A mosaic-type trimeric RBD-based COVID-19 vaccine candidate induces potent neutralization against Omicron and other SARS-CoV-2 variants
Figures
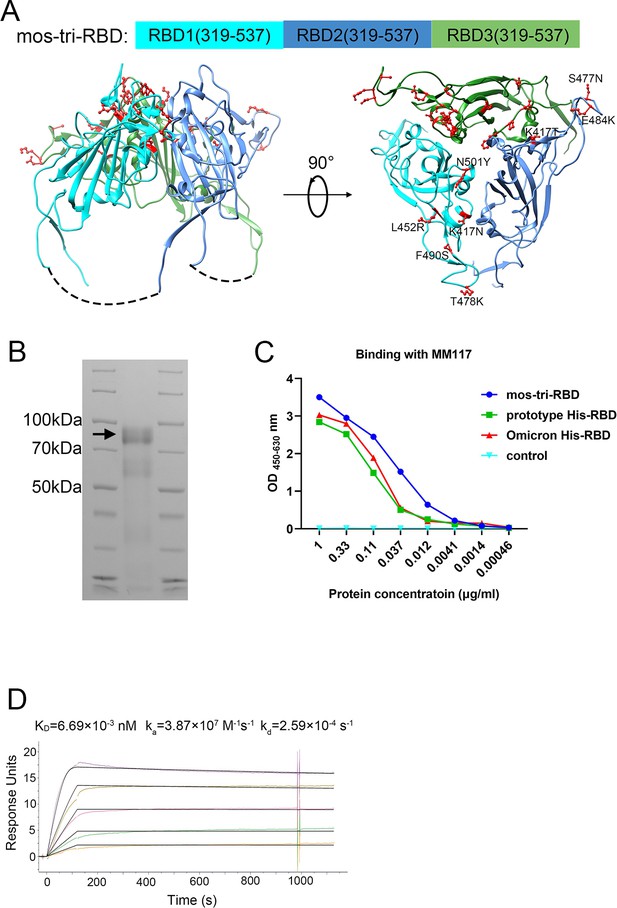
Design, expression and characterization of the mosaic-type trimeric form of RBD (mos-tri-RBD).
(A) Schematic illustration of the designed mos-tri-RBD. In mos-tri-RBD, three heterologous RBDs were connected end to end into a single chain and co-assembled into a trimeric structure. For the three RBDs, one was derived from the Omicron (BA.1) variant (green color), and the other two were artificially designed harboring the key immune-evasion-related mutations that emerged in SARS-CoV-2 variants, in which one contained the mutations of K417N, L452R, T478K, F490S, and N501Y (cyan color), and the other one contained K417T, S477N, and E484K (blue color). These mutations are highlighted in the red ball-and-stick model in the figure. Each RBD subunit in mos-tri-RBD was composed of the residues 319–537 from the spike protein. The dotted curves in the figure represent the direct connection between the C-terminus of the former RBD and the N-terminus of the latter RBD. The schematic structure of mos-tri-RBD was drawn by Chimera software (Pettersen et al., 2004) based on the PDB file with accession number 6zgi. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of the recombinant mos-tri-RBD. (C) Concentration-dependent binding ability of mos-tri-RBD with an RBD-specific monoclonal neutralizing antibody MM117 tested using ELISA. (D) Binding avidity of mos-tri-RBD with the receptor hACE2 measured using SPR assay. In this figure, different curves represent different concentrations of analyte (top to bottom: 263.70 ng/ml, 131.85 ng/ml, 65.93 ng/ml, 32.96 ng/ml, and 16.48 ng/ml). Both the original (color curves) and fitted (black curves) data are displayed.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
The raw files of SDS-PAGE results.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78633/elife-78633-fig1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 1—source data 2
Concentration-dependent binding ability of mos-tri-RBD with the antibody MM117.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78633/elife-78633-fig1-data2-v2.xlsx
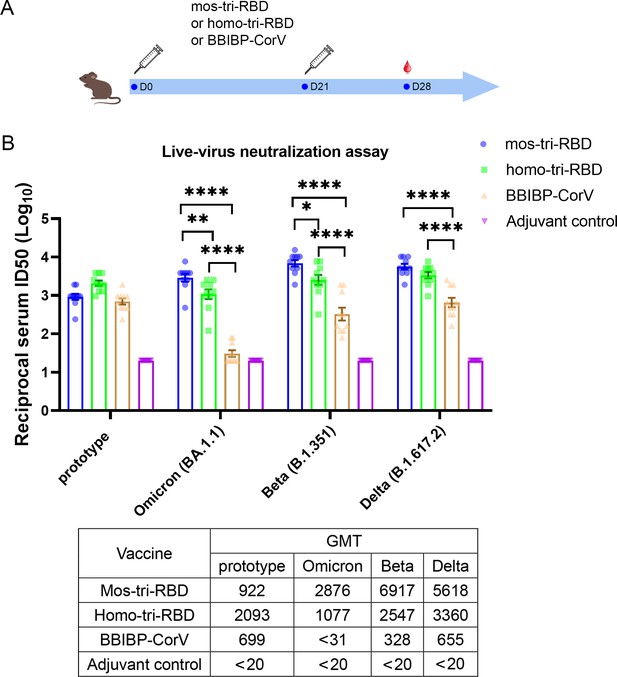
Evaluation of the cross-reactive immunogenicity of mos-tri-RBD against multiple SARS-CoV-2 strains, including prototype, Omicron, Beta and Delta strains, using live-virus neutralization assay.
(A) Timeline of rat immunization and serum collections. A group of Wistar rats (n=10 with half male and half female) were immunized intramuscularly with two doses of mos-tri-RBD with three weeks apart. Another three groups of rats received two doses of homo-tri-RBD, BBIBP-CorV and adjuvant, respectively, were used for comparison (n=10 rats per group with half male and half female). Sera from all the immunized rats were collected on day 7 after the last vaccination. (B) The reciprocal neutralizing ID50 titers in the sera elicited by mos-tri-RBD compared with those elicited by homo-tri-RBD and BBIBP-CorV against the live-viruses of SARS-CoV-2 prototype strain, and Omicron, Beta, and Delta variants. The quantification limit of the live-virus neutralization assay was 20, and the ID50 titers below the limit of quantification (LOQ) were set to 20. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by the LSD t-test was used for the comparison of data between different groups. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. GMT values are displayed in the lower part of the figure.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Individual data of live-virus neutralizing ID50 titers against several SARS-CoV-2 circulating strains in the sera elicited by mos-tri-RBD compared with those elicited by homo-tri-RBD and BBIBP-CorV.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78633/elife-78633-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
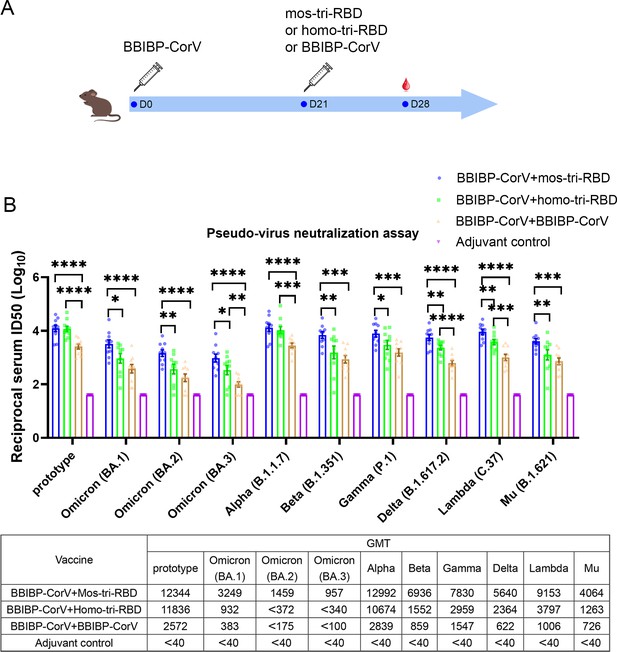
Evaluation of the cross-reactive immunogenicity of mos-tri-RBD as a booster shot against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron as well as other VOCs and VOIs using pseudo-virus neutralization assays.
(A) Timeline of rat immunization and serum collections. Three groups of Wistar rats (n=10 rats per group with half male and half female) were primed with a dose of BBIBP-CorV and boosted by mos-tri-RBD, homo-tri-RBD or BBIBP-CorV with three weeks apart. Another group of rats (n=10 with half male and half female) vaccinated with two doses of adjuvant served as control. The sera of all the immunized rats were collected on day 7 post-boosting immunization. (B) The reciprocal neutralizing ID50 titers in the sera elicited by ‘BBIBP-CorV +mos-tri-RBD’ vaccination compared with those elicited by ‘BBIBP-CorV +homo-tri-RBD’ and ‘BBIBP-CorV +BBIBP-Corv’ vaccinations against the pseudo-viruses of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron as well as other VOCs and VOIs. The quantification limit of the pseudo-virus neutralization assay was 40, and the ID50 titers below the LOQ were set to 40. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by the LSD t-test was used for the comparison of data between different groups. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. GMT values are displayed in the lower part of the figure.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Individual data of pseudo-virus neutralizing ID50 titers against various SARS-CoV-2 circulating strains in the sera elicited by ‘BBIBP-CorV +mos-tri-RBD’ vaccination compared with those elicited by ‘BBIBP-CorV +homo-tri-RBD’ and ‘BBIBP-CorV +BBIBP-CorV’ vaccinations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78633/elife-78633-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
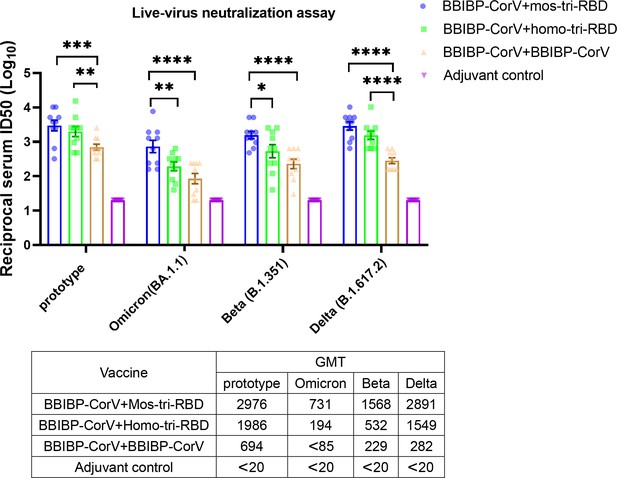
Evaluation of the cross-reactive immunogenicity of mos-tri-RBD as a booster shot against multiple SARS-CoV-2 strains, including prototype, Omicron, Beta, and Delta strains, using live-virus neutralization assay.
The reciprocal neutralizing ID50 titers in the sera elicited by ‘BBIBP-CorV +mos-tri-RBD’ vaccination compared with those elicited by ‘BBIBP-CorV +homo-tri-RBD’ and ‘BBIBP-CorV +BBIBP-Corv’ vaccinations against the live-viruses of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron as well as other immune-evasive variants. The quantification limit of the live-virus neutralization assay was 20, and the ID50 titers below the LOQ were set to 20. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by the LSD t-test was used for the comparison of data between different groups. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. GMT values are displayed in the lower part of the figure.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Individual data of live-virus neutralizing antibody ID50 titers against several SARS-CoV-2 circulating strains in the sera elicited by ‘BBIBP-CorV +mos-tri-RBD’ vaccination compared with those elicited by ‘BBIBP-CorV +homo-tri-RBD’ and ‘BBIBP-CorV +BBIBP-CorV’ vaccinations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78633/elife-78633-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx

The gene sequence of the spike region of the Omicron BA.1.1 virus used in the live virus neutralization assay.
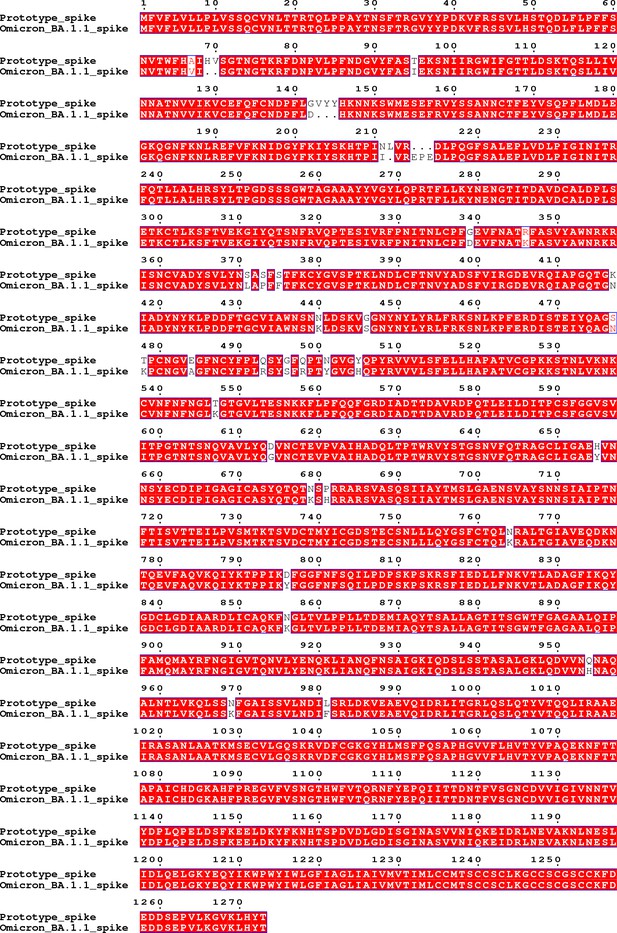
The amino acid sequence of the spike region of the Omicron BA.1.1 virus used in the live virus neutralization assay aligned with that of the prototype virus.
The sequence alignment result shows that there are 40 residue mutations, deletions or insertions in the spike region compared to that of the prototype virus, including A67V, del69-70, T95I, G142D, del143-145, N211I, del212, insert EPE, G339D, R346K, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K and L981F.
Tables
The details on the eight selected mutations integrated into the two artificially designed RBDs.
| Mutations | Rank of the observed frequency | VOCs and VOIs carrying the mutations |
|---|---|---|
| L452R | 1 | Delta |
| T478K | 2 | Delta, Omicron |
| N501Y | 3 | Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Omicron, Mu |
| E484K | 4 | Beta, Gamma, Mu |
| K417T | 5 | Gamma |
| S477N | 6 | Omicron |
| K417N | 8 | Beta, Omicron |
| F490S | 10 | Lambda |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (SARS-CoV-2 virus) | Live SARS-CoV-2 prototype virus (QD-01 strain) | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | ||
| Strain, strain background (SARS-CoV-2 virus) | Live SARS-CoV-2 Omicron virus (NPRC 2.192100005 strain) | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | ||
| Strain, strain background (SARS-CoV-2 virus) | Live SARS-CoV-2 Beta virus (GD84 strain) | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | ||
| Strain, strain background (SARS-CoV-2 virus) | Live SARS-CoV-2 Delta virus (GD96 strain) | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC | ||
| Strain, strain background (SARS-CoV-2 pseudo-virus) | SARS-CoV-2 prototype, Omicron (BA.1), Omicron (BA.2), Omicron (BA.3), Alpha, Beta, Delta, Gamma, Lambda and Mu pseudo-viruses | Wang et al., 2021; Li et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021; Nie et al., 2020 | ||
| Cell line (CHO) | CHO-K1 cell line | ATCC | Cat#CCL-61, RRID:CVCL_0214 | |
| Cell line (Homo-sapiens) | Huh-7 cells | JCRB | Cat#JCRB0403; RRID: CVCL_0336 | |
| Cell line (Chlorocebus sabaeus) | Vero cells | National Institute for Food and Drug Control (NIFDC), Beijing, China | ||
| Biological sample (Wistar rats) | Serum samples from immunized Wistar rats | This paper | Freshly isolated from immunized rats | |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-RBD | Sino Biological Inc, China | Cat#40592-MM117 | ELISA (1 µg/mL) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-mouse IgG-HRP | ZSGB-BIO | Cat#ZB-2305; RRID: AB_2747415 | ELISA (1:10000) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | Plasmid-SARS-CoV-2-mos-tri-RBD | This paper | Reference to “protein expression and purification” section | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant mos-tri-RBD protein (mammalian cell-expressed) | This paper | Reference to “protein expression and purification” section | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant monomeric his-tagged RBD of the prototype SARS-CoV-2 strain (Baculovirus-insect cell-expressed) | Sino Biological Inc, China | Cat#40592-V08B | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant monomeric his-tagged RBD of the Omicron (B.1.1.529) SARS-CoV-2 strain (HEK 293 cell-expressed) | Sino Biological Inc, China | Cat#40592-V08H121 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant hACE2 protein (mammalian cell-expressed) | Sino Biological Inc, China | Cat#10108-H08H | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SPR | BIAcore 8 k, GE Healthcare | N/A | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Aluminum hydroxide adjuvant | This paper | N/A | Produced by the reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide |
| Software, algorithm | UCSF Chimera | Chimera team at University of California | https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/ | |
| Software, algorithm | BIAcore Insight Evaluation Software | GE Healthcare | ||
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism version 8 | GraphPad Software | https://www.graphpad.com/ |





