Novel risk loci for COVID-19 hospitalization among admixed American populations
Figures
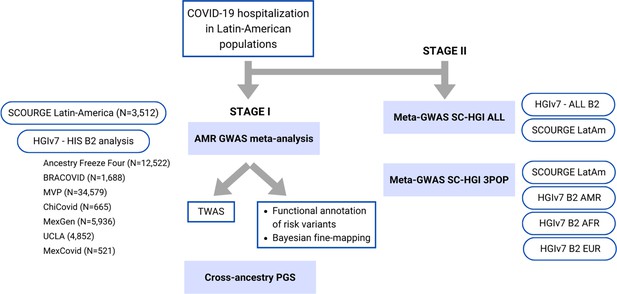
Flow chart of this study.
Stage I of the study involved a meta-analysis of the Latin American genome-wide association studies (GWAS) from SCOURGE and the COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative. The resulting meta-analysis was leveraged to prioritize genes by using a transcriptome-wide association study (TWAS), Bayesian fine-mapping and functional annotations, and to assess the generalizability of polygenic risk score (PGS) cross-population models in Latin Americans. Stage II involved two additional cross-population GWAS meta-analyses to further investigate the replicability of findings.
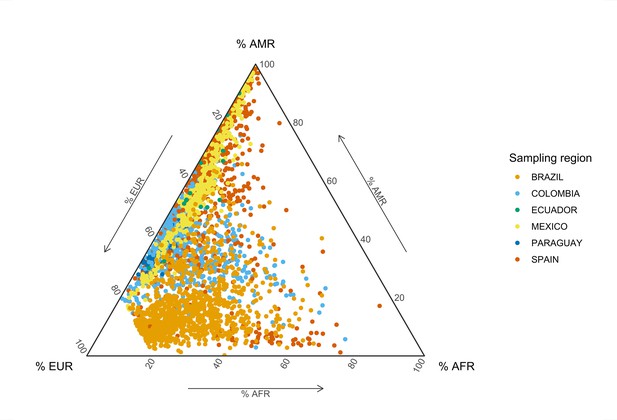
Global genetic inferred ancestry (GIA) composition in the SCOURGE Latin American cohort.
European (EUR), African (AFR), and Native American (AMR) GIA was derived with ADMIXTURE from a reference panel composed of Aymaran, Mayan, Nahuan, and Quechuan individuals of Native American genetic ancestry and randomly selected samples from the EUR and AFR 1KGP populations. The colors represent the different geographical sampling regions from which the admixed American individuals from SCOURGE were recruited.
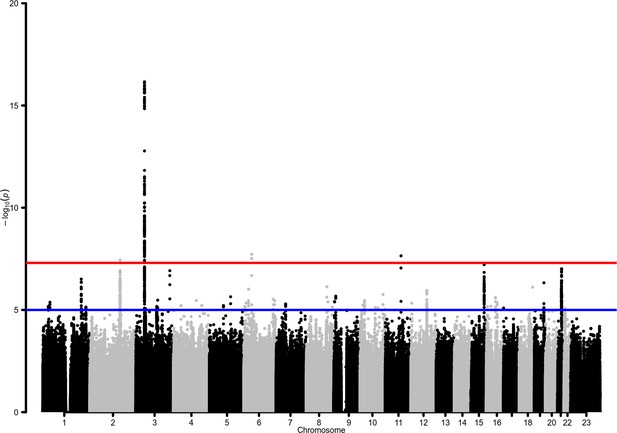
Manhattan plot for the admixed AMR genome-wide association studies (GWAS) meta-analysis.
Probability thresholds at p=5 × 10–8 and p=5 × 10–5 are indicated by the horizontal lines. Genome-wide significant associations with COVID-19 hospitalizations were found on chromosome 2 (within BAZ2B), chromosome 3 (within LZTFL1), chromosome 6 (within FOXP4), and chromosome 11 (within DDIAS).
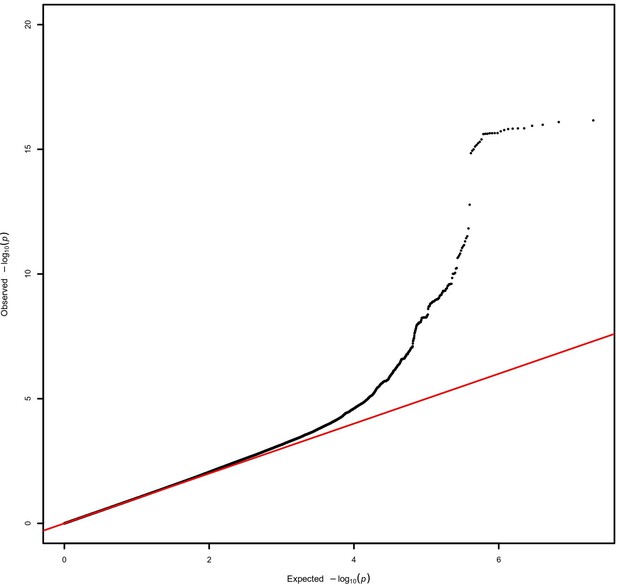
Quantile–quantile plot for the AMR genome-wide association studies (GWAS) meta-analysis.
A lambda inflation factor of 1.015 was obtained.
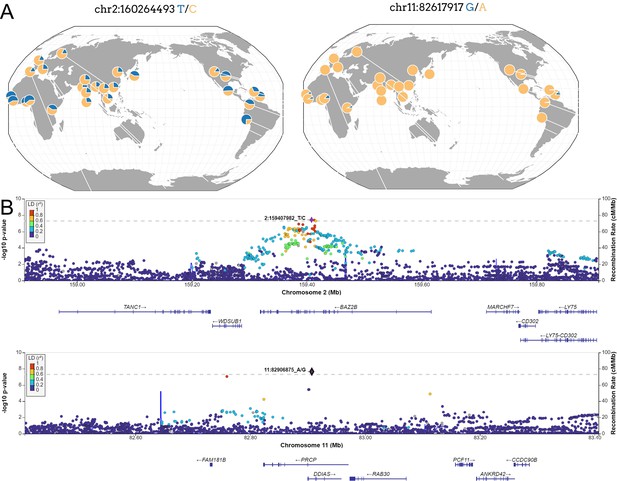
New loci associated with COVID-19 hospitalization in Admixed american populations.
(A) Regional association plots for rs1003835 at chromosome 2 and rs77599934 at chromosome 11. (B) Allele frequency distribution across the 1000 Genomes Project populations for the lead variants rs1003835 and rs77599934. Retrieved from The Geography of Genetic Variants Web or GGV.
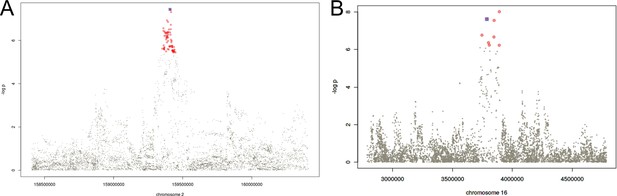
Regional association plots for the fine mapped loci in chromosomes 2 (A) and 16 (B).
Colored in red, the variants allocated to the credible set at the 95% confidence according to the Bayesian fine mapping. In blue, the sentinel variant.
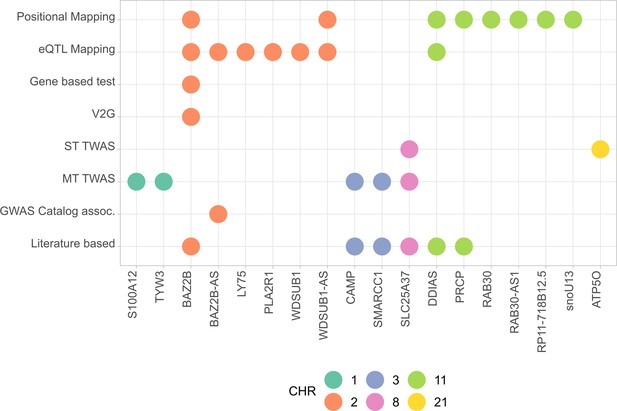
Summary of the results from gene prioritization strategies used for genetic associations in AMR populations.
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) catalog association for BAZ2B-AS was with FEV/FCV ratio. Literature-based evidence is further explored in ‘Discussion’.
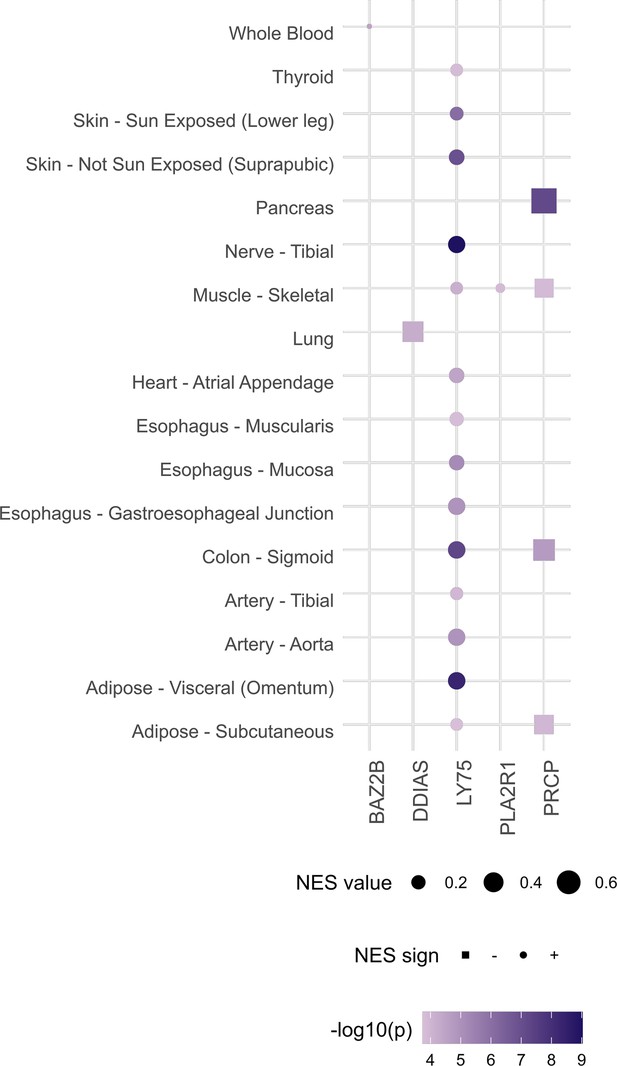
Gene‒tissue pairs for which either rs1003835 or rs60606421 are significant expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) at false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 (data retrieved from https://gtexportal.org/home/snp/).
rs1003835 (chromosome 2) maps to BAZ2B, LY75, and PLA2R1 genes. As for the lead variant of chromosome 11, rs77599934, since it was not an eQTL, we used an LD proxy variant (rs60606421). DDIAS and PRCP genes map closely to this variant. NES and p-values correspond to the normalized effect size (and direction) of eQTL-gene associations and the p-value for the tissue, respectively.
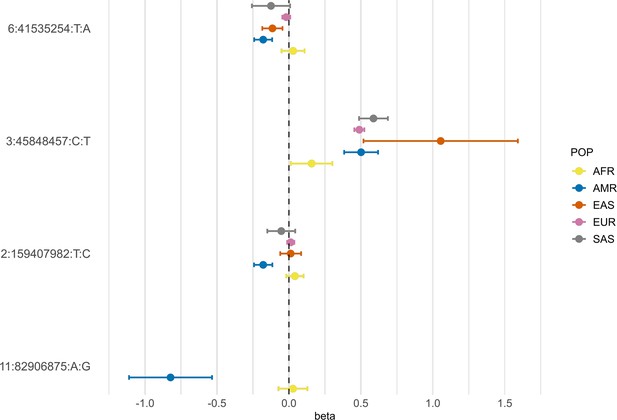
Forest plot showing effect sizes and the corresponding confidence intervals for the sentinel variants identified in the AMR meta-analysis across populations.
All beta values with their corresponding CIs were retrieved from the B2 population-specific meta-analysis from the HGI v7 release, except for AMR, for which the beta value and IC from the HGIAMR-SCOURGE meta-analysis are represented.
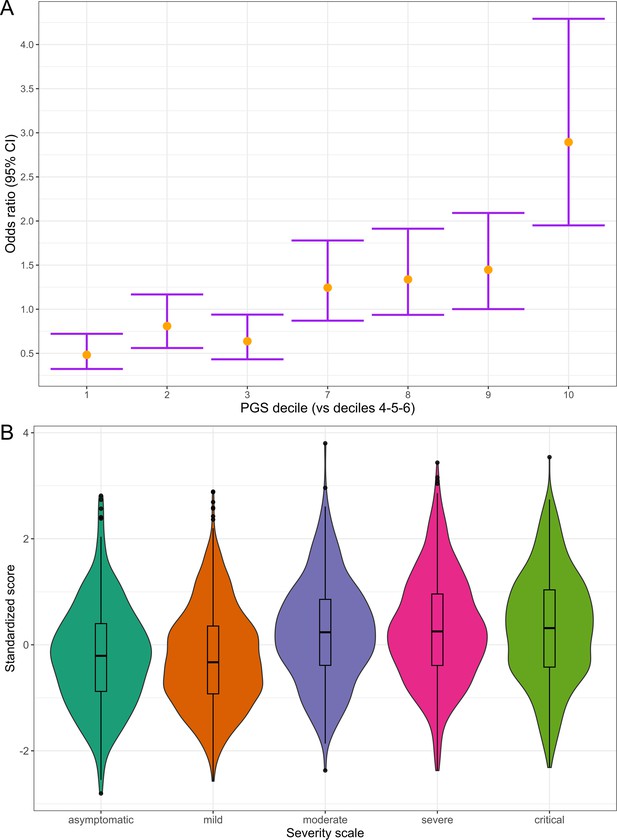
Polygenic risk distribution for COVID-19 hospitalization.
(A) Polygenic risk stratified by polygenic risk score (PGS) deciles comparing each risk group against the lowest risk group (OR–95% CI). (B) Distribution of the PGS in each of the severity scale classes. 0, asymptomatic; 1, mild disease; 2, moderate disease; 3, severe disease; 4, critical disease.
Tables
Demographic characteristics of the SCOURGE Latin American cohort.
| Variable | Non-hospitalized (N = 1887) | Hospitalized(N = 1625) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean years ±SD | 39.1 ± 11.9 | 54.1 ± 14.5 | |
| Sex, N (%) | |||
| Female (%) | 1253 (66.4) | 668 (41.1) | |
| Global genetic inferred ancestry, % mean ± SD | |||
| European | 54.4 ± 16.2 | 39.4 ± 20.7 | |
| African | 15.3 ± 12.7 | 9.1 ± 11.6 | |
| Native American | 30.3 ± 19.8 | 51.3 ± 26.5 | |
| Comorbidities, N (%) | |||
| Vascular/endocrinological | 488 (25.9) | 888 (64.5) | |
| Cardiac | 60 (3.2) | 151 (9.3) | |
| Nervous | 15 (0.8) | 61 (3.8) | |
| Digestive | 14 (0.7) | 33 (2.0) | |
| Onco-hematological | 21 (1.1) | 48 (3.00) | |
| Respiratory | 76 (4.0) | 118 (7.3) | |
Lead independent variants in the admixed AMR genome-wide association studies (GWAS) meta-analysis.
| SNP rsID | chr:pos | EA | NEA | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | EAF cases | EAF controls | Nearest gene | Mamba PPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs13003835 | 2:159407982 | T | C | 1.20 (1.12–1.27) | 3.66E-08 | 0.563 | 0.429 | BAZ2B | 0.30 |
| rs35731912 | 3:45848457 | T | C | 1.65 (1.47–1.85) | 6.30E-17 | 0.087 | 0.056 | LZTFL1 | 0.95 |
| rs2477820 | 6:41535254 | A | T | 0.84 (0.79–0.89) | 1.89E-08 | 0.453 | 0.517 | FOXP4-AS1 | 0.18 |
| rs77599934 | 11:82906875 | G | A | 2.27 (1.7–3.04) | 2.26E-08 | 0.016 | 0.011 | DDIAS | 0.95 |
-
EA: effect allele; NEA: noneffect allele; EAF: effect allele frequency in the SCOURGE study; PPR: posterior probability of replicability.
Novel variants in the SC-HGIALL and SC-HGI3POP meta-analyses (with respect to HGIv7).
Independent signals after LD clumping.
| SNP rsID | chr:pos | EA | NEA | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Nearest gene | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs76564172 | 16:3892266 | T | G | 1.31 (1.19–1.44) | 9.64E-09 | CREBBP | SC-HGI3POP |
| rs66833742 | 19:4063488 | T | C | 0.94 (0.92–0.96) | 1.89E-08 | ZBTB7A | SC-HGI3POP |
| rs66833742 | 19:4063488 | T | C | 0.94 (0.92–0.96) | 2.50E-08 | ZBTB7A | SC-HGIALL |
| rs2876034 | 20:6492834 | A | T | 0.95 (0.93–0.97) | 2.83E-08 | CASC20 | SC-HGIALL |
-
EA: effect allele; NEA: non-effect allele.
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial assay or kit | Chemagic DNA Blood 100 kit | PerkinElmer Chemagen Technologies GmbH | ||
| Software, algorithm | Axiom Analysis Suite | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Version 4.0.3.3 | |
| Software, algorithm | PLINK | Purcell et al., 2007; https://www.cog-genomics.org/plink/ | RRID:SCR_001757 | Version 1.9; v2 |
| Software, algorithm | TOPMed Imputation Server | https://imputation.biodatacatalyst.nhlbi.nih.gov/ | Version 2 | |
| Software, algorithm | ADMIXTURE | Alexander et al., 2009; https://dalexander.github.io/admixture/ | RRID:SCR_001263 | Version 1.3.0 |
| Software, algorithm | SAIGEgds | Zheng and Davis, 2021; https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/SAIGEgds.html | Version 1.10.0 | |
| Software, algorithm | METAL | Willer et al., 2010; https://csg.sph.umich.edu/abecasis/metal/ | RRID:SCR_002013 | Version 2011-03-25 |
| Software, algorithm | FUMA | Watanabe et al., 2017; https://fuma.ctglab.nl/ | RRID:SCR_017521 | Version 1.5.2 |
| Software, algorithm | MAMBA | McGuire et al., 2021; https://github.com/dan11mcguire/mamba | Version 1 | |
| Software, algorithm | S-PrediXcan; S-MultiXcan | Barbeira et al., 2018; https://github.com/hakyimlab/MetaXcan | RRID:SCR_016739 | Version 1 |
| Software, algorithm | GTEx v8 mashr prediction models | https://predictdb.org/post/2021/07/21/gtex-v8-models-on-eqtl-and-sqtl/ | ||
| Other | GWAS Catalog | https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/ | RRID:SCR_012745 | Section ‘Definition of the genetic risk loci and putative functional impact’ |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Participating centers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Independent variants with p-value<1 × 10–05 in the SC-HGI_AMR GWAS meta-analysis (hg38).
EA: effect allele; NEA: non-effect allele; EAF: effect allele frequency; EAF_avg: averaged effect allele frequency; FreqSE: standard error of averaged effect allele frequency; SCOURGE_AMR: SCOURGE Latin-America; HGIB2_AMR: HGI meta-analysis of AMR studies.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Annotated SNPs in moderate-to-strong LD with lead SNPs of the genome-wide significant loci in the SC-HGI_AMR GWAS meta-analysis, with ANNOVAR.
NEA: non-effect allele; EA: effect allele; r2: maximum r2 of the SNP with one of the independent SNPs; IndSigSNP: the independent SNP which has the maximum r2 value with the SNP; dist: distance to the nearest gene; func: functional consequence of the SNP on the gene; CADD: CADD score; RDB: RegulomeDB score; minChrState: the minimum 15-core chromatin state across 127 tissues/cell types; commonChrState: the most common 15-core chromatin state across 127 tissues/cell types; posMapFilt: 1 if the SNP was used for positional mapping, 0 otherwise; eqtlMapFilt: 1 if the SNP was used for eQTL mapping, 0 otherwise.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Results from the MAGMA gene-based analysis in the SC-HGI_AMR GWAS meta-analysis (hg37).
NSNPS: number of SNPs in the gene; NPARAM: the number of relevant parameters used in the model; ZSTAT: z statistics.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp4-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Prioritized genes by eQTL and positional mapping by FUMA in the SC-HGI_AMR GWAS meta-analysis results (hg37).
HUGO: HGNC gene symbol; pLI: pLI score from ExAC database, probability of being intolerant to loss of function (higher the score, higher the intolerance); ncRVIS: non-coding residual variation intolerance score (higher the score, higher intolerance to non-coding variation); posMapSNPs: number of SNPs mapped by positional mapping; posMapMaxCADD: the maximum CADD score of mapped SNPs by positional mapping; eqtlMapSNPS: the number of SNPs mapped to the genes based on eQTL mapping; eqtlMapminP: the minimum eQTL p-value of mapped SNPs; eqtlMapminQ: the minimum eQTL FDR of mapped SNPs; eqtlMapts: tissue of mapped eQTLs; eqtlDirection: consequential direction of mapped eQTL SNPs after aligning the risk alleles; minGwasP: minimum GWAS p-value of mapped eQTLs; IndSigSNPs: independent SNPs that are in LD with the mapped SNPs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp5-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
Fine-mapped credible set derived with corrcoverage (95%) for the associated region in chromosome 2 (BAZ2B).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp6-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 7
VEP annotations for the variants included in the fine-mapped credible sets for the novel associated loci in chromosome 2 (hg38).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp7-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 8
V2G scores for the variants included in the fine-mapped credible sets in the novel risk loci from chromosomes 2 and 16 (hg38).
Shaded in green, the prioritized gene by the V2G score.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp8-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 9
MultiXcan results for the SC-HGI_AMR GWAS meta-analysis.
N: number of tissues available for the gene; n_indep: number of independent components of variation kept among the tissues' predictions; p_i_best: best p-value of single tissue S-prediXcan association; t_i_best: name of best single tissue S-prediXcan association; p_i_worst: worst p-value of single tissue S-prediXcan association; t_i_worst: name of worst single tissue S-prediXcan association; eigen_max: eigenvalue of the top independent component in the SVD decomposition of predicted expression correlation; eigen_min: eigenvalue of the last independent component in the SVD decomposition of predicted expression correlation; eigen_min_kept: eigenvalue of the smallest independent component that was kept in the SVD decomposition of predicted expression correlation; z_min: minimum z-score among single-tissue S-prediXcan associations; z_max: maximum z-score among single-tissue S-prediXcan associations; z_mean: mean z-score among single tissue S-prediXcan associations; z_sd: standard deviation of the mean z-score among single-tissue S-prediXcan associations; tmi: trace of T*T', where T is the correlation of predicted expression levels for different tissues multiplied by its SVD pseudo-inverse and is an estimate for the number of independent components of variation in predicted expression across tissues.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp9-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 10
Top 10 genes for the TWAS trained with the GALA II-SAGE models in admixed Americans.
Bonferroni correction thresholds: Pooled p<4.19E-06; PR p<4.99E-06; MX p<5.19E-06; AA p<4.67E-06. Var_g: variance of the gene expression; pred_perf_r2: cross-validated R2 of tissue model’s correlation to gene’s measured transcriptome; pref_perf_qval: qval of tissue model’s correlation to gene’s measured transcriptome; n_snps_used: number of snps from GWAS used in S-prediXcan analysis; n_snp_in_cov: number of snps in the covariance matrix; n_snps_in_model: number of snps in the model; best_gwas_p: the highest p-value from GWAS snps used in this model; largest_weight: the largest weight in this model.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp10-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 11
Independent variants with p-value<1e-05 in the SC-HGI_ALL GWAS meta-analysis (hg38).
EA: effect allele; NEA: non-effect allele; EAF_avg: averaged effect allele frequency; FreqSE: standard error of averaged effect allele frequency.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp11-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 12
Results of the 40 lead variants associated with COVID-19 hospitalization in the HGIv7 (hg38).
SC-HGI_ALL: meta-analysis SCOURGE-HGI_ALL; SC-HGI_AMR: meta-analysis SCOURGE-HGI_AMR; SC-HGI_3POP: meta-analysis SCOURGE-HGI_3POP.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp12-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 13
Independent variants with p-value<1e-05 in the SC-HGI_3POP GWAS meta-analysis (hg38).
EA: effect allele; NEA: non-effect allele; EAF_avg: average effect allele frequency; FreqSE: standard error of averaged effect allele frequency.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp13-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 14
Instruments used in the polygenic risk score model (hg38).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp14-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 15
Multinomial regression results.
Reference class for the multinomial regression is ‘asymptomatic’.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-supp15-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/93666/elife-93666-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





