Bone circuitry and interorgan skeletal crosstalk
Figures
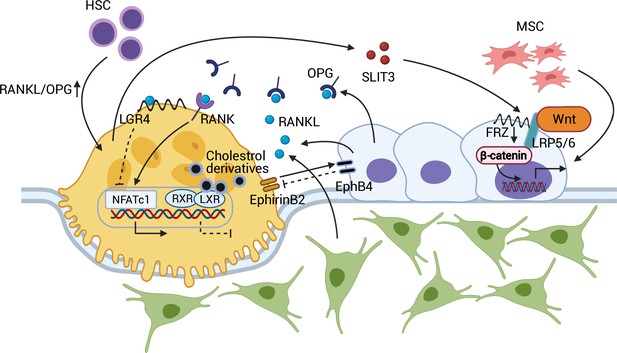
Coupling between osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
RANKL/OPG regulates osteoclastogenesis through RANK and downstream NFATc1 activation. RANKL-LGR4 binding creates a negative feedback loop by inhibiting NFATc1. LXR-RXR suppresses osteoclastogenesis upon binding of cellular cholesterol derivatives. EphB4-EphrinB2 interaction promotes osteoblastogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis. SLIT3 from osteoclasts activates WNT/β-catenin and stimulates osteoblast migration and proliferation. Abbreviations: Hematopoietic stem cell (HSC); mesenchymal stem cell (MSC); receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β (RANK); receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand (RANKL); leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 4 (LGR4); liver X receptors (LXRs); retinoic acid receptor (RXR); nuclear translocation of nuclear factor of activated T cells cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1 (NFATc1); slit guidance ligand 3 (SLIT3); osteoprotegerin (OPG); frizzled (Frz).
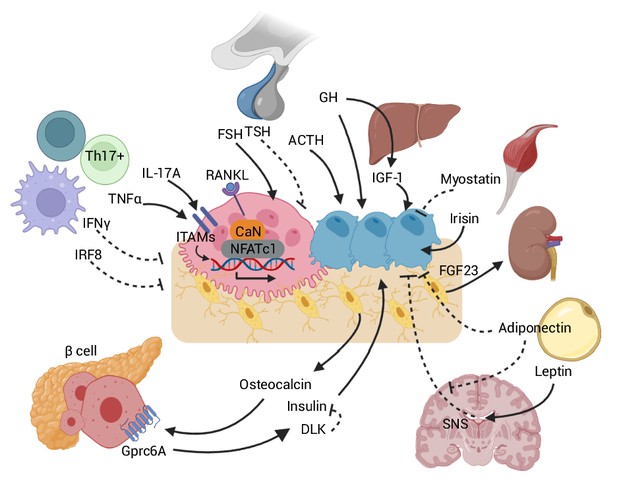
Skeletal crosstalk with other organs.
Pituitary hormones directly regulate bone remodeling. FSH stimulates osteoclastogenesis, whereas TSH inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption. ACTH promotes osteoblastic bone formation. GH triggers anabolic signals directly and indirectly through IGF-1. Leptin-mediated SNS activation negatively regulates bone remodeling. The inhibitory peripheral action of adiponectin on bone opposes its centrally mediated action by blocking SNS. OCN, upon binding to the GPRc6A receptor on pancreatic β-cells, can enhance β-cell proliferation and insulin secretion. Insulin binding on osteoblasts can, in turn, promote OCN production. DLK from β-cells counteracts OCN activity by inhibiting the stimulatory effect of insulin. Osteocytes release FGF23, which promotes renal phosphate excretion. Myokines, such as myostatin and irisin, also directly affect bone remodeling. Immune-bone interactions notably occur through various cytokines, such as TNFα, IL-17A, IFNγ, and IRF8. Abbreviations: Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), growth hormone (GH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β (RANK), sympathetic nervous system (SNS), delta-like protein (DLK), interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8), interferon (IFN), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin (IL), immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM), calcineurin (CaN), G protein-coupled receptor class C group 6 member A (GPRC6A), osteocalcin (OCN), fibroblast growth factor (FGF).





