Non-coding RNAs in drug and radiation resistance of bone and soft-tissue sarcoma: a systematic review
Figures
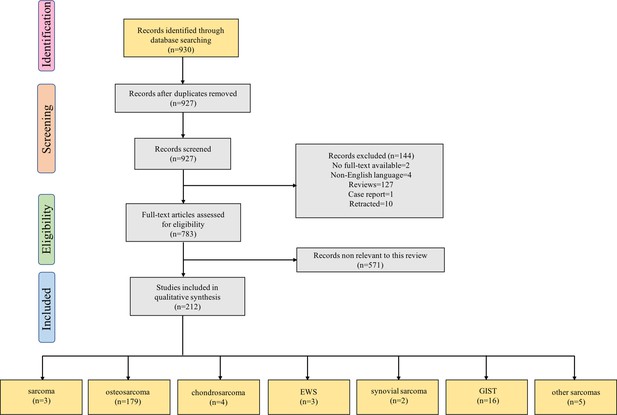
Flow diagram for Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews showing the literature selection process used to identify the studies included in the review.
The last group of boxes show the number of studies on different pathological types of sarcomas. Among them, the box ‘sarcoma’ represents three studies focused on the role of non-coding RNAs in multiple pathological types of sarcoma. Moreover, the box ‘other sarcomas’ represents five studies focused on rhabdomyosarcoma, uterine leiomyosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, and atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor. Abbreviations: EWS, Ewing’s sarcoma; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
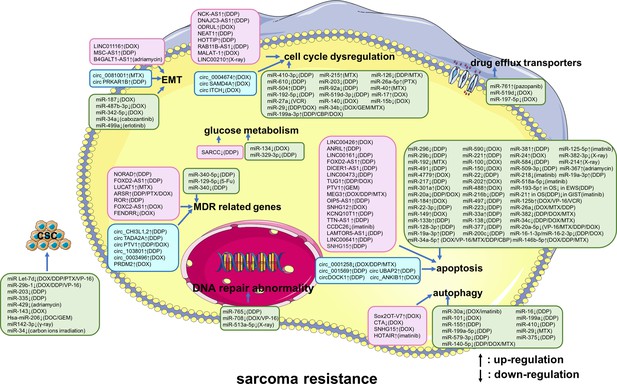
A summary diagram of miRNAs, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) that participate in drug or radiation resistance in sarcoma.
Several miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs have been found to be involved in sarcoma treatment resistance by influencing apoptosis, DNA repair, the cell cycle, glucose metabolism, autophagy, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, drug efflux, multiple drug resistance, and cancer stem cell behavior, through regulating the expression of potential target genes and related signaling pathways. These phenotypes are disordered in one or more sarcomas of different histological types, including osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, Ewing’s sarcoma, synovial sarcoma, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, uterine leiomyosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, and atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors. Specially, these phenotypes are all disordered in osteosarcoma. Abbreviations: 5-Fu, 5-flurouracil; CBP, carboplatin; DDP, cisplatin; DOC, docetaxel; DOX, doxorubicin; GEM, gemcitabine; MTX, methotrexate; PTX, paclitaxel; VCR, vincristine; VP-16, etoposide.
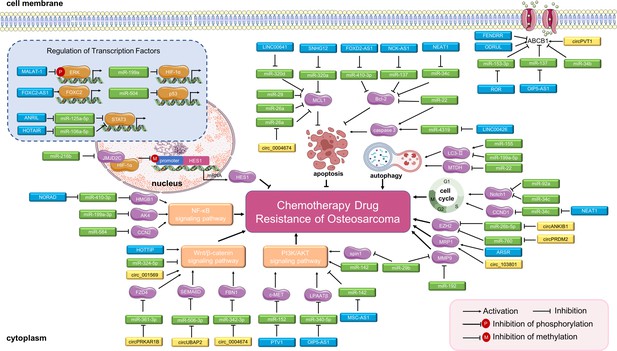
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), and miRNAs in osteosarcoma chemoresistance.
The main molecular mechanisms by which dysregulated ncRNAs (lncRNAs, circRNAs and miRNAs) mediate chemotherapy drug resistance in osteosarcoma are summarized. miRNAs usually bind directly to target genes and regulate their expression and related signaling pathways. LncRNAs and circRNAs can bind directly to target genes or can serve as miRNA sponges to regulate the expression of target genes and related signaling pathways, thereby mediating osteosarcoma chemoresistance. Abbreviations: ABCB1, ATP-binding cassette, subfamily B, member 1; AKT, protein kinase B; CCN2, CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; CCND1, cell cycle-related cyclin D1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; EZH2, enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2; FBN1, fibrillin-1; FOXC2, forkhead box C2; HES1, hairy and enhancer of split-1; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1; LPAATβ, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase; MCL1, myeloid cell leukemia 1; MMP-9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; MRP1, multidrug resistance-associated protein-1; MTDH, metadherin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Tables
The targets of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) that regulate therapeutic resistance in sarcoma.
| Therapeutic strategies | Themes | No. of studies | ncRNA frequently involved | Key genes or pathways involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | ||||
| Osteosarcomas (OS) | Studies of long ncRNAs (lncRNAs) | 43 | lncRNA SNHG15, lncRNA OIP5-AS1, lncRNA TUG1, and lncRNA ANRIL | NF-κB, STAT3, PI3K/AKT, Bax, Bcl-2, caspase3, cleaved caspase3, ABCB1, and MCL1 |
| Studies on miRNAs | 101 | miR-29b, miR-21, miR-22, miR-199a-3p, miR-34a-5p, miR-34a, miR-140–5 p, miR-203, miR-19a-3p, miR-140, miR-29, miR-221, and miR-100 | MMP-9, KRAS, Bcl-2, PI3K/AKT, NF-κB, c-Myc, LC3-Ⅰ, LC3-Ⅱ, HIF-1α, MCL1, North1, Wnt/β-catenin, mTOR, p53, and SOX2 | |
| Studies on circular RNAs (circRNAs) | 21 | circPTV1 and circRNA_0004674 | Wnt/β-catenin, EZH2 | |
| Other sarcomas | Studies on ncRNAs | 13 | Various | p53, and AKT |
| Targeted therapy | ||||
| Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) | Studies on lncRNAs | 4 | lncRNA CCDC26 | Various |
| Studies on miRNAs | 6 | miR-125a-5p | ||
| Other sarcomas | Studies on miRNAs | 4 | Various | Various |
| Immunotherapy | ||||
| Sarcomas | Studies on lncRNAs | 1 | Various | N/A |
| Radiotherapy | ||||
| Sarcomas | Studies on ncRNAs | 6 | Various | Various |
| Biomarker | ||||
| Sarcomas | Studies on ncRNAs | 13 | Various | N/A |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Summary of non-coding RNAs in sarcoma therapeutic resistance.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79655/elife-79655-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Quality assessment of the included studies according to Würzburg Methodological Quality Score (W-MeQS).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79655/elife-79655-supp2-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
References of studies excluded in the systematic review (N=715).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79655/elife-79655-supp3-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Description of the 212 original studies of non-coding RNAs in sarcoma.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79655/elife-79655-supp4-v2.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79655/elife-79655-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx





