Exploring the role of the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for immunotherapy and drug resistance
Figures
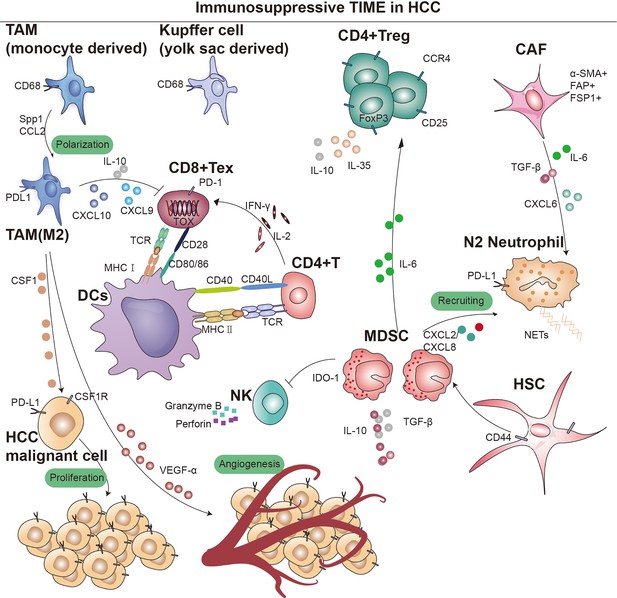
Overview of immunosupressive cells in the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) immune microenvironment.
Key cell types and cellular component implicated in immune surveillance are indicated in this figure. TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; CD4+ Treg, regulatory CD4+ T cells; CD8+ Tex, exhausted CD8+ T cells; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; DCs, dendritic cells; TCR, T-cell receptor; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; MHC I, major histocompatibility complex class I; MHC II, major histocompatibility complex class II.
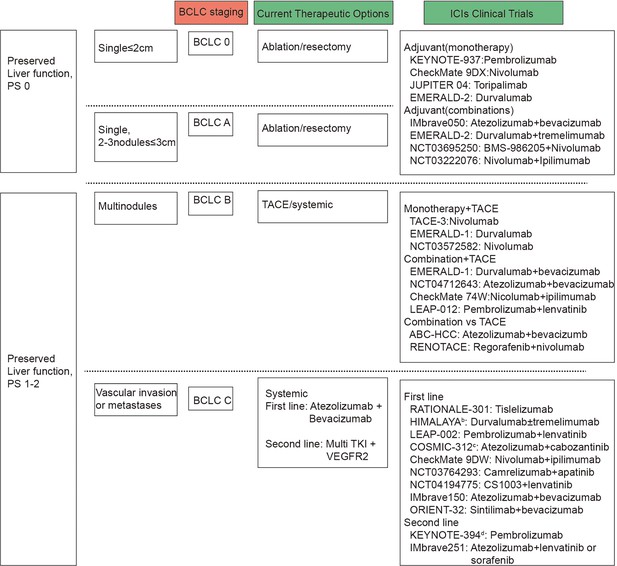
Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) clinical trials by BCLC staging.
BCLC staging are based on tumor number and size, vascular invasion or metastases, preserved liver function and performance status. Presented on the right side of the figure are the clinical trials carried out for patients with liver cancer, categorized according to the BCLC staging system, alongside the primary therapeutic interventions applied.
Tables
Clinical trials of target inhibitors or immune checkpoints in the tumor microenvironment.
| Clinical trial | Phase | Target | Intervention/treatment | State | Output | PMID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-line ICI therapy | IMBrave150(NCT03434379) | III | PD-L1;VEGF | Atezolizumab: 1200 mg IV d1, Q3W Bevacizumab: 15 mg/kg IV d1, Q3W | Completion (Nov 17, 2022) | ORR:27.3% OS:19.2m PFS:6.83m | 34902530 34051880 32402160 |
| ORIENT-32(NCT03794440) | II/III | PD-1;VEGF | Sintilimab: 200 mg IV d1, Q3W IBI305: 15 mg/kg IV d1, Q3W | Completion (Jan 22, 2021) | Not yet posted | 34143971 | |
| CheckMate 459(NCT02576509) | I/II | PD-1 | Nivolumab: Specified dose on specified days | Active | OS:16.39m vs 14.69m ORR:15.4% vs 7.0% PFS:3.68m vs 3.75m | 34914889 | |
| GO30140(NCT02715531) | I | PD-L1;VEGF | 5-FU: 400 mg/m2 IV, followed by 2400 mg/m2 IV, Q2W Atezolizumab: 1200 mg Q3W Bevacizumab: 15 mg/kg Q3W | Completion (May 31, 2021) | OS:17.1m PFS:7.3m | 32502443 | |
| KEYNOTE-524(NCT03713593) | III | VEGFR2 (KDR)/VEGFR3;PD-1 | Lenvatinib: PO, QD Pembrolizumab: 200 mg, Q3W | Active | PFS:8.2 vs 8.1 OS:21.2 vs 19.0 ORR:26.1 vs 17.5 | ||
| RATIONALE 208(NCT03419897) | III | PD-1 | Tislelizumab: 200 mg IV d1, Q3W | Completion (July 6, 2022) | ORR:13.3% OS:13.2m | 36872927 34518988 | |
| Second-line ICI therapy | KEYNOTE-224(NCT02702401) | III | PD-1 | Pembrolizumab: 200 mg IV, Q3W | Completion (Sept 22, 2021) | ORR:18.3% vs 4.4% OS:13.9m vs 10.6m ORR:18.3% vs 4.4% | 31790344 |
| KEYNOTE-240(NCT02702401) | III | PD-1 | Pembrolizumab | Completion (Sept 22, 2021) | PFS:3.0m vs 2.8m OS:13.9m vs 10.6m ORR:18.3% vs 4.4% | 31790344 | |
| CheckMate 040(NCT01658878) | I/II | PD-1 | Nivolumab: IV, on specific days | Active | Not yet posted | 34051329 33001135 32710922 31176752 28434648 | |
| RESCUE(NCT03463876) | II | PD-1;VEGF | SHR-1210: 200 mg IV, Q2W apatinib: 250 mg PO,QD | Completion (Mar 10, 2021) | ORR:34.3% PFS:5.7m | 33087333 | |
| NCT02519348 | II | PD-L1;CTLA-4;VEGF | Tremelimumab 300 mg plus durvalumab 1500 mg, followed by durvalumab 1500 mg Q4W, durvalumab monotherapy 1500 mg Q4W, tremelimumab monotherapy 750 mg Q4W (7doses) and then tremelimumab Q7W, or tremelimumab 75 mg once every 4 weeks plus durvalumab 1500 mg once every 4 weeks (4 doses), followed by durvalumab 1500 mg Q4W | Active | ORR:17.05% PFS:3.52m | 34292792 | |
| NCT01008358 | II | CTLA-4 | Tremelimumab: 15 mg/kg on day 1 of every 90-day cycle | Completion (May 2012) | OS:8.2m | 23466307 | |
| NCT03695250 | I/II | IDO1 PD-1 | IDO1 Inhibitor BMS-986205: PO QD on days 1–14 Nivolumab: IV over 30 min on day 1 | Completion (March 12, 2021) | ORR:12.5% | ||
| NCT02989922 | II | PD-1 | Camrelizumab (3 mg/kg,Q3W) | Completion (June 2019) | OS:13·8m | 32112738 35101942 |





