LIN37-DREAM prevents DNA end resection and homologous recombination at DNA double-strand breaks in quiescent cells
Figures
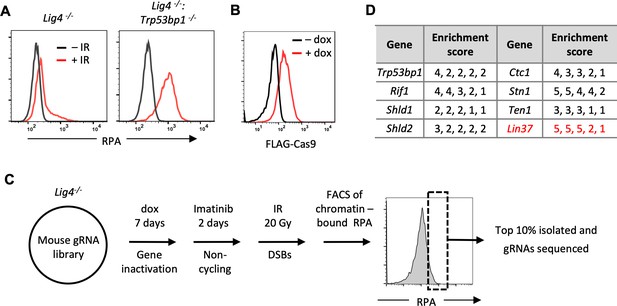
An unbiased genome-scale gRNA screen for novel DNA end protection factors.
(A) Flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA before and after IR of non-cycling Lig4−/− and Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/− abl pre-B cells. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of FLAG-Cas9 in Lig4−/− cells with (+dox) and without (−dox) doxycycline to induce expression of FLAG-Cas9. (C) Schematic diagram of the genome-scale guide RNA screen for genes preventing DNA end resection in non-cycling Lig4−/− abl pre-B cells. (D) Enrichment score (fold enrichment) of individual gRNAs to a subset of genes identified in the RPA high population. gRNA, guide RNA; IR, ionizing radiation.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
RPA screen result in non-cycling Lig4−/− abl pre-B cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
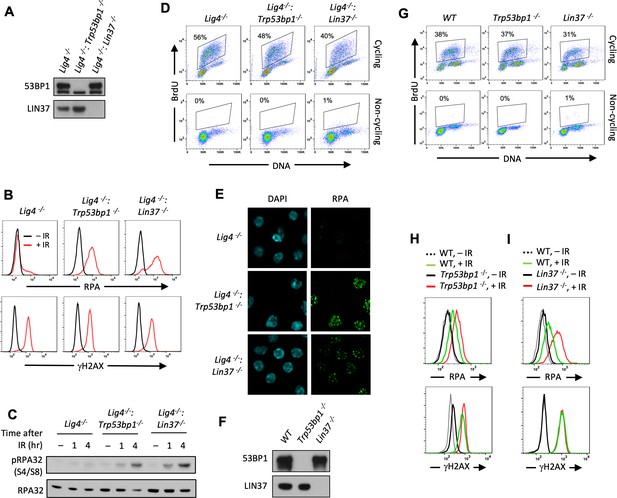
Non-cycling LIN37-deficient cells accumulate chromatin-bound RPA after IR-induced damage.
(A) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA (top) and γH2AX (bottom) before and after IR of non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. The experiments were repeated in two independently generated cell lines at least twice. (C) Western blot analysis of RPA32 and phosphorylated RPA 32 (pRPA32(S4/S8)) of non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells treated without or with IR after indicated times. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of cycling and non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells for BrdU incorporation and DNA content (7-AAD). Percentage of cells in S-phase is indicated. (E) Representative images of IR-induced RPA foci in non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells from two independent experiments. (F) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− MCF10A cells. (G) Flow cytometric analysis of BrdU pulsed cycling (top) or non-cycling (bottom) WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− MCF10A cells as in (D). (H, I) Flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA (top) and γH2AX (bottom) before or after IR of non-cycling WT and (H) Trp53bp1−/− or (I) Lin37−/− MCF10A cells. IR, ionizing radiation; WT, wild type.
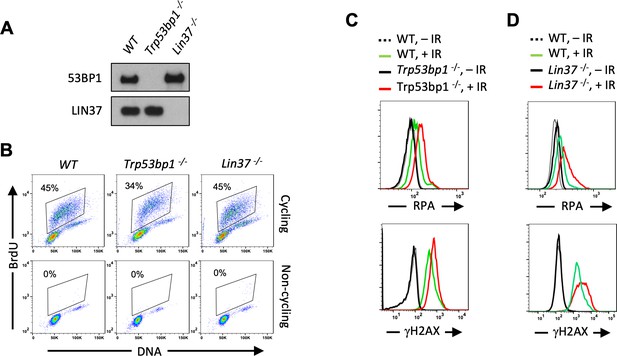
Non-cycling LIN37-deficient cells accumulate chromatin-bound RPA after IR-induced damage.
(A) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of BrdU and DNA (7-AAD) of BrdU pulsed cycling (top) or non-cycling (bottom) WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. Percentage of cells in S-phase is indicated. (C, D) Flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA (top panels) and γH2AX (bottom panels) before or after IR of non-cycling WT and Trp53bp1−/− (C) or Lin37−/− (D) abl pre-B cells. The experiments were repeated in two independently generated cell lines at least twice. IR, ionizing radiation.
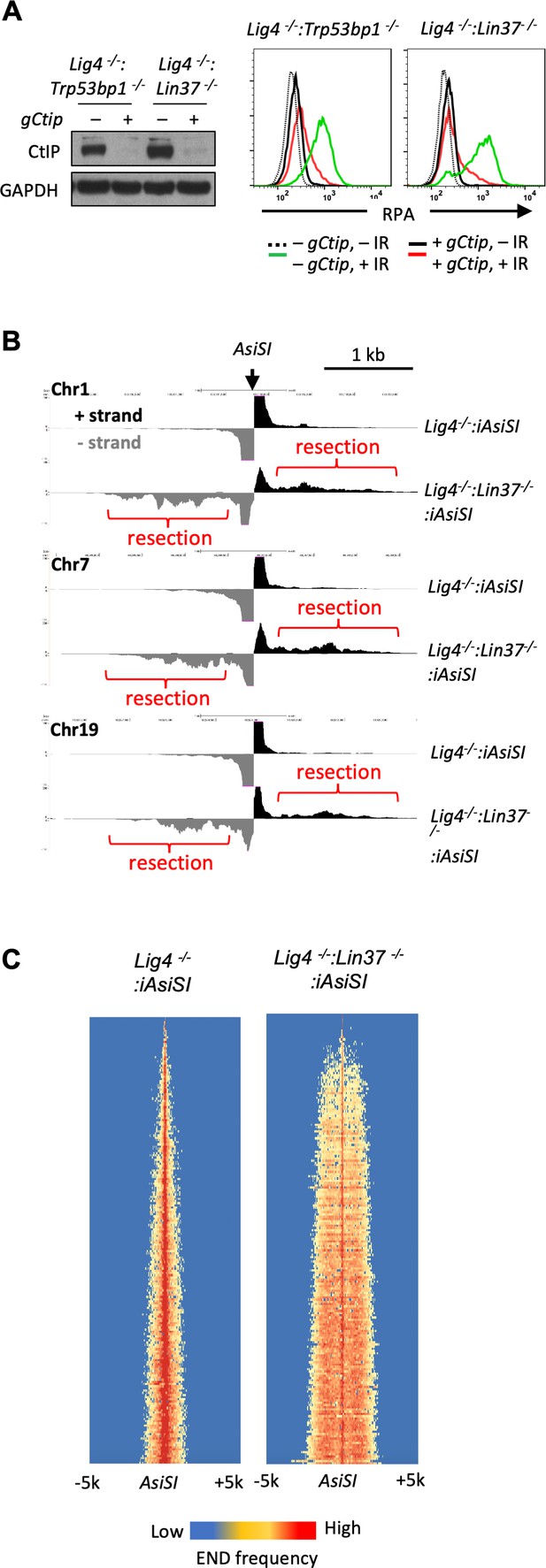
LIN37 prevents DNA end resection in non-cycling cells.
(A) Cas9-induced Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells with (+) and without (−) the Ctip gRNA (gCtip). Western blot analysis with indicated antibodies (left) and flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA before and after IR of the non-cycling cells (right) are shown. Representative of three experiments. (B) End-seq tracks of representative AsiSI sites on mouse chromosomes 1, 7, and 19 in non-cycling Lig4−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. (C) The heatmaps of End-seq at AsiSI DSBs across the mouse genome (y-axis) after AsiSI induction in non-cycling Lig4−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. Two experiments were carried out in two independently generated Lig4−/−:iAsiSI and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/−:iAsiSI clones. DSB, double-strand break; End-seq, End Sequencing; gRNA, guide RNA; IR, ionizing radiation.
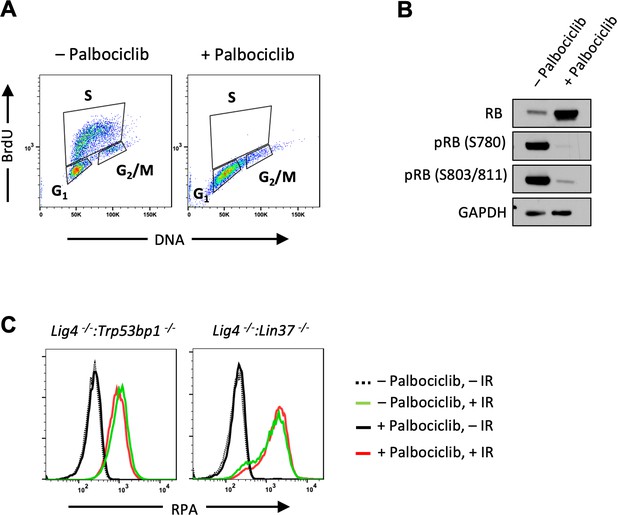
CtIP promotes resection in non-cycling abl pre-B cells independent of CDK4/6 activity.
(A) Flow cytometric analysis of BrdU incorporation and DNA content (7-AAD) of WT abl pre-B cells after treated with Palbociclib. (B) Western blot analysis of WT abl pre-B cells treated with or without Palbociclib using indicated antibodies. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA before or after IR of non-cycling Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells treated with or without Palbociclib 1 hr prior to IR. IR, ionizing radiation; WT, wild type.
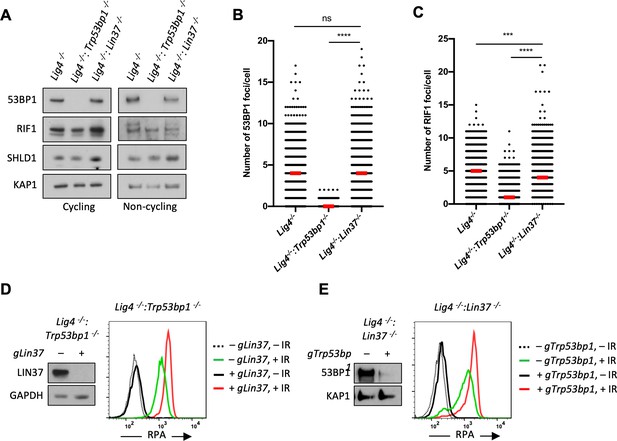
53BP1 and LIN37 have distinct DNA end protection functions.
(A) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in cycling and non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. (B, C) Quantification of 53BP1 (B) or RIF1 (C) foci after IR treatment of non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. Red bars indicate the median number of foci in each sample. More than 1000 cells were analyzed in each cell line in two independent experiments (****p<0.0001, ***p=0.0002, Mann-Whitney test). (D, E) Flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA before and after IR of non-cycling Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/− (D) or Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− (E) abl pre-B cells after bulk gene inactivation of Lin37 (gLin37) or Trp53bp1 (gTrp53bp1), respectively. Representative of three experiments. IR, ionizing radiation.
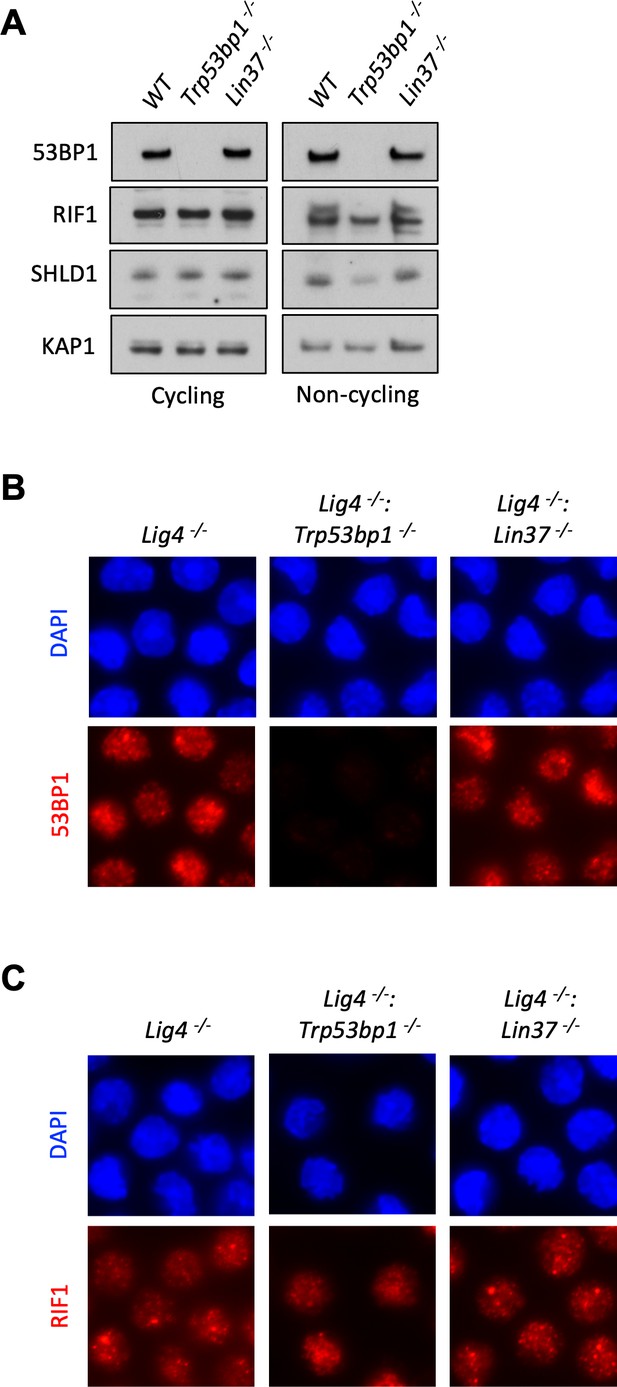
53BP1 and LIN37 have distinct DNA end protection functions.
(A) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in cycling and non-cycling WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. (B, C) Representative images of 53BP1 (B) or RIF1 (C) foci after IR treatment of non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. IR, ionizing radiation.
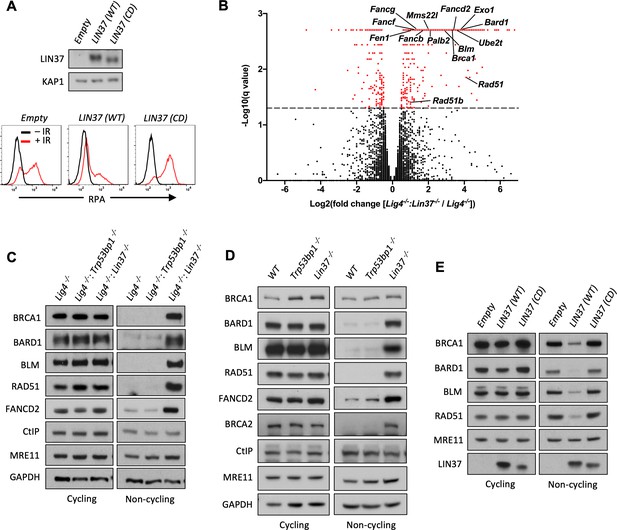
LIN37 suppresses the expression of HR protein expression in non-cycling cells.
(A) Western blot analysis (top) and flow cytometric analysis for chromatin-bound RPA after before or after IR (bottom) of non-cycling Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells with empty lentivirus or lentivirus expressing wild type (WT) LIN37 or the LIN37 (CD) mutant. Representative of three experiments. (B) Volcano plot of RNA-Seq analysis of non-cycling Lig4−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells showing log2 values of the ratio of normalized transcript levels of Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− to Lig4−/− cells (X-axis) and −log10 of the q-values of fold enrichment of each gene (Y-axis). The dashed line indicates q=0.05. Genes with q-values≤0.05 are denoted as red dots. (C) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in cycling and non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. (D) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in cycling or non-cycling WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− MCF10A cells. (E) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in cycling and non-cycling Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells with empty lentivirus or lentivirus expressing WT LIN37 or the LIN37 (CD) mutant. HR, homologous recombination; IR, ionizing radiation; RNA-Seq, RNA sequencing.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
RNA-Seq result and GO analysis in non-cycling Lig4−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells.
GO, gene ontology; RNA-Seq, RNA sequencing.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
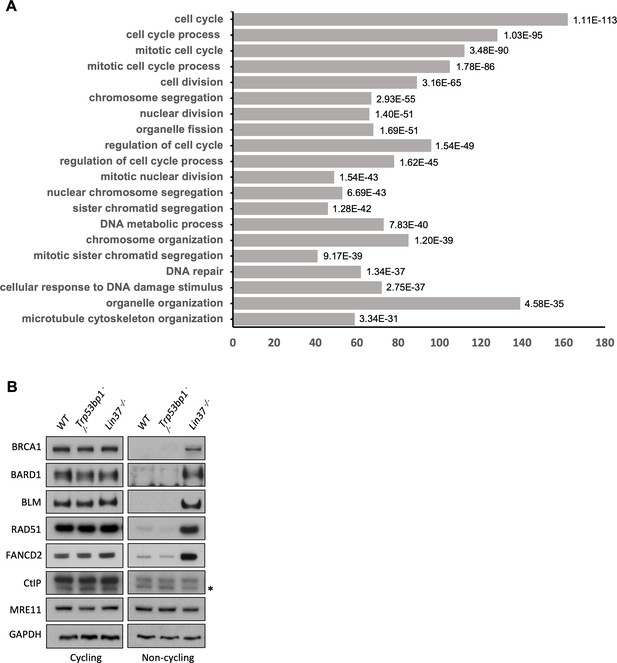
LIN37 suppresses HR protein expression in non-cycling cells.
(A) Gene ontology (GO) analysis of genes upregulated in non-cycling Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. Enriched GO terms with the 20 lowest p-values (on the right of each bar) are shown. (B) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in cycling or non-cycling WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. HR, homologous recombination; WT, wild type.
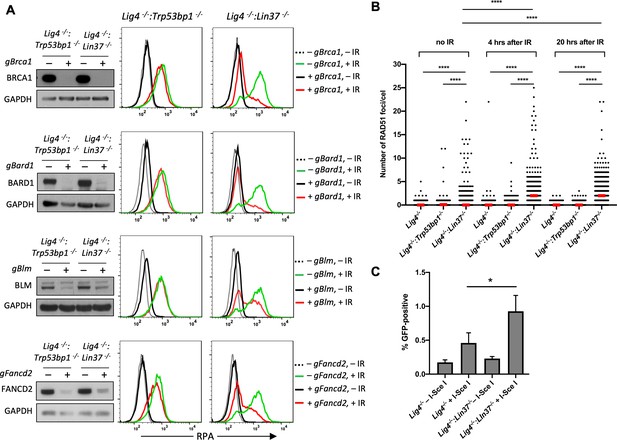
LIN37 prevents resection and HR through suppressing HR protein expression in non-cycling cells.
(A) Western blot analysis of proliferating Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/− or Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells with or without indicated gRNAs following Cas9 induction for bulk gene inactivation using the indicated antibodies (left). Flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA before and after IR of the same cells after rendered non-cycling by imatinib treatment (right). Representative of three experiments. (B) Quantification of RAD51 foci in non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells before IR treatment and 4 and 20 hr after IR. Red bars indicate the median number of RAD51 foci in each sample of more than 1000 cells analyzed for each cell line. Representative of two independent experiments (****p<0.0001, Mann-Whitney test). (C) Flow cytometric analysis of HR-mediated DSB repair in non-cycling Lig4−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells using the HPRT-DR-GFP reporter. The percentage of GFP-positive cells is shown. Error bars are ± SEM from three experiments (*p=0.0124, t-test). DSB, double-strand break; gRNA, guide RNA; HR, homologous recombination; IR, ionizing radiation.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
RPA screen result in non-cycling Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-fig6-data1-v1.xlsx
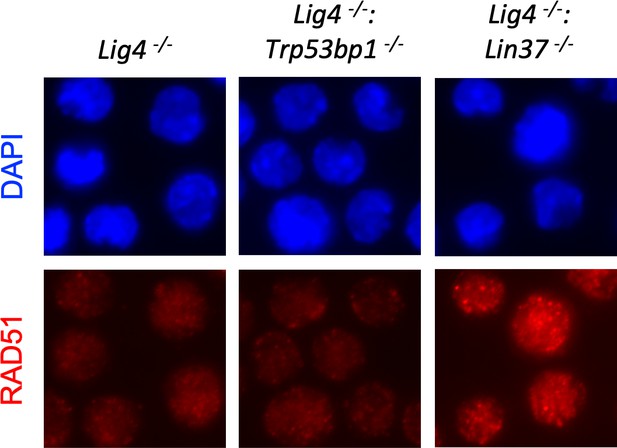
LIN37 deficiency leads to RAD51 focus formation in non-cycling abl pre-B cells.
Representative images of RAD51 IR-induced foci in non-cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells. IR, ionizing radiation.
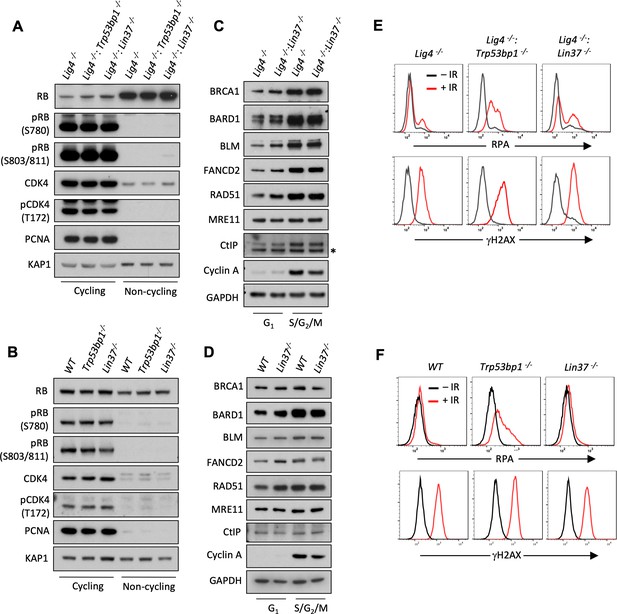
LIN37 function in DNA end protection is restricted to G0.
(A, B) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in cycling and non-cycling abl pre-B cells (A) or MCF10A cells (B). (C, D) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins in cycling G1 or S/G2/M abl pre-B cells (C) or MCF10A cells (D), isolated by flow cytometric cell sorting based on the PIP-FUCCI reporter. Representative of two independent experiments. Asterisk indicates non-specific recognizing bands. (E, F) Flow cytometric analysis of chromatin-bound RPA and γH2AX before and after IR treatment of G1-phase Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells (E) or WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− MCF10A cells (F). Representative of three experiments. IR, ionizing radiation; WT, wild type.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
RNA-Seq result and GO analysis in cycling G1 Lig4−/− and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells.
GO, gene ontology; RNA-Seq, RNA sequencing.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-fig7-data1-v1.xlsx
-
Figure 7—source data 2
GO analysis of genes upregulated in non-cycling G0 and/or cycling G1 Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells.
GO, gene ontology.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-fig7-data2-v1.xlsx
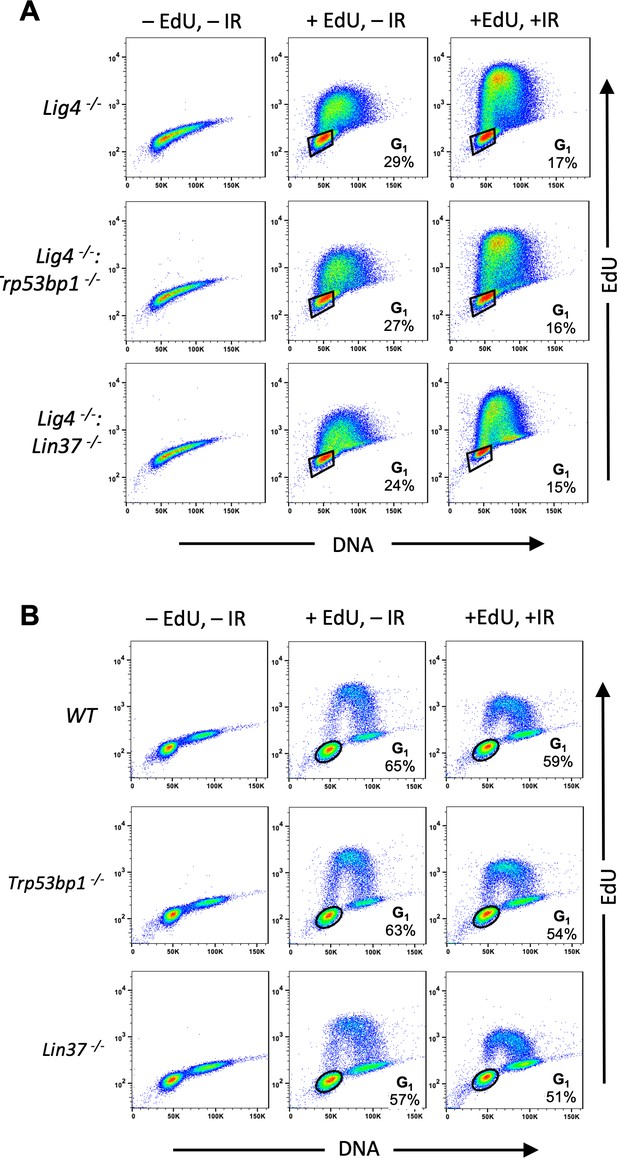
Identification of G1-phase cells in proliferating cells.
(A, B) Flow cytometric analysis of EdU incorporation and DNA content (7-AAD) of cycling Lig4−/−, Lig4−/−:Trp53bp1−/−, and Lig4−/−:Lin37−/− abl pre-B cells (A) or cycling WT, Trp53bp1−/−, and Lin37−/− MCF10A cells (B). Cells were treated (+EdU) or not treated (−EdU) with EdU and analyses were carried out before or after IR. The percentage of G1-phase cells is shown. IR, ionizing radiation; WT, wild type.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Anti-53BP1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Bethyl Laboratories | A300-272A | WB (1:3000) |
| Antibody | Anti-53BP1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Novus Biologicals | NB100-305 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-LIN37 (Mouse monoclonal) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-515686 | WB (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-BLM (Rabbit polyclonal) | Bethyl Laboratories | A300-572A | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Anti-BRCA1 (Mouse monoclonal) | R and D Systems | Custom made (Andre Nussenzweig, NCI) | WB (1:1000); for mouse BRCA1 |
| Antibody | Anti-BRCA1 (Mouse monoclonal) | Millipore Sigma | 07-434 | WB (1:1000); for human BRCA1 |
| Antibody | Anti-RAD51 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Millipore Sigma | ABE257 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Anti-RAD51 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab176458 | IF (1:250) |
| Antibody | Anti-BARD1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PA5-85707 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-CtIP (Rabbit polyclonal) | N/A | Custom made (Richard Baer, Columbia University) | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-MRE11 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Novus Biologicals | NB100-142 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Anti-RIF1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | ab13422 | WB (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-RIF1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | N/A | Custom made (Davide Robbiani, Rockefeller University) | IF (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Anti-C20orf196/ SHLD1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | PA5-559280 | WB (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-GAPDH (Mouse Monoclonal) | Millipore Sigma | G8795 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Anti-KAP1 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Genetex | GTX102226 | WB (1:2000) |
| Antibody | Anti-FANCD2 (Rabbit monoclonal) | R and D Systems | MAB93691 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-BRCA2 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Proteintech | 19791-1-AP | WB (1:500); for human BRCA2 |
| Antibody | Anti-Rb1 (Mouse monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | LF-MA0173 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Phospho -Rb (Ser780) (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | 8180T | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Phospho -Rb (Ser807/ 811) (Rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | 8516T | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-PCNA (Rabbit polyclonal) | Bethyl Laboratories | A300-276A | WB (1:3000) |
| Antibody | Anti-CDK4 (Rabbit polyclonal) | Novus Biologicals | NBP1-31308 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-CDK4 (phosphor Thr172) (Rabbit polyclonal) | GeneTex | GTX00778 | WB (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-RPA32 (4E4) (Rat monoclonal) | Cell Signaling Technology | 2208S | WB (1:1000); FC (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-phospho-H2AX (ser139) (Mouse monoclonal) | Millipore Sigma | 05-636 | FC (1:1000) |
| Antibody | HRP, goat anti-mouse | Promega | W4021 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | HRP, goat anti-rabbit IgG | Promega | W4011 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 555, donkey anti-rabbit IgG | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A-31572 | IF (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 488,goat anti-rat IgG | BioLegend | 405418 | FC (1:500) |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 647,goat anti-mouse IgG | BioLegend | 405322 | FC (1:500) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCW-Cas9 (plasmid) | Addgene | 50661 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pX330-U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 (plasmid) | Addgene | 42230 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pKLV-U6 gRNA(BbsI)-PGKpuro-2ABFP (plasmid) | Addgene | 50946 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pLenti-CMV-Blast-PIP-FUCCI (plasmid) | Addgene | 138715 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Genome-wide CRISPR guide RNA library V2 (plasmid) | Addgene | 67988 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Lin37 cDNA BC013546 (plasmid) | transOMIC | TCM1004 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | TRE-Thy1.1 (plasmid) | This study | N/A | Available upon request |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pHPRT-DR-GFP (plasmid) | Marian Jasin, MSKCC | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCBASceI (plasmid) | Marian Jasin, MSKCC | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCBA (plasmid) | Marian Jasin, MSKCC | N/A | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | MCA10A | ATCC | CRL-10317 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | MCA10A: iCas9 | This study | Clone 25 | Available upon request |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | MCA10A: Trp53bp1−/−: iCas9 | This study | Clones 7 and 50 | Available upon request |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | MCA10A: Lin37−/−:iCas9 | This study | Clones 5 and 21 | Available upon request |
| Cell line (Mus musculus) | WT:iCas9 abl pre-B cells | This study | M63.1.MG36.iCas9.302 | Available upon request |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | Trp53bp1−/−:iCas9 abl pre-B cells | This study | Clones 1 and 27 | Available upon request |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | Lin37−/−:iCas9 abl pre-B cells | This study | Clones 9 and 59 | Available upon request |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | Lig4−/−:iCas9 abl pre-B cells | This study | A5.83.MG9.iCas9.16 | Available upon request |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | Lig4−/−: Trp53bp1−/−:iCas9 abl pre-B cells | This study | Clones 81 and 82 | Available upon request |
| Cell line (M. musculus) | Lig4−/−:Lin37−/−:iCas9 abl pre-B cells | This study | Clones 6 and 42 | Available upon request |
| Chemical compound, drug | Imatinib | Selleckchem | S2475 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Doxycycline | Sigma-Aldrich | D9891 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Puromycin | Sigma-Aldrich | P9620 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EGF | PeproTech | AF-100-15 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hydrocortisone | Sigma-Aldrich | H-0888 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Cholera Toxin | Sigma-Aldrich | C-8052 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Insulin | Sigma-Aldrich | I-1882 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Cytofix/Cytoperm solution | BD Biosciences | 554722 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Perm/Wash Buffer | BD Biosciences | 554723 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Click-iT EdU Alexa Fluor 647 Flow Cytometry Assay Kit | Life Technologies | C10419 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SG Cell Line 4D X Kit L | Lonza | V4XC-3024 | |
| Other | 7-AAD (DNA stain) | BD Biosciences | 559925 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | pKLV lib330F | This study (designed based on Tzelepis et al., 2016) | PCR primers | AATGGACTATCATATGCTTACCGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | pKLV lib490R | This study (designed based on Tzelepis et al., 2016) | PCR primers | CCTACCGGTGGATGTGGAATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | PE.P5_pKLV lib195 Fwd | This study (designed based on Tzelepis et al., 2016 and standard Illumana adaptor sequences) | PCR primers | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTGGCTTTATATATCTTGTGGAAAGGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | P7 index180 Rev | This study (designed based on Tzelepis et al., 2016 and standard Illumana adaptor sequences) | PCR primers | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATINDEXGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCCAGACTGCCTTGGGAAAAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Lin37 iso1_5′XhoI_S | This study (designed based on cDNA BC013546) | PCR primers | GCCCTCGAGATGTTCCCGGTAAAGGTGAAAGTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Lin37 3′NotI_AS | This study (designed based on cDNA BC013546) | PCR primers | GCCGCGGCCGCTCACTGCCGGTCATACATCTCCCGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Lin37 CD1_AS | This study (designed based on cDNA BC013546 and Mages et al., 2017) | PCR primers | TACAGTGGTGTGTTCTCACTGAACTGGGCCAAGTCCACAGCCCCG GCAAATAGCTTGATC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Lin37 CD2_S | This study (designed based on cDNA BC013546 and Mages et al., 2017) | PCR primers | ACTTGGCCCAGTTCAGTGAGAACACACCACTGTACCCCATCGCCGGCGCCTGGATGCGCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | BU1 | Canela et al., 2016 | PCR primers | 5′-Phos-GATCGGAAGAGCGTCGT GTAGGGAAAGAGTGUU[Biotin-dT]U [Biotin-dT]UUACACTCTTTC CCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATC* T-3′ [*phosphorothioate bond] |
| Sequence-based reagent | BU2 | Canela et al., 2016 | PCR primers | 5′-Phos-GATCGGAAGAGCACACG TCUUUUUUUUAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATC*T-3′ [*phosphorothioate bond] |
| Sequence-based reagent | 53 bp1 gRNA sequence | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | GAACCTGTCAGACCCGATC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Lin37 gRNA sequences | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | AAGCTATTTGACCGGAGTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Brca1 gRNA sequence | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | GTCTACATTGAACTAGGTA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Ctip gRNA sequence | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | ATTAACCGGCTACGAAAGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Bard1 gRNA sequence | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | AAATCGTAAAGGCTGCCAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Blm gRNA sequence | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | GATTTAACGAAGGAATCGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fancd2 gRNA sequence | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | TCTTGTGATGTCGCTCGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Trp53bp1 (human) gRNA sequence | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | TCTAGTGTGTTAGATCAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Lin37 (human) gRNA sequence | Sequence is from Tzelepis et al., 2016 | N/A | TCTAGGGAGCGTCTGGATG |
| Software, algorithm | Image J | NIH | RRID:SCR_003070 | |
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo | FlowJo | RRID:SCR_008520 | |
| Software, algorithm | Prism | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Software, algorithm | SeqKit | Shen et al., 2016 | RRID:SCR_018926 | |
| Software, algorithm | Bowtie | Langmead et al., 2009 | RRID:SCR_005476 | |
| Software, algorithm | SAMtools | Li et al., 2009 | RRID:SCR_002105 | |
| Software, algorithm | BEDtools | Quinlan and Hall, 2010 | RRID:SCR_006646 | |
| Others | LSRII flow cytometer | BD Biosciences | RRID:SCR_002159 | |
| Others | FACSAria II Cell Sorter | BD Biosciences | RRID:SCR_018934 | |
| Others | Lionheart LX automated microscope | BioTex Instrument | RRID:SCR_019745 | |
| Others | 4-D Nucleofector | Lonza | NA |
Additional files
-
Source data 1
Compiled PDF file that contains raw images with the regions shown in the manuscript labeled.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-data1-v1.pdf
-
Source data 2
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-data2-v1.zip
-
Source data 3
Raw images from Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-data3-v1.zip
-
Source data 4
Raw images from Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-data4-v1.zip
-
Source data 5
Raw images from Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-data5-v1.zip
-
Source data 6
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-data6-v1.zip
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/68466/elife-68466-transrepform-v1.pdf





