A novel MARV glycoprotein-specific antibody with potentials of broad-spectrum neutralization to filovirus
Figures
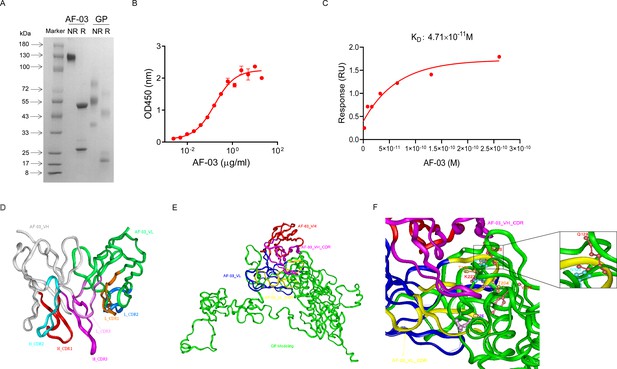
Binding activity of monoclonal antibody (mAb) AF-03 to Marburg virus (MARV) glycoprotein (GP) and its epitopes.
(A) AF-03 and MARV GP proteins are examined by SDS-PAGE. NR, non-reducing; R, reducing. (B) The binding capacity of AF-03 to MARV GP is determined by ELISA. The absorbance is detected at 450 nm. (C) The binding kinetics of AF-03 to MARV GP is detected by SPR assay. Experiments are independently repeated at least three times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown. (D) The 3D ribbon structures of the AF-03 Fv fragment. The red ribbon denotes H-CDR1, the light blue denotes H-CDR2, the pink denotes H-CDR3, the orange denotes L-CDR1, the deep blue denotes L-CDR2, and the purple denotes L-CDR3. (E) AF-03 and MARV GP complex derived from theoretical modeling. The green ribbon denotes the orientation of the MARV GP fragment, the yellow denotes AF-03 VLCDR, the pink denotes AF-03 VHCDR, the deep blue denotes AF-03 VL and the red ribbon denotes AF-03 VH. (F) By molecular docking analysis of van der Waals interaction, intermolecular hydrogen bonding, polarity interaction, and electrostatic interaction, the key amino acid residues of MARV GP are screened. A zoom-in shows the predicted co-location of AF-03 CDR with Q128 and N129.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Raw image for Figure 1A, D-F and numerical data for Figure 1B, C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig1-data1-v1.zip
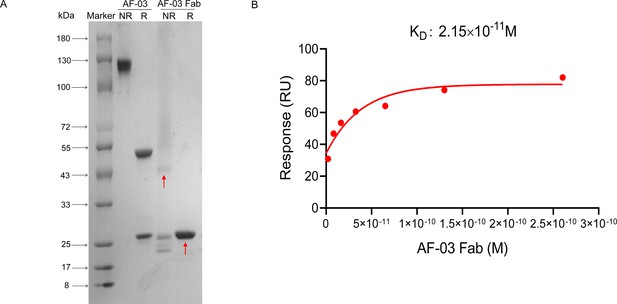
Binding activity of monovalent AF-03 Fab to Marburg virus (MARV) glycoprotein; (GP).
(A) Monovalent Fab of AF-03 was prepared by papain digestion and identified by SDS-PAGE. NR, non-reducing; R, reducing. The arrow denotes monovalent Fab. (B) The binding kinetics of monovalent AF-03 Fab to MARV GP was detected by surface plasmon resonance (SPR).Experiments are independently repeated two times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw image for Figure 1—figure supplement 1A and numerical data for Figure 1—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
AF-03 Epitope Identification.
(A) The neutralization activity of AF-03 or MR78 to mutated pseudovirus (Q128S-N129S, Q204A-T205A-Q206A, Y218A, K222A, C226Y) is evaluated in HEK293T cells. The inhibition rate is analyzed. (B) The binding of AF-03 and MR78 to mutant glycoprotein (GP) (Q128S-N129S or C226Y) is examined by ELISA, respectively. *p<0.05. (C) Secondary structure of Marburg virus (MARV) GP and mutants are detected by circular dichroism (CD). (D) The epitope overlapping between AF-03 and MR78 is examined by the competitive ELISA. Experiments are independently repeated at least three times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Numerical data for Figure 2A-D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig2-data1-v1.zip
In vitro and in vivo neutralization of Marburg virus (MARV) pseudovirus infection by AF-03.
(A) Pseudotypic MARV-Uganda is incubated with AF-03, MR78, or control mAb at 37 °C for 1 hr before infecting HEK293T cells (left) and hepatocyte cell line (Huh7) cells (right), respectively. Luciferase is assayed and inhibition rates are calculated. (B) Pseudotypic MARV-Angola, Musoke and Ravn virus (RAVN) infect HEK293T cells, respectively and neutralization activity of AF-03 to these species is determined. (C) AF-03 (10, 3, 1 mg/kg) is administrated at 24 and 4 hr before intraperitoneal injection of MARV pseudovirus. On day 4, bioluminescence signals are detected by an IVIS Lumina Series III imaging system. (D) The total radiance value is based on the luminescence of (C). *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. Experiments are independently repeated at least three times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Numerical data for Figure 3A, B, D and raw image for Figure 3C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig3-data1-v1.zip
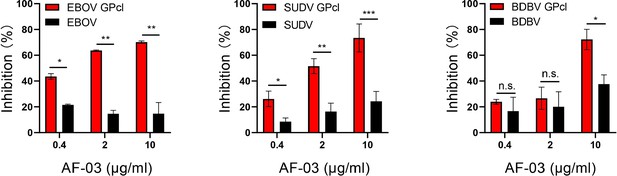
The neutralization activity of AF-03 to EBOV, SUDV, and BDBV harboring cleaved GP.
Pseudotypic Ebola virus (EBOV), Sudan virus (SUDV), and Bundibugyo virus (BDBV) are processed with thermolysin at 37 °C. Inhibition of these ebola virus entry harboring glycoprotein (GP) or GPcl by AF-03 is examined by luciferase assay. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Experiments are independently repeated at least three times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Numerical data for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig4-data1-v1.zip
Comparison of the cellular entry capacity of ebolavirus harboring cleaved or intact glycoprotein (GP).
Ebola viruses (EBOV, Sudan virus - SUDV, Bundibugyo virus - BDBV) were treated with or without thermolysin at 37 °C and then infected HEK293T cells. Luciferase intensity was assayed. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Experiments are independently repeated two times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Numerical data for Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
Cellular internalization of AF03-NL.
AF-03, AF03-NL, or human IgG1 isotype (MOCK) is incubated with cells at 4℃ for 1 hr to prevent internalization and then at 37℃ for another 2 hr to allow internalization. PE-conjugated secondary antibody is added prior to analysis by flow cytometry. (B,C) Antibody internalization reagent and pHrodo Red-labeled AF-03 or AF03-NL is incubated with cells at 37℃ for 1 hr and analyzed by flow cytometry (B) and fluorescence microscopy, (C) respectively. The red arrow denotes internalized AF03-NL. Experiments are independently repeated at least three times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Raw image for Figure 5A-C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig5-data1-v1.zip
Characterization of AF03-NL and CI-MPR1-3.
(A) AF03-NL and CI-MPR1-3 domain proteins are examined by SDS-PAGE. NR, non-reducing; R, reducing. The arrow denotes Niemann-Pick C2 (NPC2)-fused light chain. (B) The binding capacity of AF03-NL and AF-03 to CI-MPR1-3 is detected by ELISA. Experiments are independently repeated two times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw image for Figure 5—figure supplement 1A and numerical data for Figure 5—figure supplement 1B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
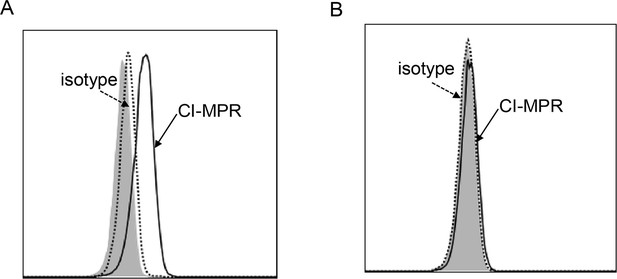
CI-MPR expression in HEK293T and hepatocyte cell line (Huh7) cells.
The CI-MPR expression in (A) HEK293T and (B) Huh7 cells is examined by flow cytometry. The representative plots from two independent experiments are shown.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw image for Figure 5—figure supplement 2A, B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig5-figsupp2-data1-v1.zip
Pan-filovirus entry inhibition by AF03-NL.
(A,B) AF-03 or AF03-NL (50–0.0007 μg/ml, fourfold dilution) is incubated with HEK293T cells at 37 °C for 2 hr prior to exposure to pseudotypic filovirus species (A) and Ebola virus (EBOV) mutants (B). Luciferase is assayed and inhibition rates are calculated. Experiments are independently repeated at least three times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Numerical data for Figure 6A, C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig6-data1-v1.zip
Comparable binding and inhibitory activity of AF03-NL and AF-03.
(A) The binding capacity of AF-03 and AF03-NL to MARV GP is detected by ELISA. (B) AF-03 orAF03-NL is incubated with HEK293T cells at 37 °C for 2 hr prior to exposure to pseudotypic Marburg virus (MARV)-Uganda. Luciferase is assayed and inhibition rates are calculated. Experiments are independently repeated two times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Numerical data for Figure 6—figure supplement 1A, B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v1.zip
The requirement of CI-MPR for the neutralization activity of AF03-NL.
(A) Niemann-Pick C2 (NPC2) protein is examined by SDS-PAGE. NR, non-reducing; R, reducing. (B) AF03-NL, AF-03, NPC2 alone, or equimolar combination of AF-03 and NPC2 is incubated with HEK293T cells at 37 °C for 2 hr prior to exposure to pseudotypic Ebola virus (EBOV). Luciferase is assayed and inhibition rates are calculated. (C) HEK293T cells are treated with siRNA-CI-MPR or negative control vector (NC), respectively and CI-MPR expression is detected by flow cytometry. AF03-NL is incubated with siCI-MPR or NC-treated HEK293T cells at 37 °C for 2 hr, respectively prior to exposure to pseudotypic EBOV. (D) CI-MPR is introduced into hepatocyte cell line (Huh7) cells and its expression is detected by flow cytometry. AF03-NL is incubated with CI-MPR or NC-knockin Huh7 cells at 37 °C for 2 hr, respectively prior to exposure to pseudotypic EBOV. Luciferase is assayed and inhibition rates are calculated. Experiments are independently repeated at least three times, and the data from one representative experiment is shown.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Raw image for Figure 7A, C left panel, Figure 7D left panel and numerical data for Figure 7B, C right panel, Figure 7D right panel.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-fig7-data1-v1.zip
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | HEK293T | ATCC | RRID:CVCL_0063 | |
| Cell line (H. sapiens) | Huh7 | ATCC | RRID:CVCL_U443 | |
| Cell line (Chinese hamster) | ExpiCHO-S | Thermo | RRID:CVCL_5J31 | |
| Gene (Marburg virus) | Uganda | This paper | GenBank: AFV31370.1 | |
| Gene (Marburg virus) | Angola | This paper | Uniprot: Q1PD50 | |
| Gene (Marburg virus) | Musoke | This paper | Uniprot: P35253 | |
| Gene (Marburg virus) | RAVN | This paper | Uniprot: Q1PDC7 | |
| Gene (Ebola virus) | TAFV | This paper | Uniprot: Q66810 | |
| Gene (Ebola virus) | RESTV | This paper | Uniprot: Q66799 | |
| Gene (Ebola virus) | BOMV | This paper | GenBank: YP_009513277.1 | |
| Gene (Ebola virus) | EBOV | Kindly gifted by the China Institute for Food and Drug Control | GenBank: AHX24649.2 | |
| Gene (Ebola virus) | BDBV | Kindly gifted by the China Institute for Food and Drug Control | GenBank: YP_003815435 | |
| Gene (Ebola virus) | SUDV | Kindly gifted by the China Institute for Food and Drug Control | GenBank: YP_138523.1 | |
| Gene (Cueva virus) | LLOV | This paper | GenBank: JF828358.1 | |
| Gene (Dianlo virus) | MLAV | This paper | GenBank: YP_010087186.1 | |
| Gene | pSG3. Δenv. cmvFluc | Kindly gifted by the China Institute for Food and Drug Control doi: 10.1038/srep45552 | ||
| Gene | pFRT-KIgG1 | Thermo | Cat# V601020 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) | Gibco | Cat# 11965e092 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pen Strep | Gibco | Cat# 15140 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Fetal bovine serum | Gibco | Cat# 10099 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ExpiCHO Expression Medium | Gibco | Cat# A29100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ExpiFectamine CHO Transfection Kit | Gibco | Cat# A29129 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Nickel column | Cytiva | Cat# 11003399 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Soluble TMB Kit | CWBIO | Cat# CW0050S | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Transfection reagent | JetPRIME | Cat# 25Y1801N5 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Bright-Glo luciferase reagent | Promega | Cat# E6120 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | thermolysin | Sigma | Cat# T7902 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Phosphoramidon | Sigma | Cat# R7385 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | D-luciferin | PerkinElmer | Cat# 122799 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | iQue Human Antibody Internalization Reagent | Sartorius | Cat# 90564 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | pH-sensitive pHrodo red succinimidyl ester | Thermo | Cat# P36600 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | polylysine | Beyotime | Cat# ST508 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | DiD | Thermo | Cat# V22887 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Hoechst33342 | Thermo | Cat# H1398 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce Fab Preparation Kit | Thermo | Cat# 44985 | |
| Antibody | horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled goat anti-human IgG secondary antibody | Invitrogen | Cat# A18817 RRID:AB_1640167 | Elisa: 1:6000 |
| Antibody | Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled Streptavidin | Thermo | Cat# S911 RRID:AB_795453 | Elisa: 1:10000 |
| Antibody | PE-labeled anti-human IgG Fc secondary antibody | Biolegend | Clone M1310G05 Cat# 41070 | |
| Antibody | FITC-conjugated anti-CI-MPR antibody | Biolegend | Clone QA19A18 Cat# 364207 | |
| Experimental animals | BALB/c | Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology | Four-week-old, female |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Numerical data for Figure 2C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-supp1-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/91181/elife-91181-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf





