VO2max prediction based on submaximal cardiorespiratory relationships and body composition in male runners and cyclists: a population study
Figures
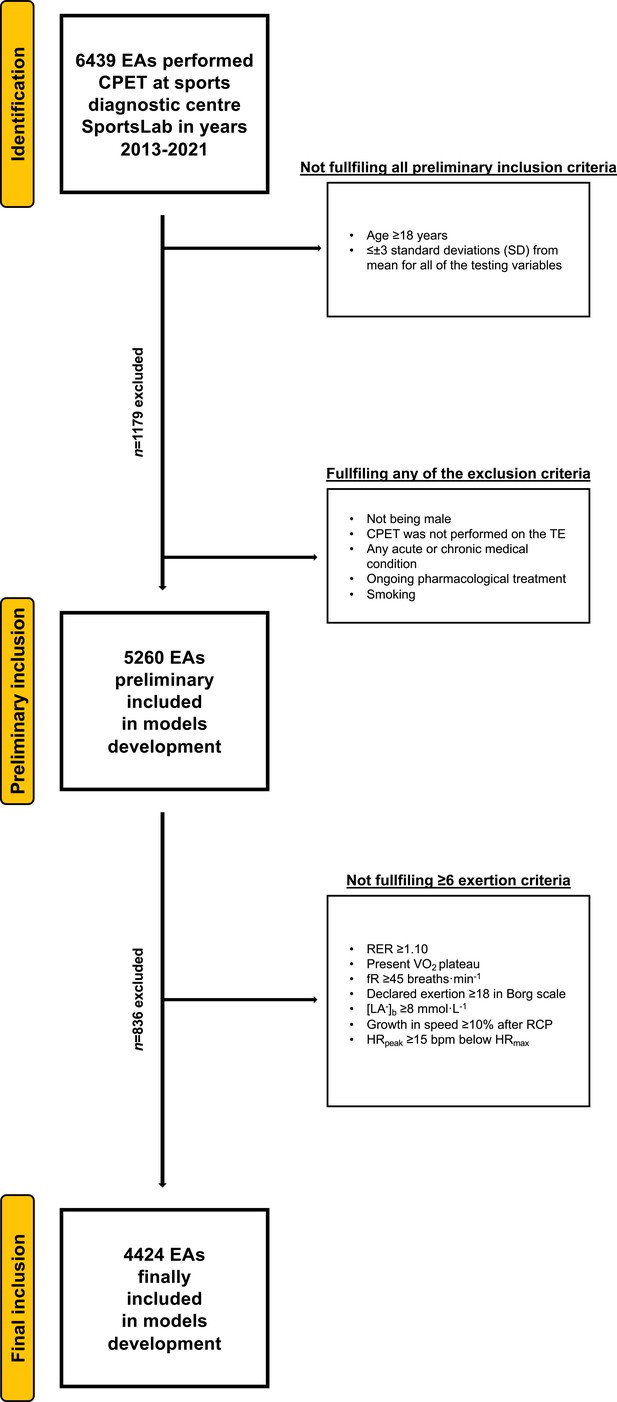
Flowchart of the preliminary inclusion and exclusion process.
Abbreviations: EA, endurance athlete; CPET, cardiopulmonary exercise testing; SD, standard deviation; TE, treadmill; RER, respiratory exchange ratio; VO2, oxygen uptake (mL·min−1·kg−1); [La−]b, lactate concentration (mmol·L−1); fR, breathing frequency (breaths·min−1); RCP, respiratory compensation point; HRpeak, peak heart rate (beats·min−1); HRmax, maximal heart rate (bpm). At both stages of the selection, some participants met several (>1) exclusion criteria.
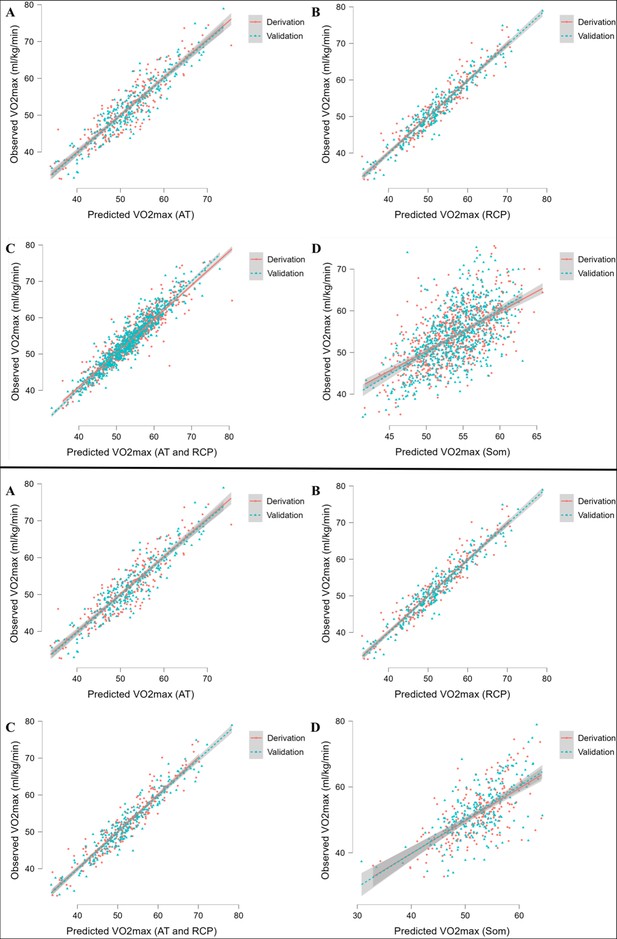
Performance of prediction equations for VO2max.
Abbreviations: VO2max; maximal oxygen uptake; AT, anaerobic threshold; RCP, respiratory compensation point; Max, maximal; Som, somatic. All values are presented in mL·min–1·kg–1. Upper panel shows performance for running equations, while the lower panel shows performance for cycling equations. Panel A shows performance of the prediction model for AT; panel B for RCP; panel C for AT and RCP; panel D for somatic-only equation.
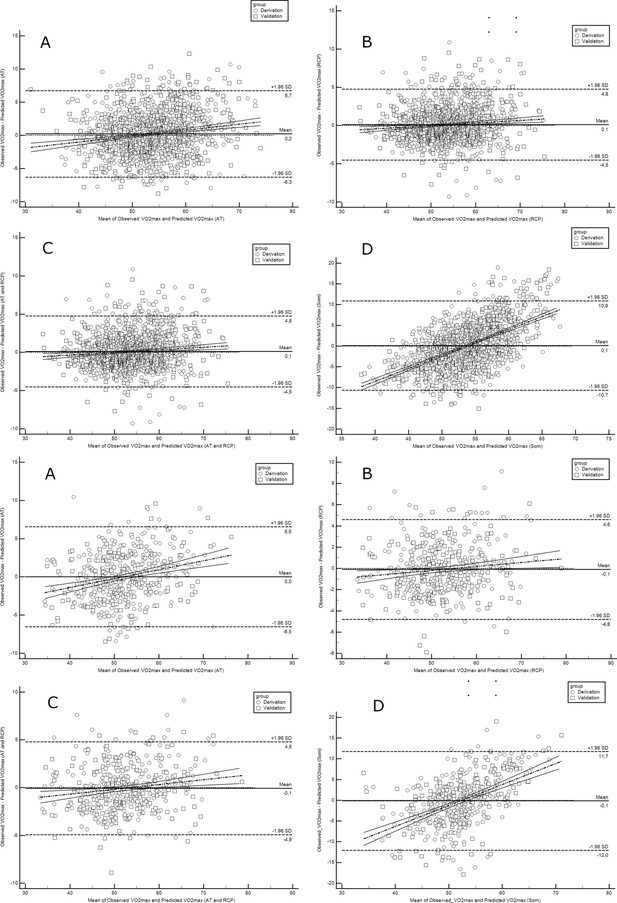
Bland-Altman plots comparing observed with predicted VO2max in runners derivation and validation cohorts.
Abbreviations: VO2max; maximal oxygen uptake; AT, anaerobic threshold; RCP, respiratory compensation point; Max, maximal; Som, somatic. All values are presented in mL·min–1·kg–1. Upper panel shows performance for running equations, while the lower panel shows performance for cycling equations. Panel A shows performance of the prediction model for AT; panel B for RCP; panel C for AT and RCP; panel D for the somatic-only equation.
Tables
Basic anthropometric characteristics for runners.
| Variable (unit) | Derivation group n=1998 | Testing group n=666 | Validation group n=666 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | CI | SD | Mean | CI | SD | Mean | CI | SD | |
| Age (years) | 36.2 | 35.6–36.9 | 8.45 | 35.9 | 35.5–36.3 | 8.05 | 35.5 | 34.9–36.2 | 8.14 |
| Height (cm) | 180.0 | 179.6–180.5 | 6.04 | 179.4 | 179.1–179.7 | 6.13 | 179.7 | 179.2–180.2 | 6.61 |
| BM (kg) | 77.7 | 77.0–78.4 | 9.35 | 77.7 | 77.3–78.1 | 9.29 | 77.9 | 77.1–78.6 | 10.1 |
| BMI (kg·m–2) | 23.9 | 23.8–24.1 | 2.43 | 24.1 | 24.0–24.2 | 2.41 | 24.1 | 23.9–24.3 | 2.56 |
| BF (%) | 15.4 | 15.1–15.7 | 4.55 | 15.5 | 15.3–15.7 | 4.52 | 15.4 | 15.1–15.8 | 4.55 |
| FM (kg) | 12.2 | 11.9–12.6 | 4.68 | 12.3 | 12.1–12.5 | 4.65 | 12.3 | 11.9–12.7 | 4.92 |
| FFM (kg) | 65.5 | 65.0–66.0 | 6.43 | 65.4 | 65.1–65.7 | 6.31 | 65.6 | 65.1–66.1 | 6.86 |
-
BM, body mass; BMI, body mass index; BF, body fat; FM, fat mass; FFM, fat-free mass; CI, 95% confidence interval; SD, standard deviation.
Basic anthropometric characteristics for cyclists.
| Variable (unit) | Derivation group n=656 | Testing group n=219 | Validation group n=219 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | CI | SD | Mean | CI | SD | Mean | CI | SD | |
| Age (years) | 37.3 | 36.6–38.0 | 9.13 | 37.1 | 35.9–38.4 | 9.50 | 37.6 | 36.5–38.8 | 8.46 |
| Height (cm) | 179.9 | 179.4–180.4 | 6.27 | 180.1 | 179.2–181.0 | 6.96 | 180.2 | 179.4–181.0 | 6.13 |
| BM (kg) | 78.8 | 78.1–79.6 | 9.80 | 79.1 | 77.7–80.5 | 10.4 | 79.8 | 78.4–81.3 | 10.9 |
| BMI (kg·m–2) | 24.3 | 24.1–24.6 | 2.63 | 24.4 | 24.0–24.7 | 2.80 | 24.6 | 24.2–25.0 | 2.96 |
| BF (%) | 16.4 | 15.7–17.1 | 4.99 | 16.1 | 15.7–16.5 | 4.81 | 16.2 | 15.5–16.8 | 4.87 |
| FM (kg) | 13.3 | 12.6–14.1 | 5.66 | 13.0 | 12.6–13.4 | 5.27 | 13.3 | 12.5–14.0 | 5.85 |
| FFM (kg) | 65.8 | 64.9–66.6 | 6.25 | 65.8 | 65.4–66.3 | 6.06 | 66.6 | 65.7–67.4 | 6.58 |
-
BM, body mass; BMI, body mass index; BF, body fat; FM, fat mass; FFM, fat-free mass; CI, 95% confidence interval; SD, standard deviation.
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) characteristics for runners.
| Variable (unit) | Derivation group n=1998 | Testing group n=666 | Validation group n=666 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | CI | SD | Mean | CI | SD | Mean | CI | SD | |
| rVO2AT (mL·min–1·kg–1) | 38.4 | 38.1–38.8 | 5.01 | 38.5 | 38.3–38.7 | 4.88 | 38.1 | 37.7–38.5 | 5.16 |
| RERAT | 0.87 | 0.86–0.87 | 0.04 | 0.87 | 0.86–0.87 | 0.04 | 0.87 | 0.86–0.87 | 0.04 |
| HRAT (beats·min–1) | 151.5 | 150.8–152.3 | 10.3 | 151.0 | 150.6–151.5 | 10.8 | 152.0 | 151.2–152.8 | 10.8 |
| VEAT (L·min–1) | 79.1 | 78.1–80.0 | 12.2 | 78.3 | 77.8–78.9 | 12.0 | 77.2 | 76.3–78.2 | 12.0 |
| SPEEDAT (km·h–1) | 11.0 | 10.9–11.1 | 1.45 | 11.0 | 11.0–11.1 | 1.36 | 10.9 | 10.8–11.0 | 1.42 |
| LAAT (mmol·L–1) | 2.08 | 2.02–2.14 | 0.63 | 1.80 | 1.76–1.83 | 0.62 | 2.35 | 2.27–2.42 | 0.72 |
| rVO2RCP (mL·min–1·kg–1) | 47.5 | 47.0–48.0 | 5.88 | 47.7 | 47.4–48.0 | 6.15 | 47.3 | 46.8–47.8 | 6.16 |
| RERRCP | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.03 |
| HRRCP (beats·min–1) | 173.4 | 172.7–174.1 | 9.21 | 173.2 | 172.8–173.6 | 9.30 | 174.3 | 173.5–175.0 | 9.50 |
| VERCP (L·min–1) | 114.7 | 113.5–116.0 | 15.9 | 113.9 | 113.1–114.6 | 16.7 | 112.7 | 111.4–114.0 | 16.2 |
| SPEEDRCP (km·h–1) | 14.0 | 13.9–14.1 | 1.77 | 14.1 | 14.0–14.1 | 1.70 | 13.9 | 13.8–14.1 | 1.75 |
| LARCP (mmol·L–1) | 4.72 | 4.63–4.82 | 1.04 | 4.40 | 4.34–4.45 | 1.04 | 4.81 | 4.69–4.93 | 1.14 |
| rVO2max (mL·min–1·kg–1) | 53.8 | 53.3–54.3 | 6.67 | 54.3 | 54.0–54.6 | 6.95 | 53.8 | 53.3–54.3 | 7.09 |
-
CI, 95% confidence interval; SD, standard deviation; rVO2AT, oxygen uptake at anaerobic threshold relative to body mass; RERAT, respiratory exchange ratio at anaerobic threshold; HRAT, heart rate at anaerobic threshold; VEAT, pulmonary ventilation at anaerobic threshold; SPEEDAT, velocity at anaerobic threshold; LAAT, blood lactate concentration at anaerobic threshold; rVO2RCP, oxygen uptake at respiratory compensation point relative to body mass; RERRCP, respiratory exchange ratio at respiratory compensation point; HRRCP, heart rate at respiratory compensation point; VERCP, pulmonary ventilation at respiratory compensation point; SPEEDRCP, velocity at respiratory compensation point; LARCP, blood lactate concentration at respiratory compensation point; rVO2max, maximal oxygen uptake relative to body mass.
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) characteristics for cyclists.
| Variable (unit) | Derivation group n=656 | Testing group n=219 | Validation group n=219 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | CI | SD | Mean | CI | SD | Mean | CI | SD | |
| rVO2AT (mL·min–1·kg–1) | 33.0 | 32.5–33.4 | 5.84 | 33.2 | 32.4–33.9 | 5.68 | 33.7 | 32.9–34.5 | 5.89 |
| RERAT | 0.87 | 0.87–0.87 | 0.04 | 0.87 | 0.87–0.88 | 0.04 | 0.87 | 0.87–0.88 | 0.04 |
| HRAT (beats·min–1) | 142.2 | 141.3–143.1 | 11.7 | 140.7 | 139.1–142.3 | 11.8 | 141.2 | 139.7–142.6 | 10.8 |
| VEAT (L·min–1) | 64.9 | 64.0–65.7 | 11.0 | 65.1 | 63.7–66.5 | 10.6 | 67.4 | 66.0–68.9 | 11.2 |
| rPOWAT (W·kg–1) | 2.28 | 2.24–2.32 | 0.48 | 2.27 | 2.21–2.34 | 0.48 | 2.33 | 2.27–2.39 | 0.46 |
| LAAT (mmol·L–1) | 1.86 | 1.82–1.90 | 0.51 | 1.84 | 1.77–1.90 | 0.50 | 1.80 | 1.74–1.87 | 0.51 |
| rVO2RCP (mL·min–1·kg–1) | 44.0 | 43.5–44.6 | 7.38 | 44.4 | 43.4–45.4 | 7.32 | 44.9 | 43.8–45.9 | 7.63 |
| RERRCP | 1.01 | 1.01–1.01 | 0.04 | 1.01 | 1.01–1.02 | 0.04 | 1.01 | 1.01–1.02 | 0.04 |
| HRRCP (beats·min–1) | 168.8 | 168.0–169.7 | 10.5 | 167.7 | 166.2–169.2 | 11.3 | 168.4 | 167.1–169.6 | 9.11 |
| VERCP (L·min–1) | 106.2 | 104.8–107.6 | 17.7 | 107.6 | 105.3–109.8 | 16.8 | 110.4 | 107.9–112.9 | 18.7 |
| rPOWRCP (W·kg–1) | 3.34 | 3.29–3.38 | 0.63 | 3.33 | 3.25–3.42 | 0.63 | 3.40 | 3.32–3.48 | 0.61 |
| LARCP (mmol·L–1) | 4.54 | 4.47–4.61 | 0.97 | 4.61 | 4.48–4.75 | 1.04 | 4.47 | 4.34–4.61 | 1.03 |
| rVO2MAX (mL·min–1·kg–1) | 51.7 | 51.1–52.4 | 7.99 | 52.0 | 50.9–53.1 | 8.01 | 52.3 | 51.2–53.4 | 8.08 |
-
CI, 95% confidence interval; SD, standard deviation; rVO2AT, oxygen uptake at anaerobic threshold relative to body mass; RERAT, respiratory exchange ratio at anaerobic threshold; HRAT, heart rate at anaerobic threshold; VEAT, pulmonary ventilation at anaerobic threshold; rPOWAT, power at anaerobic threshold relative to body mass; LAAT, blood lactate concentration at anaerobic threshold; rVO2RCP, oxygen uptake at respiratory compensation point relative to body mass; RERRCP, respiratory exchange ratio at respiratory compensation point; HRRCP, heart rate at respiratory compensation point; VERCP, pulmonary ventilation at respiratory compensation point; LARCP, blood lactate concentration at respiratory compensation point; rPOWRCP, power at respiratory compensation point relative to body mass; rVO2max, maximal oxygen uptake relative to body mass.
VO2max prediction equations for cyclists.
| Model’s category | Multiple linear regression equation | R2 | Derivation group performance | Validation group performance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | |||
| AT | VO2max = 21.29 + 0.95 * rVO2AT + 1.74 * rPOWAT - 0.30 * BF | 0.811 | 3.62 | 2.89 | 3.42 | 2.72 |
| RCP | VO2max = 8.57 + 1.08 * rVO2RCP - 0.04 * VERCP | 0.913 | 2.12 | 1.66 | 2.03 | 1.64 |
| AT+RCP | VO2max = 10.57 + 0.98 * rVO2RCP - 0.12 * BF | 0.909 | 2.26 | 1.78 | 2.11 | 1.72 |
| SOM | VO2max = 82.36–0.14 * BM - 0.66 * BF - 0.22 * Age | 0.43 | 6.06 | 4.70 | 6.11 | 4.74 |
-
AT, equation based on anaerobic threshold; RCP, equation based on respiratory compensation point; SOM, equation based on somatic variables only; R2, adjusted R2; RMSE, root mean square error; MAE, mean absolute error (mL·min–1·kg–1); VO2max, maximal oxygen uptake relative to body mass (mL·min–1·kg–1); rVO2AT, oxygen uptake at anaerobic threshold relative to body mass (mL·min–1·kg–1); rPOWAT, power at anaerobic threshold relative to body mass (W·kg–1); rVO2RCP, oxygen uptake at respiratory compensation point relative to body mass (mL·min–1·kg–1); VERCP, pulmonary ventilation at respiratory compensation point (L·min–1); BF, body fat (%); BM, body mass (kg).
VO2max prediction equations for runners.
| Model’s category | Multiple linear regression equation | R2 | Derivation group performance | Validation group performance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | |||
| AT | VO2max = 19.78 + 1.05 * rVO2AT + 0.94 * SPEEDAT - 0.12 * FFM - 0.06 * VEAT - 0.07 * HRAT | 0.775 | 3.43 | 2.61 | 3.60 | 2.74 |
| RCP | VO2max = 1.98 + 1.03 * rVO2RCP + 0.23 * SPEEDRCP | 0.899 | 2.0 | 1.58 | 2.08 | 1.60 |
| AT+RCP | VO2max = 1.98 + 1.03 * rVO2RCP + 0.23 * SPEEDRCP | 0.899 | 2.0 | 1.58 | 2.08 | 1.60 |
| SOM | VO2max = 72.37–0.77 * BF - 0.19 * Age | 0.35 | 5.53 | 4.36 | 5.54 | 4.37 |
-
AT, equation based on anaerobic threshold; RCP, equation based on respiratory compensation point; SOM, equation based on somatic variables only; R2, adjusted R2; RMSE, root mean square error; MAE, mean absolute error (mL·min–1·kg–1); VO2max, maximal oxygen uptake relative to body mass (mL·min–1·kg–1); rVO2AT, oxygen uptake at anaerobic threshold relative to body mass (mL·min–1·kg–1); SPEEDAT, velocity at anaerobic threshold (km·h–1); FFM, fat free mass (kg); VEAT, pulmonary ventilation at anaerobic threshold (L·min–1); HRAT, heart rate at anaerobic threshold (beats·min–1); BF, body fat (%); rVO2RCP, oxygen uptake at respiratory compensation point relative to body mass (mL·min–1·kg–1); SPEEDRCP, velocity at respiratory compensation point (km·h–1).
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86291/elife-86291-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx
-
Source code 1
Source code in Python for transforming files in the database.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86291/elife-86291-code1-v2.zip
-
Reporting standard 1
TRIPOD checklist.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86291/elife-86291-repstand1-v2.docx





