Systems genetics approaches for understanding complex traits with relevance for human disease
Figures
Figure 1
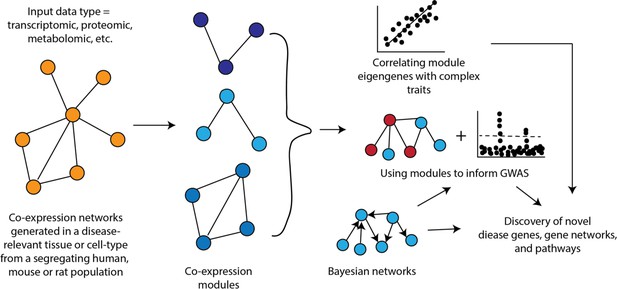
Systems genetics strategy for integration of clinical (and other complex) traits with molecular traits.
In this cartoon, individuals in a cohort are examined for clinical or other complex traits of interest. Tissues from the same individuals are also examined using various omics technologies that quantitate to molecular traits. Genetic and environmental variations among the individuals will perturb the clinical and molecular traits. The relationships among the traits can then be statistically modelled using genetic mapping, correlation structure, causal inference, and network modelling. Figure adapted from Civelek and Lusis, 2014.
Tables
Table 1
Commonly used genetic reference populations (GRPs) and outbred populations in mice and rats.
| GRPs | Species | Inbred or outbred | # of strains | Description | Data repository |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BXD | Mouse | Inbred | 140 | Recombinant inbred lines generated from C57BL/6J and DBA/2J founders | https://genenetwork.org/ |
| HMDP | Mouse | Inbred | ~100 | A set of ~100 classical laboratory inbred strains and multiple recombinant inbred line panels | http://systems.genetics.ucla.edu |
| CC | Mouse | Inbred | ~50–75 | A panel of ~75 recombinant inbred lines derived from eight genetically diverse inbred founders | http://csbio.unc.edu/CCstatus/index.py |
| HRDP | Rat | Inbred | 99 | A set of ~100 classical laboratory inbred strains and recombinant inbred line panels | http://phenogen.org https://genenetwork.org/ |
| HXB/BXH | Rat | Inbred | 30 | Recombinant inbred lines generated from the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR/OlaIpcv) and Brown Norway (BN.Lx/Cub) founders | http://phenogen.org https://genenetwork.org/ |
| DO | Mouse | Outbred | An outbred population derived from eight genetically diverse inbred founders | https://genenetwork.org/ |
Table 2
Commonly used human biobanks for epidemiological and genetics studies.
| Cohort | Ancestry (N) | Disease traits | Biomarkers | Genomics | Transcriptomics | Proteomics | Metabolomics | Data repository |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK Biobank | European, Asian, African, Other (502,492) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ | |
| FinnGEN | European (500,000*) | ✓ | ✓ | https://www.finngen.fi/en | ||||
| Biobank Japan | Asian (260,000) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | https://biobankjp.org/en/ | |
| China Kadoorie Biobank | Asian (512,000) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | https://www.ckbiobank.org/ | |
| TOPMed | European, African, Hispanic, Asian (205,092) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | https://topmed.nhlbi.nih.gov/ |
| BioVU | European (300,000†) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | https://victr.vumc.org/biovu-description/ | |||
| Millions Veteran Program | European, African, Hispanic, Asian (950,000†) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | https://www.mvp.va.gov/pwa/ | |||
| Geisinger MyCode | European (300,000†) | ✓ | ✓ | https://www.geisinger.org/precision-health/mycode |
-
*
Indicates goal of subject recruitment.
-
†
Recruitment still ongoing. Citations for the studies are provided in the text.
Download links
A two-part list of links to download the article, or parts of the article, in various formats.
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Systems genetics approaches for understanding complex traits with relevance for human disease
eLife 12:e91004.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.91004