Structure of the Calvin-Benson-Bassham sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase from the model microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Figures
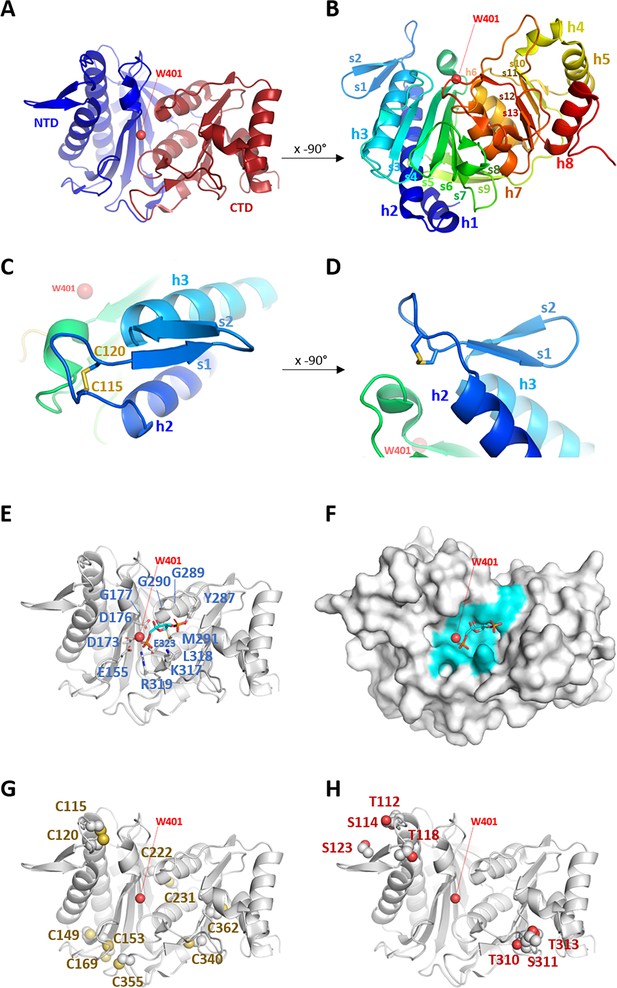
Crystal structure of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase).
(A) Topology is displayed as cartoon with main chain colored from blue (amino-terminus) to red (carboxy-terminus). (B) Rotated view of A. by x-axis over –90°. (C) Close-up view of region A113SCAGTAC120 with disulfide bond shown in sticks. (D) Rotated view of C. by x-axis over –90°. (E) Putative active site residues inferred from alignment with fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) bound to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) (5l0a, human muscle fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase E69Q mutant in active R-state in complex with fructose-1,6-bisphosphate) are represented in sticks. Residue numbering is according to Chlamydomonas sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase (SBPase) Uniprot entry P46284. (F) Surface representation in the B. orientation with putative active site residues colored in cyan. Water molecule 401 (W401) oxygen is represented as a red sphere. (G) Cysteines site chains are represented in spheres. (H) Threonines and serines side chains reported to be the target of phosphorylations are represented in spheres.
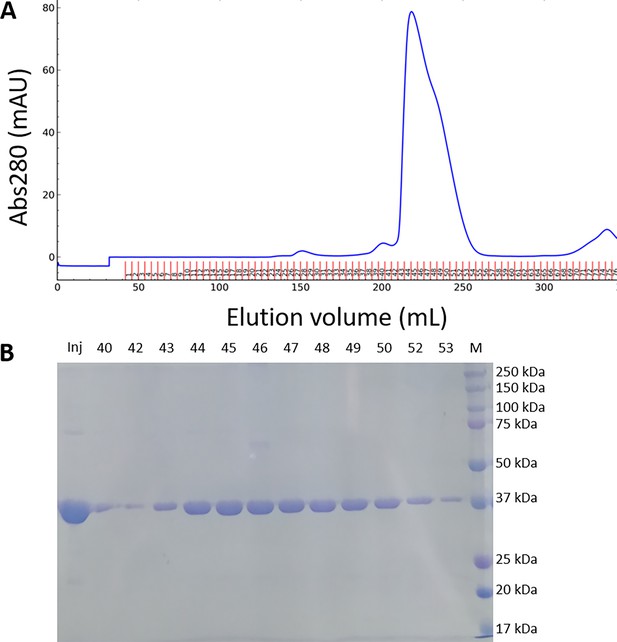
Purification of recombinant Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase).
(A) Size-exclusion chromatography profile recorded at absorbance λ=280 nm on Superdex 200 26/600 GL column. (B) Electrophoresis of affinity-chromatography fractions on 12% acrylamide gel in denaturing and reducing conditions. Gel was stained with Coomassie blue. Mw: molecular mass standards ladder.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Original gel image shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/87196/elife-87196-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.tif
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Original gel image shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 1B (labelled).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/87196/elife-87196-fig1-figsupp1-data2-v1.tif
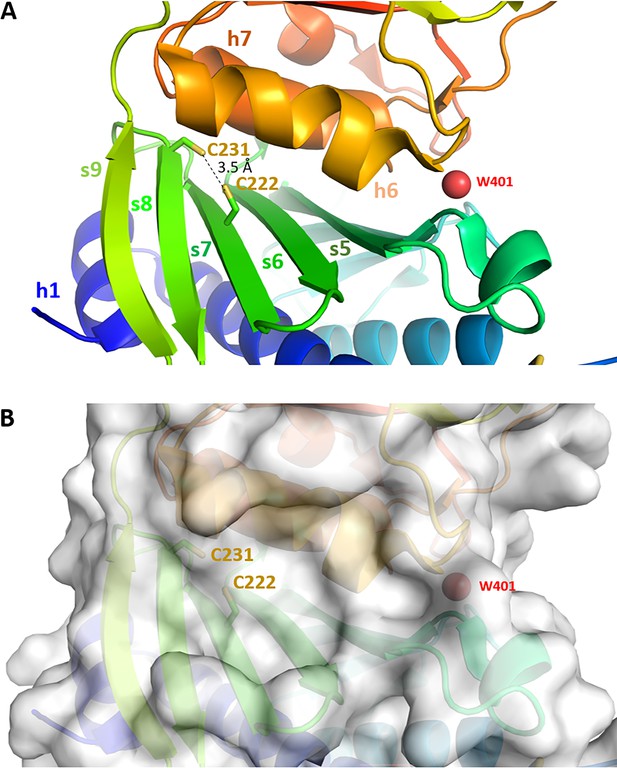
Cysteines pair C222-C231 close-up view.
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) structure 7b2o zoomed around the pair of cysteines 222 and 231 suggests they may form a reversible disulfide bridge, with a thiol-to-thiol distance of 3.5 Å.
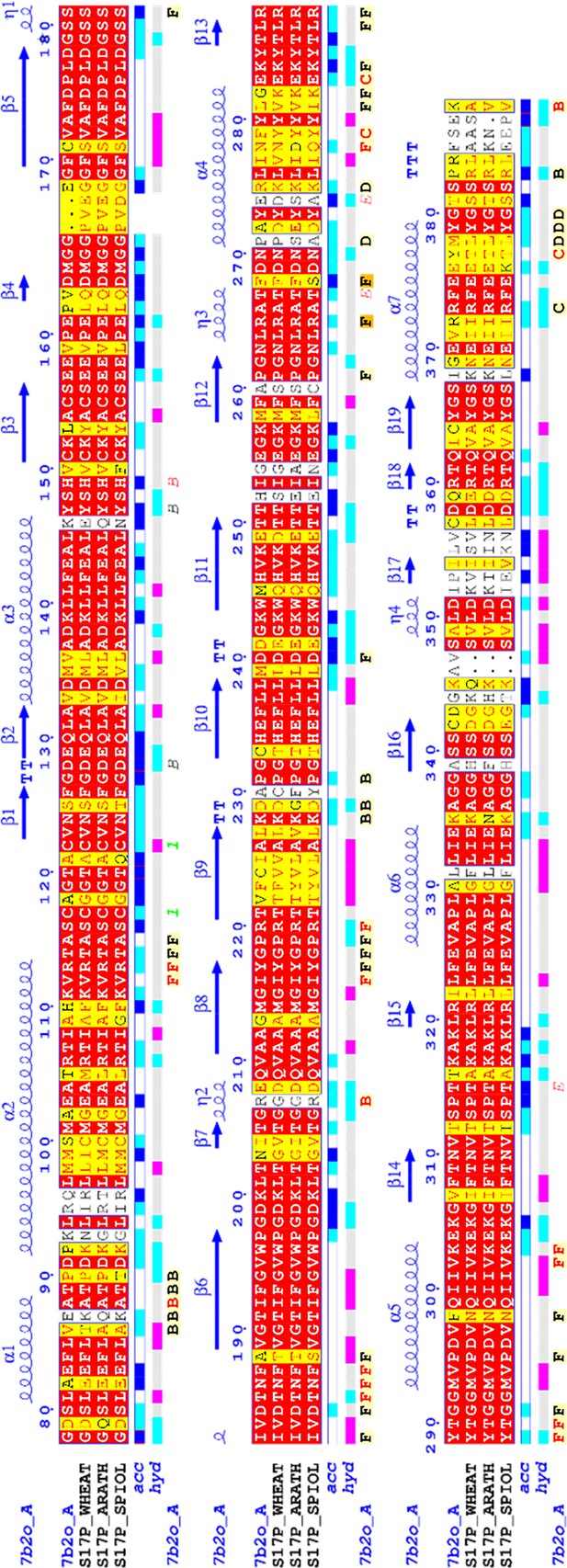
Sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase (SBPase) multiple sequences alignment.
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) mature sequence was used for a BLAST search. Retrieved homolog sequences were aligned and colored-coded according to residue conservation. Illustration made with EndScript (Robert and Gouet, 2014).
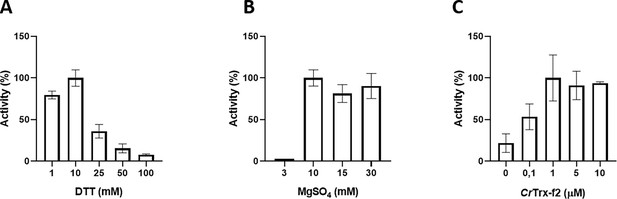
Functional characterization of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) in vitro.
Reported enzymatic activity of CrSBPase assayed for (A) reduction by reduced dithiothreitol (DTTred) and 10 mM of MgSO4, (B) Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) and 10 mM DTTred, and (C) recombinant thioredoxin f2 from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (CrTRX-f2) and 10 mM MgSO4, 1 mM DTT.
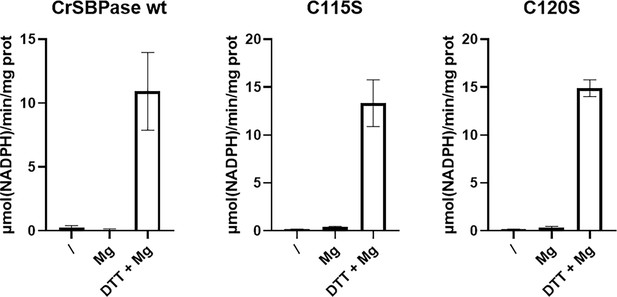
Regulatory properties of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) activity.
Specific activities of wild-type form (wt) and cysteine mutants (C115S and C120S) were evaluated by treating each CrSBPase form without DTT and Mg2+ (/), with only Mg2+ (Mg), or with both DTT and Mg2+ (DTT +Mg). Specific activities are reported as µmol(NADPH) min–1 mg(SBPase)–1.
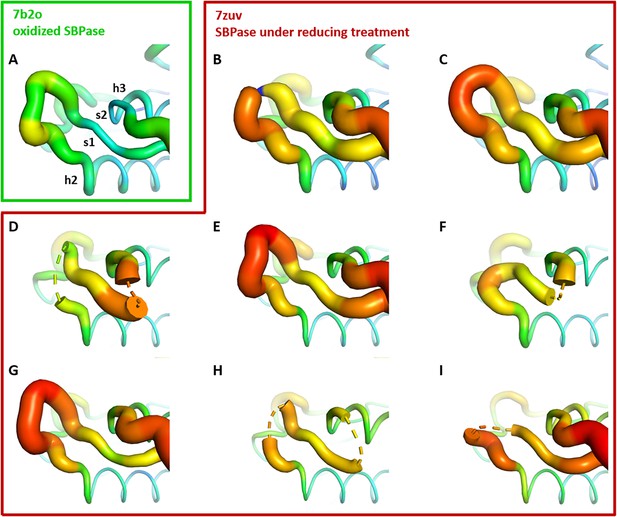
Crystallographic structures of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) under reducing treatment: Local disorder of the A113SCAGTAC120 loop.
Main chain was traced according to crystallographic b-factor, with large orange sections representing high b-factor values and thin blue sections representing low b-factors. (A-I). Aligned structures of CrSBPase protomers without redox treatment (A, 7b2o chain A) or in the presence of 10 mM TCEP reducing agent (B-I, 7zuv chains A-H).
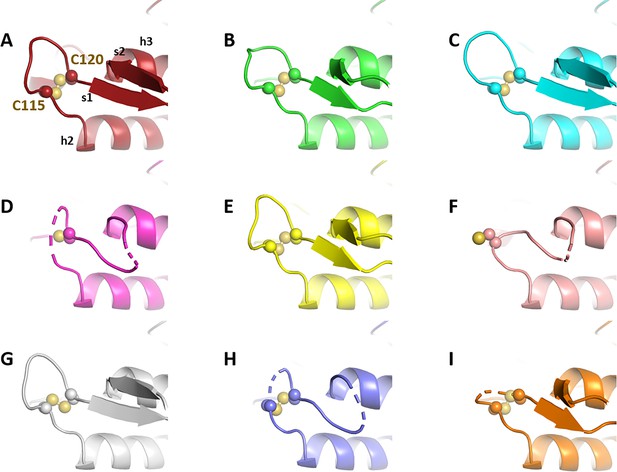
Crystallographic structures of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) under reducing treatment: Local main chain rearrangement and variety of cysteine states of the A113SCAGTAC120 loop.
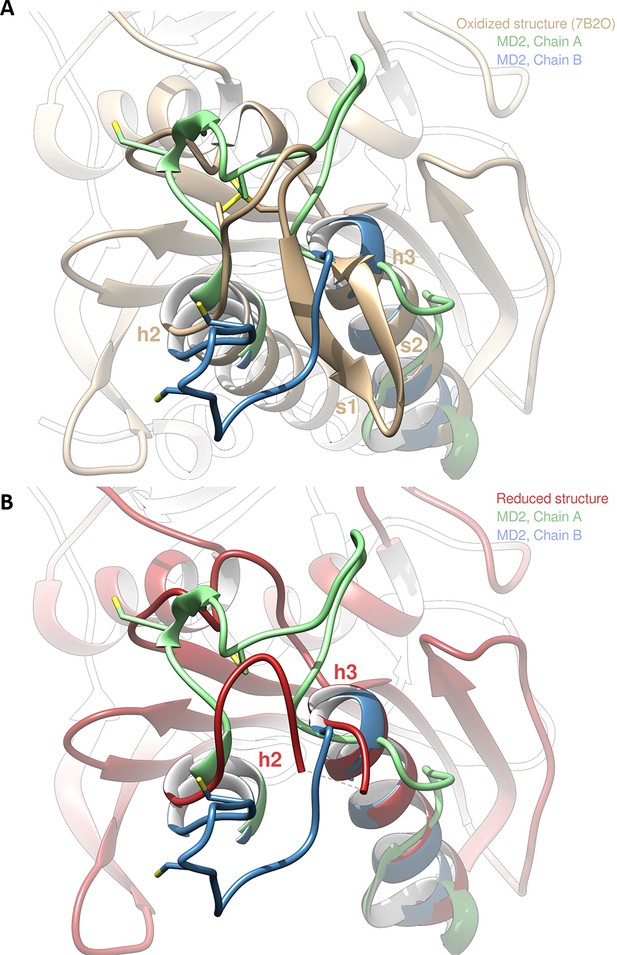
Molecular dynamics simulation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) after reduction.
(A) Overlap of the crystallographic structure of oxidized CrSBPase and representative structures of equilibrated reduced CrSBPase during molecular dynamics simulation 2 (MD2). For structures extracted from MD, only residues 109–148 are displayed since most of the other residues closely overlap those of the crystallographic structure. (B) Overlap of the crystallographic structure of reduced CrSBPase and representative structures of equilibrated reduced CrSBPase during MD2. For structures extracted from MD, only residues 109–148 are displayed.
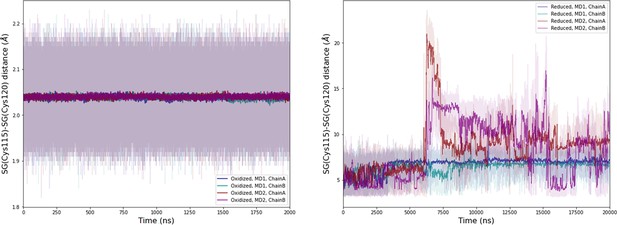
Computational detail of molecular dynamic simulation: SG(Cys115)/SG(Cys120) distances along the molecular dynamics (MD) trajectories for each chain (left: oxidized state, right: reduced state).
Light colors: raw data saved every 100 ps, dark colors: moving average on 20 ns blocs.
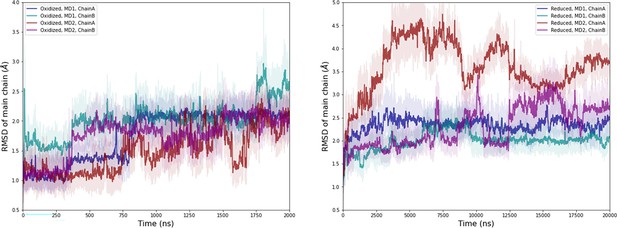
Computational detail of molecular dynamic simulation: RMSD of main chain along the molecular dynamics (MD) trajectories for each chain (left: oxidized state, right: reduced state).
Light colors: raw data saved every 100 ps, dark colors: moving average on 20 ns blocs.
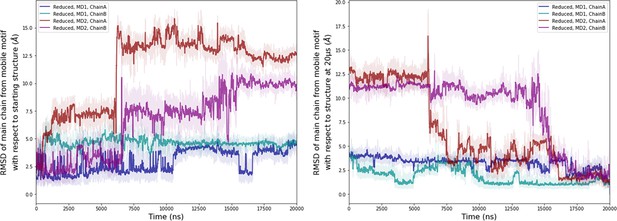
Computational detail of molecular dynamic simulation.
RMSD of main chain of the mobile motif in the reduced state (residues 112–131) along the molecular dynamics (MD) trajectories for each chain (left: RMSD with respect to the starting conformation of MD, right: RMSD with respect to the conformation at 20 µs). Light colors: raw data saved every 100 ps, dark colors: moving average on 20 ns blocs.
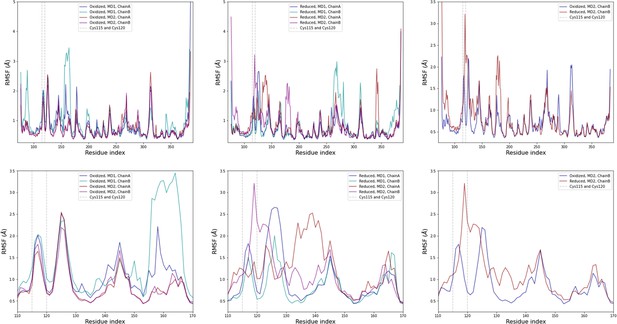
Computational detail of molecular dynamic simulation: RMSF per residue for each chain (top row: full sequence, bottom row: zoom on residues 110–170; left column: oxidized state, middle column: reduced state, right column: comparison of one chain from each state).
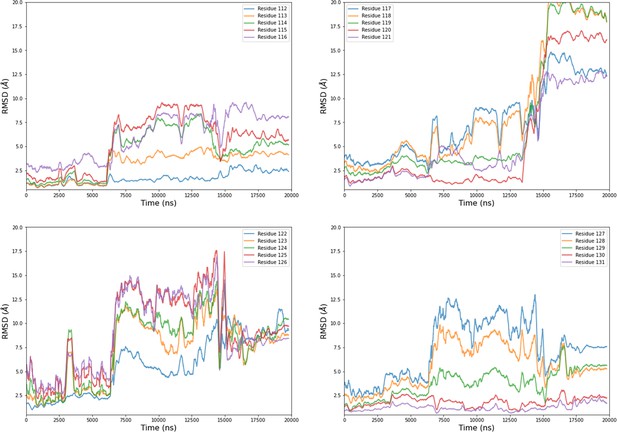
Computational detail of molecular dynamic simulation: RMSD of main chain of each residue from the mobile motif along the trajectory of chain B from MD2.
Data are moving average on 200 ns blocs.
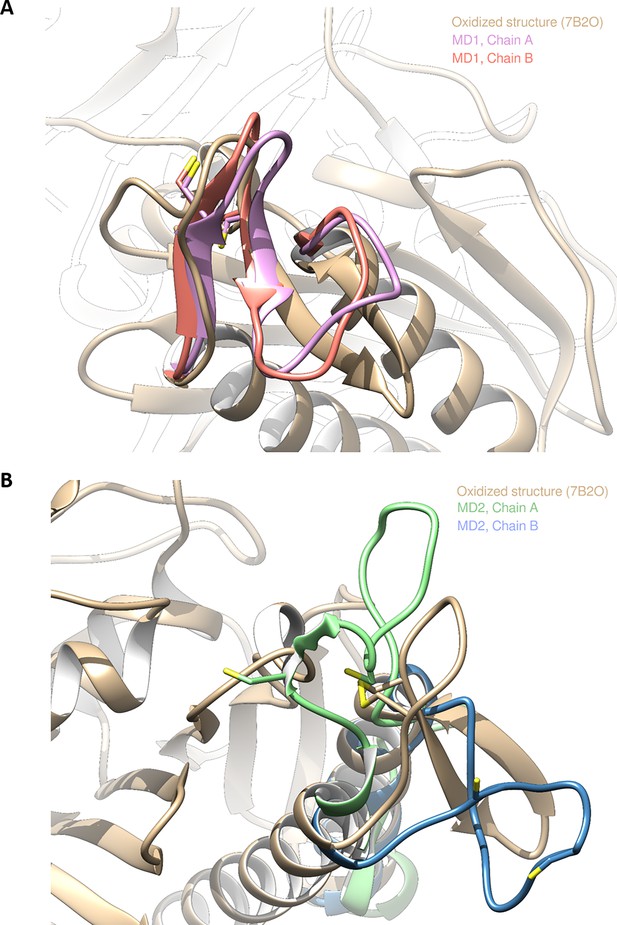
Structures of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) retrieved from molecular dynamics simulations 1 and 2.
Two independent replicas of 20 µs were performed. In one of them (MD1), the overall structure of both chains of the enzyme barely changed. To illustrate this, we present the overlap between the crystallographic oxidized structure and representative structures extracted from molecular dynamics (MD) (based on clustering the last 3 µs since each chain does not display significative changes after 17 µs). (A) Overlap of the crystallographic structure of oxidized CrSBPase and representative structures of equilibrated reduced sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase (SBPase) during MD1. For structures extracted from MD, only residues 111–132 are displayed since the other residues are closely overlapping those of the crystallographic structure. (B) Overlap of the crystallographic structure of oxidized SBPase and representative structures of equilibrated reduced CrSBPase during MD2. For structures extracted from MD, only residues 109–148 are displayed since most of the other residues are closely overlapping those of the crystallographic structure.
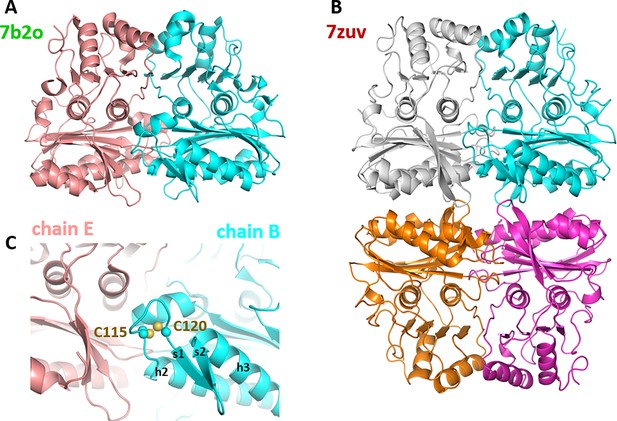
Oligomeric state of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) in the crystal.
(A) Asymmetric unit dimer of untreated CrSBPase (7b2o). Chains are represented in cartoon and colored cyan (chain B) and salmon (chain E). (B) Asymmetric unit homotetramer under reducing treatment (7zuv). Chains A (cyan), C (magenta), F (white), and H (orange) belong to the same asymmetric unit. (C) Close-up view on figure A homodimer interface. Loop 113-ASCAGTAC-120 from chain B (in cyan) is in 5 Å distance of neighboring chain E (in salmon). C115 and C120 are bonded by a disulfide bridge.
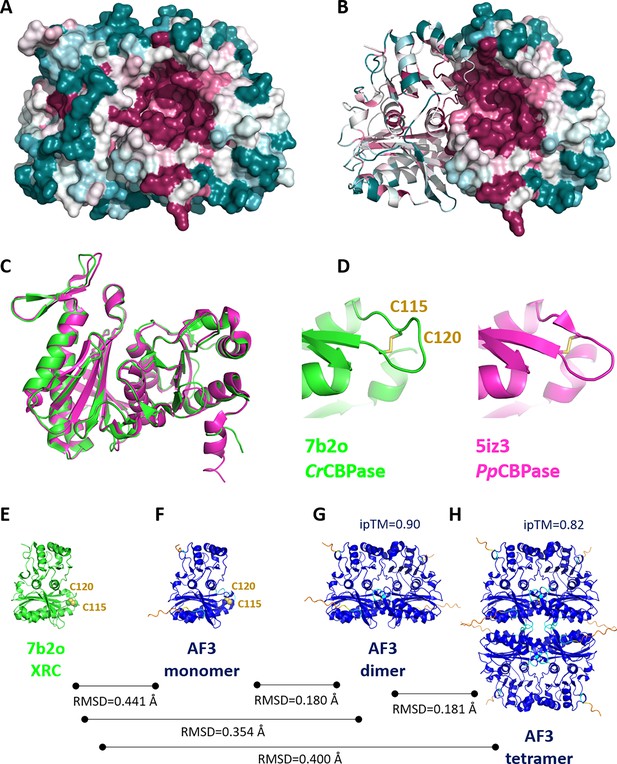
Structure, oligomerisation and sequence variations according to X-ray crystallography and AlphaFold predictions.
Surface representation of 7b2o homodimer, colored according to ConSurf (Glaser et al., 2003) conservation score from teal (lowest conservation) to purple (highest conservation) among 150 aligned homologs. (B) Hybrid cartoon and surface representation, colored according to ConSurf. (C) Superimposition of the crystal structure of PpSBPase (5iz3) (Gütle et al., 2016) and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) (7b2o, this study). (D) Close-up view on redox motif on superimposed SBPases. (E-H) Aligned chain A from 7b2o crystal structure and predicted monomer/dimer/tetramer according to AlphaFold3. Color code of AF3 models is according to plDDT: navy blue very high plDDT >90; cyan confident 90>plDDT > 70; yellow low 70>plDDT > 50; orange very low plDDT <50.
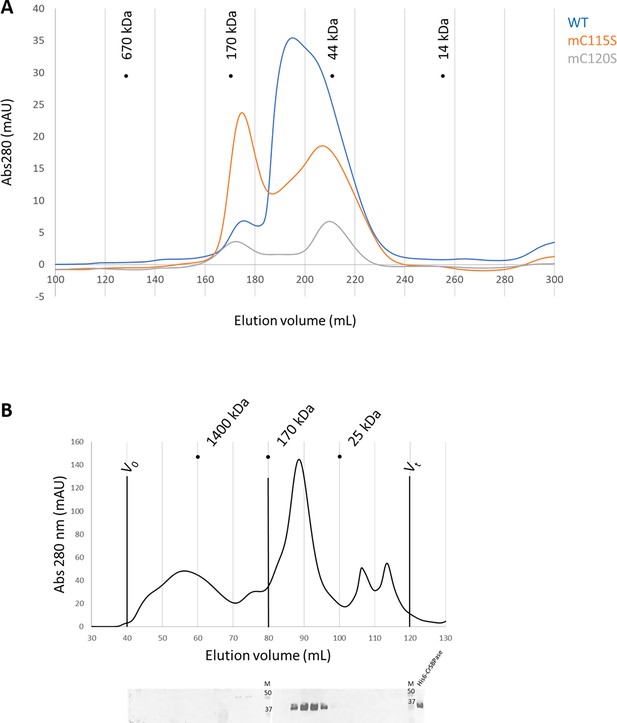
Oligomeric state of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) in vitro.
(A) Size-exclusion chromatograms of CrSBPase wild-type (blue), mutant C115S (orange), mutant C120S (gray) on Superdex 200 26/600 GL column. (B) Size-exclusion fractionation of Chlamydomonas cell extracts. Chlamydomonas cell culture was harvested, lysed and the soluble fraction of the lysate was loaded on Superose6 16/600 size-exclusion column. Chromatography fractions were analyzed by western blot with anti-CrSBPase primary antibodies. First membrane was loaded with fractions eluted from 40 to 80 mL. Second membrane was loaded with fractions eluted from 80 to 120 mL. M lane is loaded with molecular mass standards ladder. Recombinant CrSBPase was loaded on the last lane to the right.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Original western blots shown in Figure 6B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/87196/elife-87196-fig6-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Original western blots shown in Figure 6B (labelled).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/87196/elife-87196-fig6-data2-v1.zip
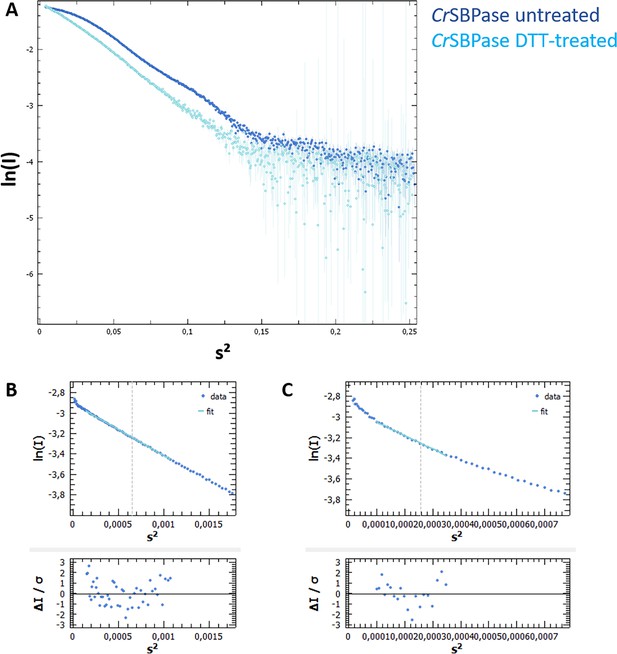
Size-exclusion chromatography coupled to small angle X-rays scattering (SEC-SAXS) of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase).
(A) X-ray scattering curve log(I)=f(s) for pure CrSBPase untreated (dark blue) or treated (light blue) with 10 mM reduced dithiothreitol (DTTred). (B) Radius of gyration of untreated protein was computed by ATSAS Primus Guinier Wizard as Rg = 39.14 ± 0.06 Å (Franke et al., 2017). (C) Radius of gyration of DTT-treated protein was computed as Rg = 62.47 ± 0.38 Å.
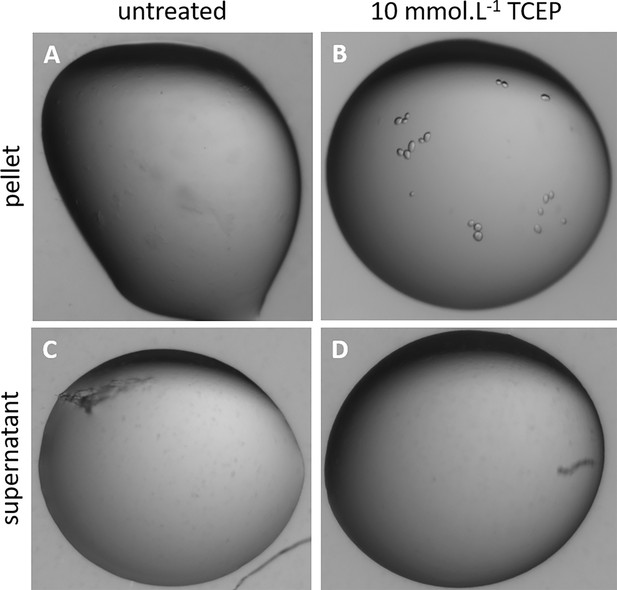
Phase separation of reduced Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) precipitates.
CrSBPase at 2 mg/mL formed amorphous precipitates after storage at 4 °C for a week. The suspension was sedimented by centrifugation at 20,000 g for 20 min and a microliter drop of the supernatant or of the pellet were treated with 10 mM tris-(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) and visualized by binocular optical microscope. (A) Untreated precipitate. (B) TCEP-treated precipitate. (C) Untreated supernatant. (D) TCEP-treated supernatant.
Videos
Molecular dynamics simulation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) 7B2O chain A upon C115-120 disulfide bridge reduction.
Molecular dynamics simulation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii SBPase (CrSBPase) 7B2O chain B upon C115-120 bridge reduction.
Tables
Primers used for point mutagenesis.
| 5'-forward C115S | CCGCACCGCCTCGAGCGCCGGTACCGCCTGCGTG |
|---|---|
| 3'-reverse C115S | CACGCAGGCGGTACCGGCGCTCGAGGCGGTGCGG |
| 5'-forward C120S | GCGCCGGTACCGCCAGCGTGAACAGCTTCGGCG |
| 3'-reverse C120S | CGCCGAAGCTGTTCACGCTGGCGGTACCGGCGC |
Crystallographic data collections and models building statistics.
| 7b2o (untreated) | 7zuv (partially reduced) | |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.9801 | 0.9801 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 46.62–3.095 (3.206–3.095) | 48.54–3.11 (3.221–3.11) |
| Space group | P 21 21 2 | P 1 21 1 |
| Unit cell (Å, °) | 178.224 183.652 75.196 90 90 90 | 53.774 163.462 172.765 90 91.939 90 |
| Total reflections | 615155 (55989) | 376091 (32376) |
| Unique reflections | 45740 (4245) | 53456 (5213) |
| Multiplicity | 13.4 (12.9) | 7.0 (6.2) |
| Completeness (%) | 99.34 (94.20) | 99.65 (97.17) |
| Mean I/sigma (I) | 12.02 (1.72) | 8.54 (1.30) |
| Wilson B-factor (Ų) | 64.82 | 68.45 |
| R-merge | 0.495 (1.877) | 0.2492 (1.502) |
| R-meas | 0.5144 (1.954) | 0.2691 (1.64) |
| R-pim | 0.1386 (0.5343) | 0.1009 (0.6477) |
| CC1/2 | 0.983 (0.623) | 0.988 (0.479) |
| CC* | 0.996 (0.876) | 0.997 (0.805) |
| Reflections used in refinement | 45607 (4242) | 53417 (5193) |
| Reflections used for R-free | 1986 (183) | 1983 (191) |
| R-work | 0.1942 (0.3071) | 0.1963 (0.3239) |
| R-free | 0.2390 (0.3482) | 0.2328 (0.3740) |
| CC (work) | 0.944 (0.788) | 0.956 (0.726) |
| CC (free) | 0.912 (0.649) | 0.949 (0.596) |
| Number of non-hydrogen atoms | 14194 | 18714 |
| Macromolecules | 14190 | 18704 |
| Solvent | 4 | 10 |
| Protein residues | 1859 | 2451 |
| RMS (bonds) (Å) | 0.005 | 0.004 |
| RMS (angles) (°) | 0.75 | 0.73 |
| Ramachandran favored (%) | 94.26 | 94.80 |
| Ramachandran allowed (%) | 5.52 | 4.70 |
| Ramachandran outliers (%) | 0.22 | 0.50 |
| Rotamer outliers (%) | 0.13 | 0.55 |
| Clashscore | 4.88 | 6.60 |
| Average B-factor (Ų) | 67.00 | 68.41 |
| Macromolecules (Ų) | 67.01 | 68.40 |
| Solvent (Ų) | 49.59 | 94.37 |
-
Statistics for the highest-resolution shell are shown in parentheses.





