APOL1 renal risk variants have contrasting resistance and susceptibility associations with African trypanosomiasis
Figures
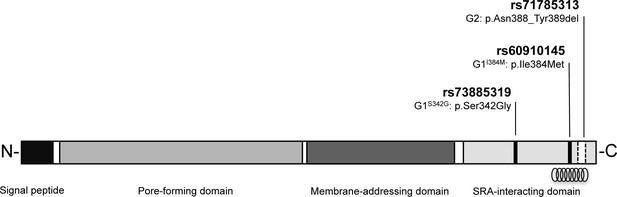
Schematic of G1 and G2 polymorphisms in human apolipoprotein L1.
Human apolipoprotein-L1 (APOL1) is a 398-amino acid protein consisting of a cleavable N-terminal signal peptide, a pore-forming domain, a membrane-addressing domain, and a serum resistance-associated (SRA)-interacting domain. The polymorphisms that characterize the G1 and G2 renal risk variants are located in the SRA-interacting domain, the target site for binding of the SRA protein expressed by the human-infective T.b.rhodesiense parasite, which results in loss of APOL1 lytic function. The location of the critical binding region (residues 370–392) for this interaction is indicated by a helical graphic. G1 consists of two missense SNPs rs73885319 (p.Ser342Gly) and rs60910145 (p.Ile384Met) while the G2 polymorphism, rs71785313 (p.Asn388_Tyr389del), is found on an alternative APOL1 haplotype, and represents an in-frame two amino acid deletion.
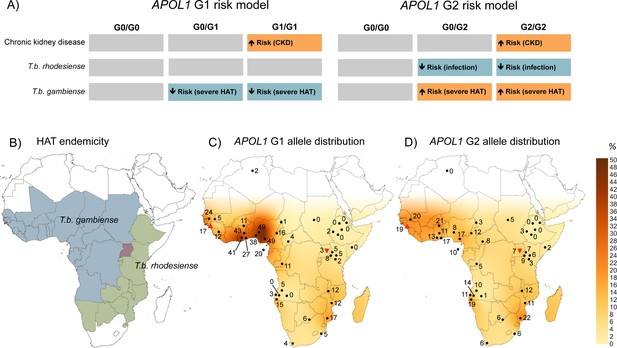
The geographical distribution of human African trypanosomiasis and APOL1 G1 and G2 allele frequencies across sub-Saharan Africa.
(A) The risk model for chronic kidney disease, T.b. rhodesiense infection, and T.b. gambiense disease outcome are summarized for the ancestral G0 APOL1 variant and heterozygous and homozygous carriers of the G1 and G2 variants. The direction of the risk association is indicated by arrow orientation and box colour: orange (increased risk), blue (reduced risk) and grey (no association). (B) WHO defines 36 countries as endemic for HAT, caused by T.b. gambiense in West Africa (blue) and T.b. rhodesiense in East Africa (green). Uganda is the only country endemic for both subspecies, although their distribution does not currently overlap (red). (C) Spatial frequency map of the APOL1 G1 variant. (D) Spatial frequency map of the APOL1 G2 variant. Spatial frequency maps were generated from merged published genotype data available for 40 populations (5287 individuals) in 21 countries (Figure 2—source data 1). Colour gradients illustrating predicted allele frequencies across Africa were extrapolated from available data using the Kriging algorithm in Surfer software version 8. The approximate locations of data points are indicated by filled black circles, a filled red triangle (Guinea study), or an inverted filled red triangle (Uganda study) next to the relative allele frequency, in percentage.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Frequency of APOL1 G1 and G2 variants in African populations.
Where data for G1 allele frequency were unavailable, data are inferred from rs73885319 only. N/A: Data not available, CEPH-HGDP: Centre d’Etude du Polymorphisme Humain - Human Genome Diversity Panel, TCGA-UCL: The Centre for Genetic Anthropology at University College London.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.017
Tables
Association between APOL1 kidney disease risk variants and T.b. rhodesiense infection
| Dominant model - Infection | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOL1 haplotype | T.b.r infected | Control | Association analysis* T.b.r infected/Control | |||
| Number | % | Number | % | OR [95% CI] | P | |
| G0 Ancestral Haplotype rs73885319 (A) + rs60910145 (T) + rs71785313 (TTATAA) | ||||||
| G0 | 184 | 100.0 | 179 | 99.4 | N.C | 0.49 |
| Non-G0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.6 | ||
| Total | 184 | 100.0 | 180 | 100.0 | ||
| G1 Haplotype† rs73885319 (A>G) + rs60910145 (T>G) | ||||||
| G1 | 9 | 4.9 | 12 | 6.7 | 0.73 [0.29 to 1.79] | 0.50 |
| Non-G1 | 173 | 95.1 | 168 | 93.3 | ||
| Total | 182 | 100.0 | 180 | 100.0 | ||
| G2 Haplotype rs71785313 (TTATAA>del6) | ||||||
| G2 | 6 | 3.3 | 26 | 14.4 | 0.20 [0.07 to 0.48] | 0.0001 |
| Non-G2 | 178 | 96.7 | 154 | 85.6 | ||
| Total | 184 | 100.0 | 180 | 100.0 | ||
-
*Two-tailed Fisher's exact test with mid-P method using a dominant genetic model (carriage of 1 or 2 copies of the designated APOL1 haplotype),
-
†Individuals with only a partial G1 haplotype were excluded from the analysis. T.b.r: T.b. rhodesiense, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval, N.C: not calculable. All raw data for Table 1 can be found in Table 1—source data 1. The association analysis of the two individual component SNPs of the G1 haplotype can be found in Table 1—source data 2.
-
Table 1—source data 1
APOL1 genotype data for T.b. rhodesiense-infected individuals and controls
*Individuals excluded from the APOL1 G1 association analysis. T.b.r: T.b. rhodesiense, G0: genotype compatible with the non-risk G0 allele for both rs73885319 and rs60910145, G1: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for both rs73885319 and rs60910145, G1M: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for rs60910145 and the non-risk G0 allele for rs73885319, G1G: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for rs73885319 and the non-risk G0 allele for rs60910145, G2: genotype compatible with the G2 CKD risk allele for rs71785313.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.005
-
Table 1—source data 2
Association between individual APOL1 G1 kidney disease risk variants and T.b. rhodesiense infection Two-tailed Fisher's exact test with mid-P method using a dominant genetic model (carriage of 1 or 2 copies of the designated APOL1 SNP).
CKD: chronic kidney disease, T.b.r: T.b. rhodesiense, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. Raw data for Table 1—source data 2 can be found in Table 1—source data 1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.006
Association between kidney disease risk variants and T.b. gambiense infection
| Dominant model - Infection | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOL1 haplotype | T.b.g infected | Control | Association analysis* T.b.g infected/Control | |||
| Number | % | Number | % | OR [95% CI] | P | |
| G0 Ancestral Haplotype rs73885319 (A) + rs60910145 (T) + rs71785313 (TTATAA) | ||||||
| G0 | 196 | 86.3 | 89 | 85.6 | 1.07 [0.54 to 2.06] | 0.84 |
| Non-G0 | 31 | 13.7 | 15 | 14.4 | ||
| Total | 227 | 100.0 | 104 | 100.0 | ||
| G1 Haplotype† rs73885319 (A>G) + rs60910145 (T>G) | ||||||
| G1 | 73 | 33.5 | 30 | 29.4 | 1.21 [0.73 to 2.03] | 0.47 |
| Non-G1 | 145 | 66.5 | 72 | 70.6 | ||
| Total | 218 | 100.0 | 102 | 100.0 | ||
| G2 Haplotype rs71785313 (TTATAA>del6) | ||||||
| G2 | 68 | 30.0 | 35 | 33.7 | 0.84 [0.51 to 1.40] | 0.50 |
| Non-G2 | 159 | 70.0 | 69 | 66.3 | ||
| Total | 227 | 100.0 | 104 | 100.0 | ||
-
*Two-tailed Fisher's exact test with mid-P method using a dominant genetic model (carriage of 1 or 2 copies of the designated APOL1 haplotype),
-
†Individuals with a partial G1 haplotype were excluded from the analysis. T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. All raw data for Table 2 can be found in Table 2—source data 1. The association analysis of the two individual component SNPs of the G1 haplotype can be found in Table 2—source data 2.
-
Table 2—source data 1
APOL1 genotype data for T.b. gambiense-infected individuals and controls
*Individuals excluded from the APOL1 G1 association analysis. T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, G0: genotype compatible with the non-risk G0 allele for both rs73885319 and rs60910145, G1: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for both rs73885319 and rs60910145, G1M: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for rs60910145 and the non-risk G0 allele for rs73885319, G1G: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for rs73885319 and the non-risk G0 allele for rs60910145, G2: genotype compatible with the G2 CKD risk allele for rs71785313.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.008
-
Table 2—source data 2
Association between individual APOL1 G1 kidney disease risk variants and T.b. gambiense infection Two-tailed Fisher's exact test with mid-P method using a dominant genetic model (carriage of 1 or 2 copies of the designated APOL1 SNP).
CKD: chronic kidney disease, T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. Raw data for Table 2—source data 2 can be found in Table 2—source data 1.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.009
Association between kidney disease risk variants and T.b. gambiense infection outcome
| Dominant model – infection outcome | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOL1 haplotype | T.b.g Disease | T.b.g Carriage | Association analysis* T.b.g Disease/Carriage | |||
| Number | % | Number | % | OR [95% CI] | P | |
| G0 Ancestral Haplotype rs73885319 (A) + rs60910145 (T) + rs71785313 (TTATAA) | ||||||
| G0 | 144 | 86.2 | 52 | 86.7 | 0.96 [0.38 to 2.25] | 0.95 |
| Non-G0 | 23 | 13.8 | 8 | 13.3 | ||
| Total | 167 | 100.0 | 60 | 100.0 | ||
| G1 Haplotype† rs73885319 (A>G) + rs60910145 (T>G) | ||||||
| G1 | 43 | 26.7 | 30 | 52.6 | 0.33 [0.17 to 0.62] | 0.0005 |
| Non-G1 | 118 | 73.3 | 27 | 47.4 | ||
| Total | 161 | 100.0 | 57 | 100.0 | ||
| G2 Haplotype rs71785313 (TTATAA>del6) | ||||||
| G2 | 59 | 35.3 | 9 | 15.0 | 3.08 [1.45 to 7.06] | 0.0025 |
| Non-G2 | 108 | 64.7 | 51 | 85.0 | ||
| Total | 167 | 100.0 | 60 | 100.0 | ||
-
*Two-tailed Fisher's exact test with mid-P method using a dominant genetic model (carriage of 1 or 2 copies of the designated APOL1 haplotype),
-
†Individuals with a partial G1 haplotype were excluded from the analysis. T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. Raw data for Table 3 can be found in Table 3—source data 1. An association analysis of the two individual component SNPs of the G1 haplotype can be found in Table 3—source data 2.
-
Table 3—source data 1
APOL1 genotype data for T.b. gambiense clinical stage trypanosomiasis patients and latent carriers
*Individuals excluded from the APOL1 G1 association analysis. T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, G0: genotype compatible with the non-risk G0 allele for both rs73885319 and rs60910145, G1: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for both rs73885319 and rs60910145, G1M: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for rs60910145 and the non-risk G0 allele for rs73885319, G1G: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for rs73885319 and the non-risk G0 allele for rs60910145, G2: genotype compatible with the G2 CKD risk allele for rs71785313.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.011
-
Table 3—source data 2
Association between individual APOL1 G1 kidney disease risk variants and T.b. gambiense infection outcome Two-tailed Fisher's exact test with mid-P method using a dominant genetic model (carriage of 1 or 2 copies of the designated APOL1 SNP).
CKD: chronic kidney disease, T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. Raw data for Table 3—source data 2 can be found in Table 3—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.012
Conditional association between kidney disease risk variants and T.b. gambiense infection outcome excluding compound heterozygotes
| Dominant model – infection outcome | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOL1 haplotype | T.b.g Disease | T.b.g Carriage | Association analysis* T.b.g Disease/Carriage | |||
| Number | % | Number | % | OR [95% CI] | P | |
| G1 Haplotype†,‡ rs73885319 (A>G) + rs60910145 (T>G) | ||||||
| G1 | 36 | 23.4 | 25 | 48.1 | 0.33 [0.17 to 0.64] | 0.0012 |
| Non-G1 | 118 | 76.6 | 27 | 51.9 | ||
| Total | 154 | 100.0 | 52 | 100.0 | ||
| G2 Haplotype‡ rs71785313 (TTATAA>del6) | ||||||
| G2 | 50 | 31.6 | 4 | 7.3 | 5.87 [2.16 to 20.01] | 0.0001 |
| Non-G2 | 108 | 68.4 | 51 | 92.7 | ||
| Total | 158 | 100.0 | 55 | 100.0 | ||
-
*Two-tailed Fisher's exact test with mid-P method using a dominant model (carriage of 1 or 2 copies of the designated APOL1 haplotype),
-
†Individuals with a partial G1 haplotype were excluded from the analysis.
-
‡Individuals with a compound heterozygote genotype (G1/G2) were excluded from the analysis. T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. Raw data for Table 4 can be found in Table 4—source data 1. An association analysis of the two individual component SNPs of the G1 haplotype can be found in Table 4—source data 2.
-
Table 4—source data 1
APOL1 genotype data for T.b. gambiense clinical stage trypanosomiasis patients and latent carriers, excluding compound heterozygotes
*Individuals excluded from the APOL1 G1 association analysis. T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, G0: genotype compatible with the non-risk G0 allele for both rs73885319 and rs60910145, G1: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for both rs73885319 and rs60910145, G1M: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for rs60910145 and the non-risk G0 allele for rs73885319, G1G: genotype compatible with the G1 CKD risk allele for rs73885319 and the non-risk G0 allele for rs60910145, G2: genotype compatible with the G2 CKD risk allele for rs71785313.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.014
-
Table 4—source data 2
Association between individual APOL1 G1 kidney disease risk variants and T.b. gambiense infection outcome, excluding compound heterozygotes Two-tailed Fisher's exact test with mid-P method using a dominant genetic model (carriage of 1 or 2 copies of the designated APOL1 SNP).
Individuals with a compound heterozygote genotype (G1/G2) were excluded from the analysis. CKD: chronic kidney disease, T.b.g: T.b. gambiense, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval. Raw data for Table 4—source data 2 can be found in Table 4—source data 1
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.015
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Sequence variants identified in protein-coding exons of the APOL1 gene in T.b.r cases and controls.
Sequence variants relative to human genome reference (NCBI Genome browser build 38, RRID:SCR_006553) were identified in exon sequences of individuals identified with a G1 or G2 genotype, and a representative number of G0 individuals. S: synonymous SNP, NS: non-synonymous SNP, T.b.r: T.b. rhodesiense. The chromosome 22 position is indicated based on NCBI Genome reference build 38.7 and reference SNP ID if present, is indicated as described by dbSNP (RRID:SCR_002338). The SNP genotype of each individual is described by the appropriate IUPAC nucleotide code. Rs71785313 (G2) genotypes are described by the presence (TTATAA) or absence (del6) of the six base-pair sequence that is deleted in the G2 variant. Due to limited sample availability, sequence data could not be obtained for two G0/G2 individuals (LIL039 and CT059).
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.018
-
Supplementary file 2
Primer information for PCR amplification and sequencing of APOL1 protein-coding exons
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25461.019





