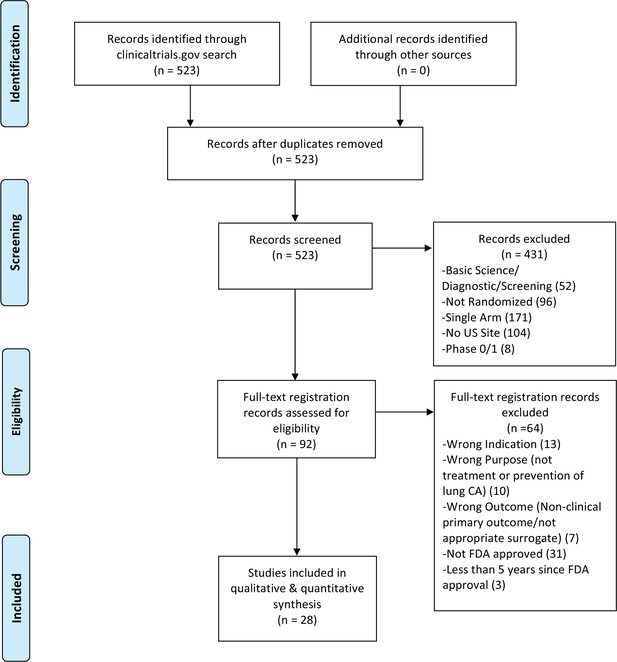
Flow diagram for trial inclusion.
(a) Trials overlapping more than one disease area (e.g. diabetes mellitus and ischemic heart disease) were allocated based on the disease evaluated in the primary outcome. (b) An indeterminate trial is an ongoing trial that has not surpassed twice the planned primary outcome completion date. (c) We used a random number generator (RAND function in Microsoft Excel) to create our 33% sample.
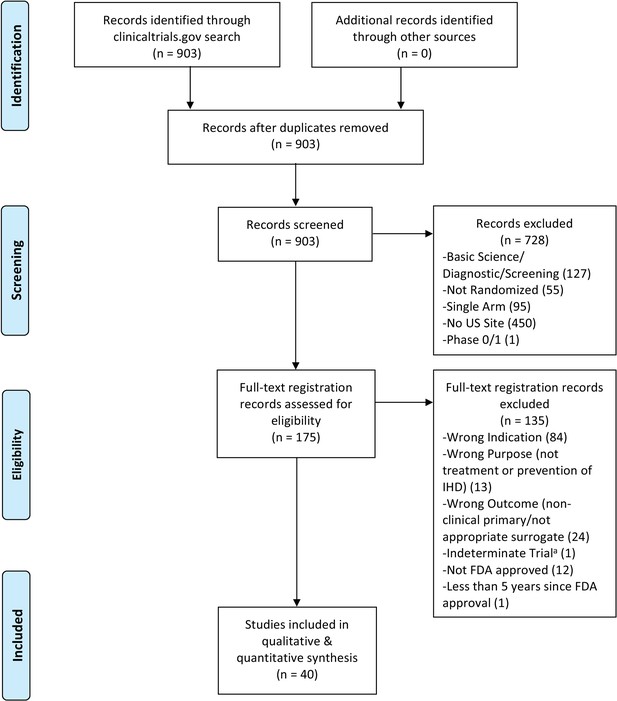
Flow diagram for ischemic heart disease interventional trials.
(a) An indeterminate trial is an ongoing trial that has not surpassed twice the planned primary outcome completion date.
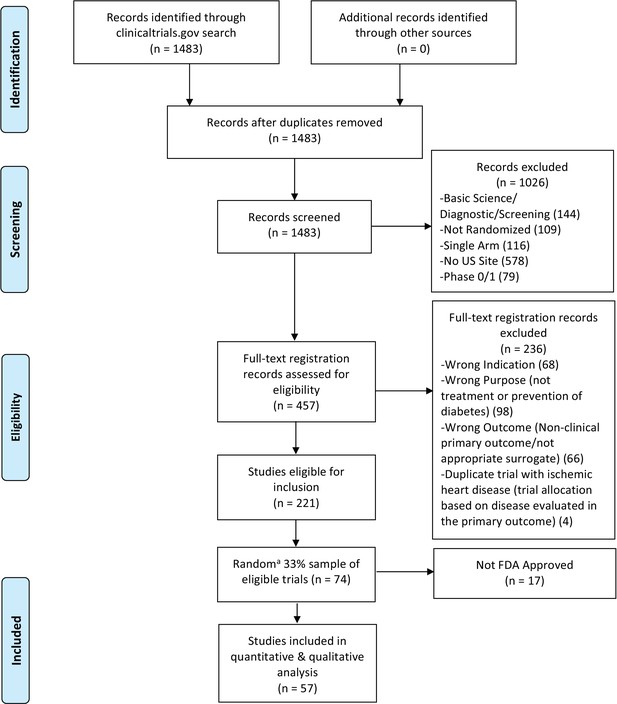
Flow diagram for diabetes mellitus interventional trials.
(a) We used a random number generator (RAND function in Microsoft Excel) to create our 33% sample.
Tables
Characteristics of intervention trial cohort.
| Category | Ischemic heart disease trialsN=40 | Diabetes mellitus trialsN=57 | Lung cancer trialsN=28 | All trialsN=125 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trial phase | ||||
| 2* | 6 (15.0) | 5 (8.8) | 13 (46.4) | 24 (19.2) |
| 3† | 11 (27.5) | 26 (45.6) | 13 (46.4) | 50 (40.0) |
| 4 | 10 (25.0) | 9 (15.8) | 0 (0.0) | 19 (15.2) |
| NA‡ | 13 (32.5) | 17 (29.8) | 2 (7.1) | 32 (25.6) |
| Intervention | ||||
| Drug/biologic | 19 (47.5) | 34 (59.6) | 24 (85.7) | 77 (61.6) |
| Combination§ | 7 (17.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.6) | 8 (6.4) |
| Device | 4 (10.0) | 4 (7.0) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (6.4) |
| Other¶ | 10 (25.0) | 19 (33.3) | 3 (10.7) | 32 (25.6) |
| Trial status | ||||
| Completed | 29 (72.5) | 53 (93.0) | 17 (60.7) | 99 (79.2) |
| Terminated | 7 (17.5) | 1 (1.8) | 7 (25.0) | 15 (12.0) |
| Active, NR | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.8) | 4 (14.3) | 5 (4.0) |
| Unknown | 4 (10.0) | 2 (3.5) | 0 (0.0) | 6 (4.8) |
| Outcome | ||||
| Clinical | 24 (60.0) | 8 (14.0) | 10 (35.7) | 42 (33.6) |
| Surrogate | 16 (40.0) | 49 (86.0) | 18 (64.3) | 83 (66.4) |
| Sponsor** | ||||
| Industry | 18 (45.0) | 27 (47.4) | 13 (46.4) | 58 (46.4) |
| Other†† | 22 (55.0) | 30 (52.6) | 15 (53.6) | 67 (53.6) |
-
*
Including phase 1/2.
-
†
Including phase 2/3.
-
‡
Includes behavioral, procedural/surgical, and device interventions .
-
§
Including Drug + Device, Drug + Procedure, Behavioral + Device, Radiation Therapy + Drug.
-
¶
Including Behavioral Intervention, Radiation Therapy, Surgical Procedure, Cellular Intervention.
-
**
As defined in ClinicalTrials.gov registration records.
-
††
Included within the designation ‘Other’ are seven trials that received funding from the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) or other U.S. Federal agencies, and 60 trials that are non-industry and non-NIH/U.S. Federal agency funded.
The proportion of informative trials by trial property.
| Category | Proportion of informative trials | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trial phase | 5.2×10–5 | ||
| 2* | 8.3 | 1.0–27.0 | |
| 3† | 50.0 | 35.5–64.5 | |
| 4 | 10.5 | 1.3–33.1 | |
| NA | 12.5 | 3.5–29.0 | |
| Intervention | 2.0×10–2 | ||
| Drug/biologic | 35.1 | 24.5–46.8 | |
| Combination‡ | 25.0 | 3.2–65.1 | |
| Device | 0.0 | 0.0–36.9 | |
| Other§ | 12.5 | 3.5–29.0 | |
| Disease area | 0.2 | ||
| Ischemic heart disease | 27.5 | 14.6–43.9 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 31.6 | 19.9–45.2 | |
| Lung cancer | 14.3 | 4.0–32.7 | |
| Sponsor¶ | 8.1×10–8 | ||
| Industry | 50.0 | 36.6–63.4 | |
| Non-industry | 6.0 | 1.7–14.6 |
-
*
Including phase 1/2.
-
†
Including phase 2/3.
-
‡
Including Drug + Device, Drug + Procedure, Behavioral + Device, Radiation Therapy + Drug.
-
§
Including Behavioral Intervention, Radiation Therapy, Surgical Procedure, Cellular Intervention.
-
¶
As defined in ClinicalTrials.gov registration records.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Index.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Proportion of trials meeting each criterion for informativeness.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp2-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Trials not fulfilling feasibility condition.
IHD: ischemic heart disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; lung CA: lung cancer; PCD: primary completion date.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp3-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Trials not reported.
IHD: ischemic heart disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; lung CA: lung cancer.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp4-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 5
Trials not cited in clinical review documents.
IHD: ischemic heart disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; lung CA: lung cancer.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp5-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 6
Trials with concerns regarding design.
IHD: ischemic heart disease; DM: diabetes mellitus; lung CA: lung cancer.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp6-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 7
Phase 4 trials not meeting all four informativeness criteria.
IHD: ischemic heart disease; DM: diabetes mellitus.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp7-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 8
ClinicalTrials.gov search criteria.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp8-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 9
Trial inclusion and exclusion criteria.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp9-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 10
Assessment of regulatory approval status.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp10-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 11
Addressing four conditions for informative clinical trials.
1Column ‘Conditions for informativeness’ extracted from column 1 in eTable 1 Zarin et al., 2019
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp11-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 12
Classification of reason for termination.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp12-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 13
Methodology for publication search.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp13-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 14
Systematic review citation search strategy and quality assessment.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp14-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 15
Clinical practice guideline and point-of-care medical database search strategies and quality assessment.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp15-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 16
Operationalization of modified Cochrane risk of bias score.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp16-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 17
Inter-rater agreement rates.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp17-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 18
Deviations to the study protocol.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp18-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 19
STROBE checklist for cohort Studies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-supp19-v2.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79491/elife-79491-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx