Immune mechanisms underlying COVID-19 pathology and post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC)
Figures
Figure 1
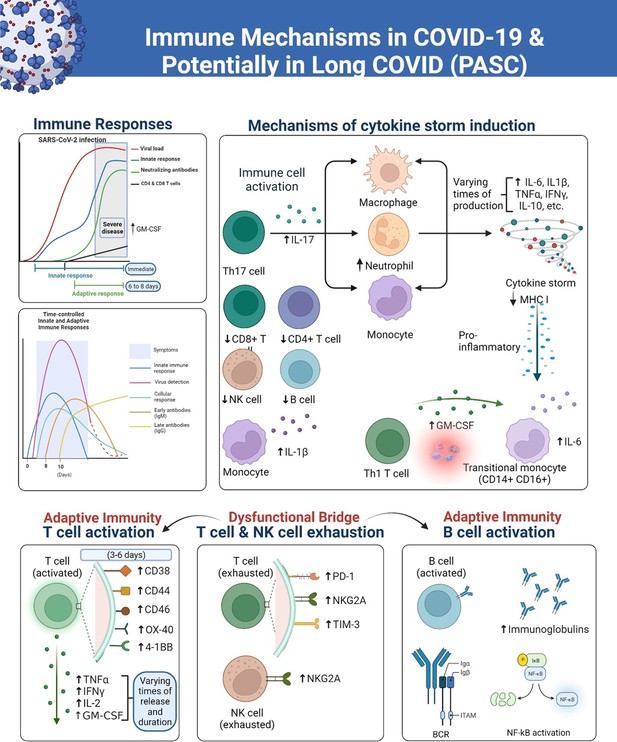
A simplified overview of responses of the immune system to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, over various time courses that lead to severe COVID-19 and long COVID (PASC) in some patients.
The innate immune response serves as the initial line of defense against the virus, involving the activation of immune cells such as monocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. These cells release cytokines and chemokines to recruit other immune cells, such as T cells and neutrophils, to the site of infection. Later in the course of the infection, the adaptive immune cells including B plasma cells release antibodies. However, the overreactive immune responses trigger inflammatory conditions that are sustained in PASC due to dysregulation of the immune system. The diagram was created using the Biorender.com software.
Download links
A two-part list of links to download the article, or parts of the article, in various formats.
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Immune mechanisms underlying COVID-19 pathology and post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC)
eLife 12:e86014.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.86014





