The potential of integrating human and mouse discovery platforms to advance our understanding of cardiometabolic diseases
Figures
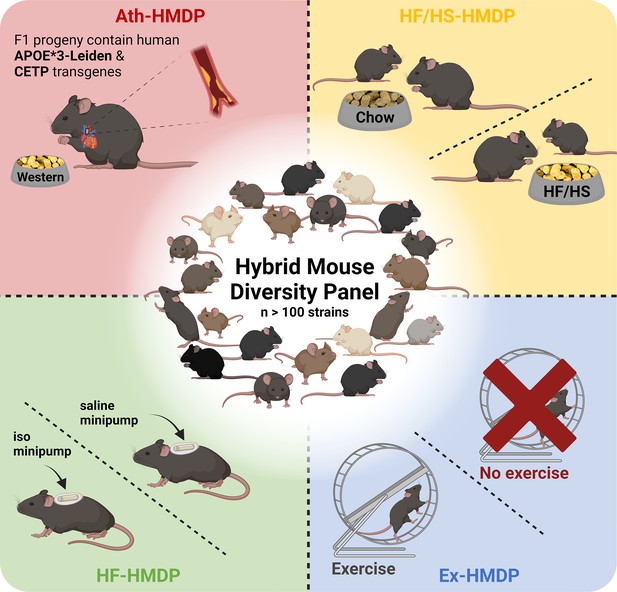
Illustrative overview of Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel (HMDP) study designs utilised for the investigation of cardiometabolic diseases and related traits.
Interventions include transgenic expression of the human apolipoprotein (APO)E*3-Leiden and the human cholesteryl ester transferase protein (CETP) transgenes with concomitant feeding of an atherosclerosis promoting western diet (Ath-HMDP; red) (Bennett et al., 2015), feeding of a high-fat, high-sucrose diet (HF/HS-HMDP; yellow) (Parks et al., 2013), induction of isoproterenol (iso)-induced HF (HF-HMDP; green) (Rau et al., 2015), and 30 days of voluntary wheel running (Ex-HMDP; blue) (Moore et al., 2019). Created with BioRender.com.
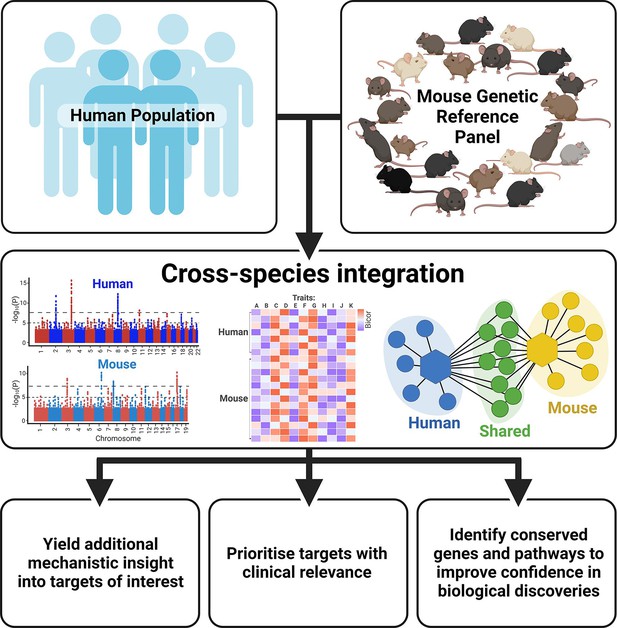
Benefits of integrating human and mouse datasets for biological discovery.
Created with BioRender.com.
Tables
Human genetic and multi-omics resources for cardiometabolic traits.
| Resource | Population | Tissue(s) | *Genetic and omics data | *Primary phenotypes | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| METSIM METabolic Syndrome In Men Study | n=10,197 Finnish males, aged 45–73 | Subcutaneous adipose tissue |
|
| Reviewed in Laakso et al., 2017 |
| MAGNet Myocardial Applied Genomics Network | n=177 cases and n=136 controls for heart failure; collected during transplant | Cardiac tissue |
|
| https://www.med.upenn.edu/magnet/ |
| STARNET Stockholm-Tartu Atherosclerosis Reverse Networks Engineering Task study | n=600 cases and n=250 controls for CAD; individuals undergoing open-thoracic surgery | Aortic root, mammary artery, liver, subcutaneous fat, visceral fat, skeletal muscle, whole blood |
|
| http://starnet.mssm.edu/ |
| GTEx Genotype-Tissue Expression project | n=948 donors, aged 21–70; Biospecimens collected <24 hr post-mortem | 54 tissue types |
|
| https://gtexportal.org/ |
| UKB UK Biobank | ~500,000 individuals of European descent from the UK; with longitudinal follow-up on some subsets | Blood, urine, and saliva samples |
|
| https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ |
| CARDIoGRAMplusC4D Coronary ARtery DIsease Genome-wide Replication and Meta-analysis plus The Coronary Artery Disease study | n=63,746 cases and n=130,681 controls for CAD or MI | - | - |
| http://www.cardiogramplusc4d.org/ |
| BHS Busselton Health Study | >5000 individuals from Busselton, Western Australia | Plasma |
|
| https://bpmri.org.au/research/key-projects-studies/busselton-health-study-2.html |
| MVP Million Veterans Project | n>900,000 veterans from the United States, aged 50–69 | Blood |
|
| https://www.mvp.va.gov |
-
*
For brevity, a subset of relevant datatypes and key references are provided in this table. We apologise to the investigators whose work could not be cited due to space limitations. See accompanying links and references for additional information.
-
WGS, whole genome sequencing; WES, whole exome sequencing; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; CAD, coronary artery disease; MI, myocardial infarction; CHIP-seq, Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing; ATAC-Seq, assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing; RNA-Seq, RNA sequencing; GWAS, genome-wide association study.
Common mouse genetic reference panels utilised for the study of cardiometabolic diseases.
| Breeding structure | Panel | Description | Strains | Advantages | Constraints | *Application of panels for cardiometabolic-related phenotypes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inbred | BXD C57BL/6J × DBA/2J | Inbred mouse panel derived from intercrosses of C57BL/6J and DBA/2J strains (Ashbrook et al., 2021) http://www.genenetwork.org | 198 strains derived from: C57BL/6J, DBA/2J |
|
|
|
| CC Collaborative Cross | Inbred mouse panel derived from intercrosses between eight progenitor strains (Collaborative Cross Consortium, 2012) | ~100 strains derived from: A/J, C57BL/6J, 129S1/SvImJ, NOD/ShiLtJ, NZO/H1LtJ, CAST/EiJ, PWK/PhJ, WSB/EiJ |
|
|
| |
| HMDP Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel | Diverse mouse panel derived from intercrosses of classical and recombinant inbred strains (Lusis et al., 2016) http://www.genenetwork.org | >130 strains derived from: C57BL/6J, DBA/2J, A/J, C3H/J, BALBc/J |
|
|
| |
| ILSXISS | Diverse panel of recombinant inbred mice derived from ILS and ISS progenitor strains (DeFries et al., 1989) http://www.genenetwork.org | ~77 strains derived from: ILS, ISS; both of which are in turn derived from: A, AKR, BALB/c, C3H/2, C57BL, DBA/2, Is/Bi and RIII |
|
|
| |
| F2 Hybrid | Het3 Um-Het3 | Heterogenous mouse population mostly used in ageing research (Nadon et al., 2008) https://www.nia.nih.gov/research/dab/interventions-testing-program-itp | Able to generate unlimited genetically distinct mice, derived from a four-way cross between (BALB/cJ × C57BL6/J) F1 females with (C3H/HeJ × DBA/2J) F1 males |
|
|
|
| Outbred | DO Diversity Outbred | Stocks of genetically unique outbred mice derived from eight CC progenitor strains (Churchill et al., 2012) | Able to generate unlimited genetically distinct stocks of mice, derived from: A/J, C57BL/6J, 129S1/SvImJ, NOD/ShiLtJ, NZO/H1LtJ, CAST/EiJ, PWK/PhJ, WSB/EiJ |
|
|
|
-
*
For brevity, a selection of key phenotypes and references are provided in this table. We apologise to the investigators whose work could not be cited due to space limitations.
-
NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; IR, insulin resistance; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; GWA, genome-wide association;
Select examples of studies that have incorporated human and mouse data for biological discovery.
| Cross-species integration | Trait/description | Cross-species conserved QTL(s), Gene(s), PROTEIN(S), or networks with trait of interest | Experimentally validated Gene(s)/PROTEIN(S) | *Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human-to-mouse integration | Atherosclerosis/CAD | PVRL2 (NECTIN-2/CD112) | – | Bennett et al., 2015 |
| Atherosclerosis/CAD | 12 gene networks | AIP, DRAP1, POLR2I, PQBP1 | Talukdar et al., 2016 | |
| Atherosclerosis/CAD and plasma lipids | 66 genes in aorta and 27 in liver for atherosclerosis 151 genes in liver for plasma lipids | – | von Scheidt et al., 2017 | |
| Biomarker for atherosclerosis/CAD | GUCY1A3 | GUCY1A3 | Kessler et al., 2017 | |
| Glucose and lipids in atherosclerosis/CAD | Glucose and lipid determining gene network | LSS | Cohain et al., 2021 | |
| Atherosclerosis/CAD and cholesterol liver networks | MAFF | MAFF | von Scheidt et al., 2021 | |
| Cross-tissue endocrine factors regulating CAD gene networks | 42 endocrine factors | EPDR1, FCN2, FSTL3, LBP | Koplev et al., 2022 | |
| Atherosclerosis/CAD | 55 genes conserved for atherosclerosis; 14 conserved for other cardiovascular-related traits | RGS19, KPTN | Li et al., 2022 | |
| Atherosclerosis/CAD and cholesterol liver networks | Liver subnetwork consisting of 50 genes, including the key driver gene, ATF3 | ATF3 | Bauer et al., 2022 | |
| Mouse-to-human integration | Blood pressure | Ubp1 | – | Koutnikova et al., 2009 |
| Diabetes-related traits | Syntenic regions identified for 49 QTLs for gene modules and physiological traits | – | Keller et al., 2018 | |
| Cross-tissue endocrine interactions regulating whole-body metabolism | Lcn5/LCN6, Notum | Lcn5/LCN6, Notum, SMOC1, ITIH5, PPBP | Seldin et al., 2018 | |
| Biomarker for heart failure | GPNMB | – | Lin et al., 2018 | |
| Hepatic fibrosis | Nine conserved pathways | – | Hui et al., 2018 | |
| Hepatic and plasma lipidome | PSMD9 | Psmd9 | Parker et al., 2019 | |
| Exercise metabolism | Dnm1l | Dnm1l | Moore et al., 2019 | |
| Diabetes-related traits | Hunk, Zfp148 (others not reported) | Ptpn18, Hunk, Zfp148 | Keller et al., 2019 | |
| Cholesterol metabolism | 54 genes | Sesn1 | Li et al., 2020 | |
| NASH/NAFLD | L-PK (Pklr) | L-PK (Pklr) | Chella Krishnan et al., 2021a | |
| NASH | Up to 42% or 35% overlap of upregulated or downregulated genes in NASH, depending on mouse strain | – | Benegiamo et al., 2023 |
-
*
For brevity, a selection of key references are provided in this table. We apologise to the investigators whose work could not be cited due to space limitations.
-
NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; CAD, coronary artery disease.





