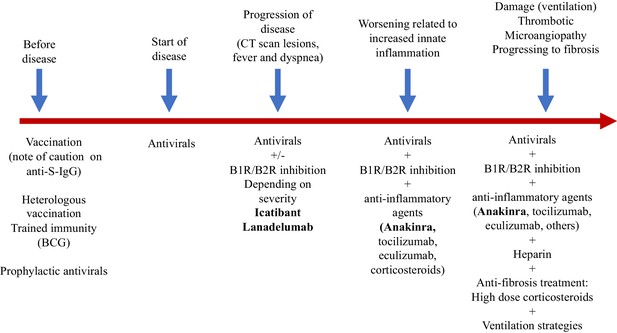
Kallikrein-kinin blockade in patients with COVID-19 to prevent acute respiratory distress syndrome
Figures
Figure 1
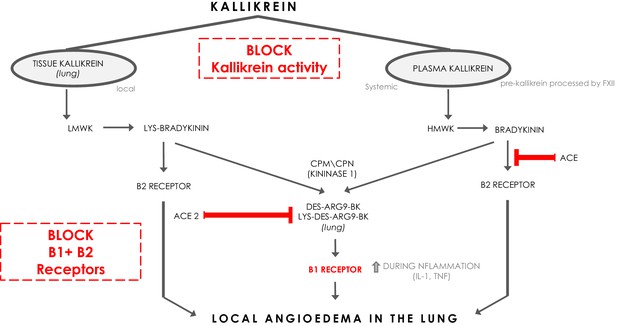
The kinin-kallikrein system and ACE/ACE2.
The pathways of processing of low-molecular-weight kininogen (LMWK) and high-molecular-weight kallikrein (HMWK) leading to Bradykinin 1 (B1) receptor agonists and Bradykinin 2 (B2) receptor agonists. CPM = carboxypeptidaseM; CPN = carboxypeptidaseN.
Figure 3
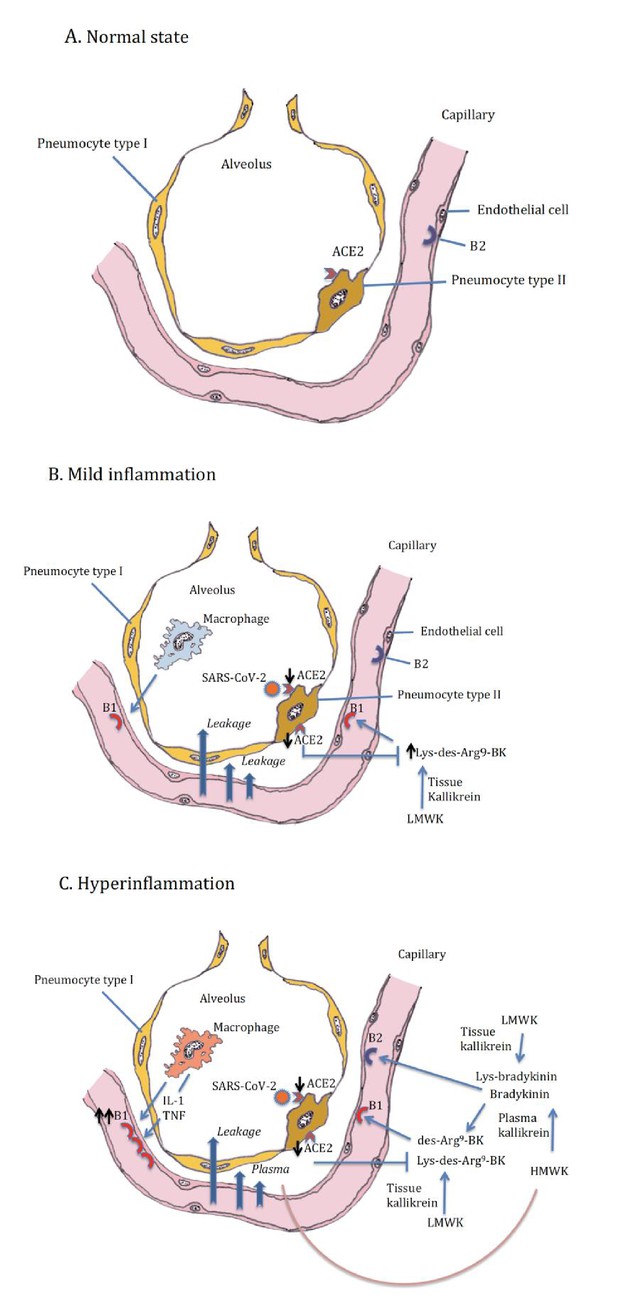
Alveolus in normal setting and during moderate and severe COVID-19, (A) normal, (B) mild inflammation, (C) hyperinflammation.
ACE2 downregulation by the SARS-CoV-2 is followed by loss of neutralizing capacity of Lys-des-arg9-bradykinin (BK) in the lung leading to plasma leakage. Subsequently plasma leakage results in more B1R ligands (des-arg9-BK) and B2R ligands (bradykinin).
Download links
A two-part list of links to download the article, or parts of the article, in various formats.
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Kallikrein-kinin blockade in patients with COVID-19 to prevent acute respiratory distress syndrome
eLife 9:e57555.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.57555