Monoclonal antibodies derived from B cells in subjects with cystic fibrosis reduce Pseudomonas aeruginosa burden in mice
Figures
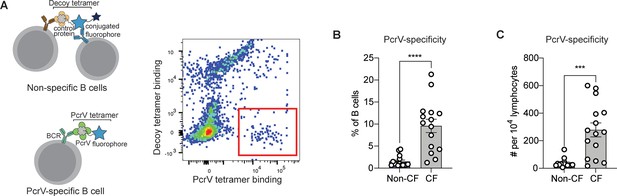
PcrV-specific B cells in people with cystic fibrosis (pwCF).
(A) Schematic of primary human B cells binding to PcrV tetramer reagent and decoy (left). Representative flow plot for B cells after enrichment. Cells binding only to the PcrV tetramer are indicated with the red box. (B–C) Percentage (B) and number (C) of PcrV-specific B cells in pwCF (CF; n=14) vs. control, blood bank donors (non-CF; n=14). Statistics determined by two-tailed Mann-Whitney tests. ***p<0.001, ****pp<0.0001. Error bars represent mean and SD.
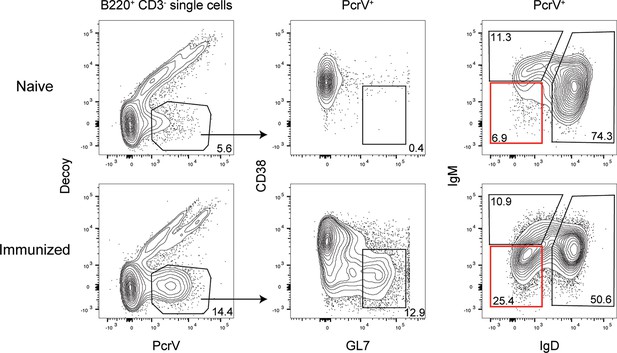
Tetramer-specific class-switched B cells in mice immunized with PcrV.
Flow cytometry plots from lymphoid tissue in representative PcrV-immunized or control (naïve) mice sacrificed on day 7 post-immunization by intraperitoneal injection. Cells were analyzed after the magnetic enrichment of tetramer-bound cells. Class-switched B cells are highlighted within the red boxes.
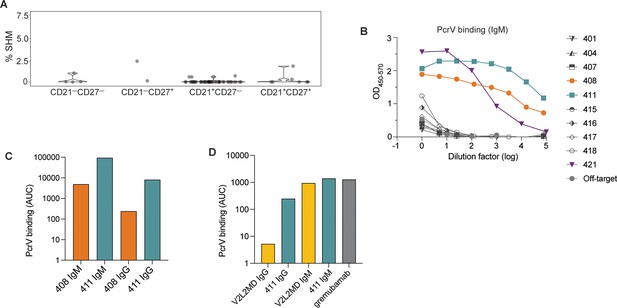
Generation of anti-PcrV mAbs derived from B cells isolated from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA)-infected cystic fibrosis (CF) donor.
(A) Percentage of somatic hypermutation (SHM) detected in B cell receptor (BCR) sequences from cells of the indicated phenotype for CF donor 1, shown as violin plot. (B) ELISAs showing PcrV binding using supernatants derived from 293T cells transfected with IgM expression plasmids containing the indicated BCR sequences. (C) Area under the curve (AUC) for representative ELISAs of purified antibodies 408 and 411 expressed alternatively as IgM vs. IgG in a single experiment. (D) AUC for representative ELISA of purified mAbs V2L2 and 411 expressed, alternatively as, IgG vs. IgM; and for the commercially sourced, clinical, bi-specific mAb, gremubamab.

Summary of data generated by single-celB cell receptor l BCR sequencing.
(A) Flow cytometry gating strategy. (B) Surface marker expression of singly-sorted cells used for B cell receptor (BCR) sequencing for each donor (x-axis). (C) Enumeration of unique heavy chain sequences obtained from PcrV-specific B cells in each donor, color-coded by the sequenced constant region.
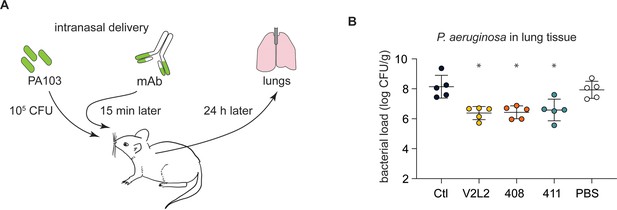
People with cystic fibrosis (pwCF)-derived, germline, anti-PcrV-specific mAbs exhibit robust anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) activity in an in vivo mouse pneumonia model.
(A) Schematic illustrating the experimental PA infection and mAb delivery protocol. (B) Bacterial load in mouse lungs at 24 h post-infection for mice that received 20 µg intranasal dose of off-target, control IgG1 mAb (Ctl), indicated anti-PcrV mAbs, or diluent alone (PBS). Error bars represent mean and SD. Asterisks show significance in Dunn’s test versus animals treated with diluent only (PBS); *p<0.05.
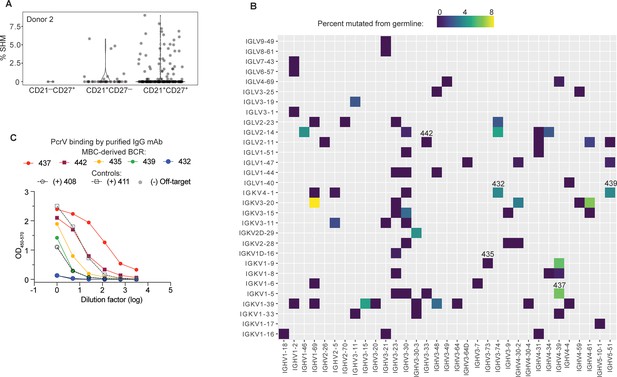
High affinity anti-PcrV mAbs derived from memory B cells isolated from cystic fibrosis (CF) Donor 2.
(A) Somatic hypermutation (%SHM) rates in B cell receptor (BCR) sequences from individual B cells with the indicated surface phenotype isolated from CF donor 2, shown as violin plot. Each circle represents a heavy or light chain sequence from a singly-sorted cell. (B) Heatmap showing paired heavy (x-axis) and light (y-axis) V genes for 79 MBCs in donor 3. The color gradient depicts SHM for the heavy chains in each pairing. Clone numbers for BCRs subsequently expressed as mAbs are included above their corresponding box. (C) PcrV binding for purified mAbs generated from five MBC BCRs (colored lines) screened in a single ELISA. The two Donor 1-derived mAbs with in vivo protective activity (408 and 411) are used as benchmarks for relative binding activity (dashed lines). The off-target control (anti-SARS-CoV-2 RBD) line appears hidden because it overlaps with the blue line (432).
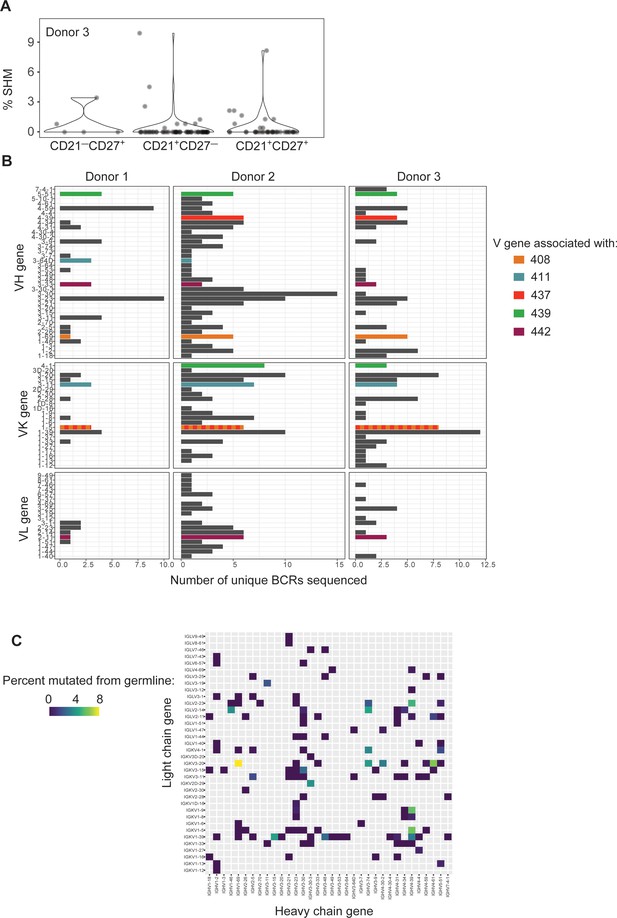
B cell receptor (BCR) sequencing of PcrV-tetramer-specific B cells derived from three cystic fibrosis (CF) donors.
(A) Percentage of somatic hypermutation (SHM) detected in BCR sequences from cells of the indicated phenotype in CF donor 3, shown as violin plot. Each circle represents a heavy or light chain sequence from a singly-sorted cell. (B) Histograms show the number of unique BCR sequences obtained for each V gene (y-axis) for heavy and light (kappa or lambda) chains. Data from each CF donor (Donors 1–3) are shown in a separate panel of graphs (with Donor number indicated at top). The bars for the V genes used by in vivo-tested monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are colored as indicated. (C) Heatmap showing pairings of heavy- (x-axis) and light (y-axis) chain V genes for 175 BCR sequences where full-length, high quality V region sequences were attained. For each heavy/light chain pair, the percentage of heavy chain sequence which differs from the germline sequence is depicted by color gradient.
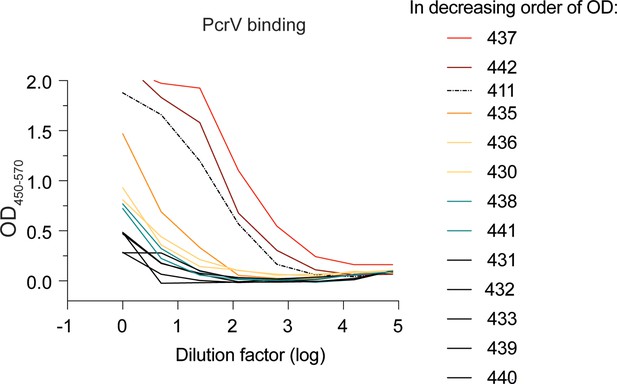
Transfectant supernatant screen of 12 MBC-derived monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).
ELISA assessing PcrV binding for supernatants from 293T cells transfected with IgG expression plasmids. Numbers (430-442) indicate the B cell receptor (BCR) sequences identified from individual, PcrV-specific, MBCs derived from cystic fibrosis (CF) donor 2. Supernatant for mAb 411 IgG (dotted line; isolated from CF Donor 1) is included as a benchmark.
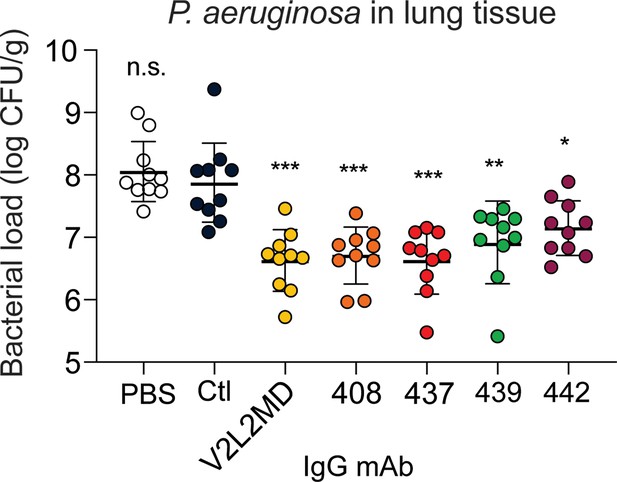
mAbs derived from cystic fibrosis (CF) memory B cell (MBC) B cell receptor (BCR) sequences control Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) infection in a murine pneumonia model.
Lung bacterial load for mice treated intranasally with 20 µg of the indicated anti-PcrV mAb, or vehicle only (PBS). Combined data from two independent experiments is shown (n=10 mice per condition). Error bars show mean and SD. Asterisks show significance in Dunn’s test versus animals treated with the off-target control antibody (Ctl); *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, n.s.: not significant.
Tables
Clinical characteristics of subjects from whom PcrV-specific B cell receptor (BCR) sequences were obtained.
ETI: elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor triple therapy. Chronic infection is defined here as positive Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) cultures in at least 2 of 3 consecutive years (Green et al., 2012; Rosenfeld et al., 2022).
| Donor | Age | On ETI? | Lung disease severity | PA infectious history |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 33 | Yes | Moderate | Chronic |
| 2 | 19 | Yes | Minimal | Culture-negative at time of blood draw. Culture-positive 6 mo. prior. Previously, 5 y. of negative cultures. |
| 3 | 18 | Yes | Minimal | Chronic |
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) | PA103 | ATCC | Cat#:29260 | sputum isolate |
| Cell line (human) | HEK-293T (epithelial-like, kidney) | ATCC | Cat#:CRL-3216; RRID:CVCL_0063 | Cell line transfected for antibody production |
| Transfected construct (human) | Antibody expression plasmids (plasmid) | Addgene | RRID:Addgene_183702 (kappa light chain);RRID:Addgene_183703 (lambda light chain); RRID :Addgene_80795 (IgG1 heavy chain) | Deposited in Addgene by Dr. Hedda Wardemann |
| Biological sample (human) | PBMC | Seattle Children’s Cystic Fibrosis Clinic | Collected from individual donors under IRB approval SCH#10325 | |
| Antibody | HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG; IgM (goat polyclonal) | SouthernBiotech | Cat#:2040–05 (IgG); Cat#: 2020–05 (IgM) | ELISA IgG (1:3000); IgM (1:1500) |
| Antibody | HRP-conjugated anti-human IgA (goat polyclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#:A18781 | ELISA (1: 1:1500) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) | pET16b PcrV (plasmid) | Sawa et al., 1999 | Plasmid encoding histidine-tagged PcrV; gift from Dr. Timothy Yahr | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Streptavidin conjugated to fluorophore | Agilent | Cat#:PJ27S (SA-APC); Cat#:PJRS25 (SA-PE) | For labeling of protein tetramer |
| Commercial assay or kit | In-Fusion HD Cloning | Takara Bio | Cat#:639650 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | EZ-Link Sulfo-NHS-LC Biotinylation Kit | Thermo Fisher | Cat#:21435 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SMART-seq v4 | Takara Bio | Cat#:634770 | cDNA synthesis |
| Chemical compound, drug | gremubamab | Invitrogen/Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#:MA5-42275 | |
| Software, algorithm | IgBlast | Ye et al., 2013 | ||
| Software, algorithm | IGMT/HighV-Quest | Alamyar et al., 2012 | ||
| Software, algorithm | Prism | GraphPad | Version 9.5 | |
| Software, algorithm | TRUST4 | Song et al., 2021 | ||
| Other | Amicon Ultracentrifugal Filter | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#:UFC9050 | For concentration and buffer exchange of purified mAbs |
| Other | HiTrap Protein G HP purification column | Cytiva/Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#:45-000-053 | For purification of IgG from concentrated transfectant supernatant |
| Other | POROS CaptureSelect IgM-XL Affinity Matrix | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#:2812892005 | For purification of IgM from concentrated transfectant supernatant |





